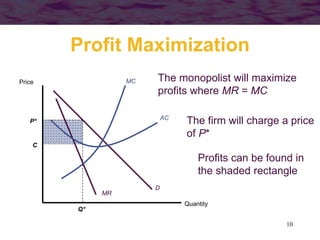
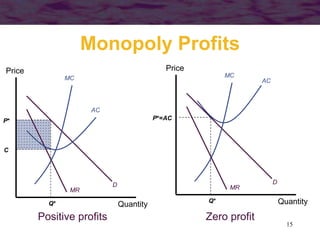
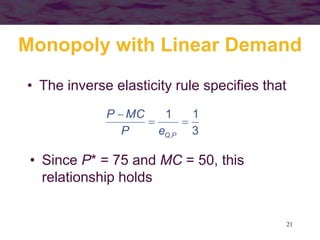
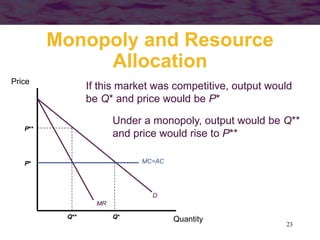
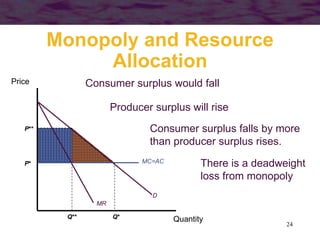
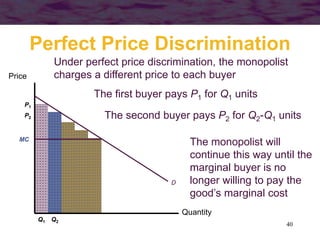
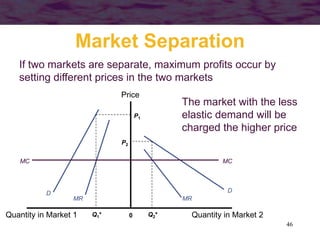
This document discusses models of monopoly and barriers to entry. It explains that a monopoly is a single supplier in a market and can choose any point on the demand curve to produce. Barriers to entry, which are the source of monopoly power, can be technical or legal. Technical barriers include economies of scale, unique knowledge, or ownership of resources. Legal barriers are created by patents, franchises, or lobbying. A monopolist maximizes profits where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and charges a price above marginal cost. The inverse elasticity rule relates the markup to demand elasticity. Monopolies can impact resource allocation, consumer surplus, and welfare losses compared to competition.





















































![63
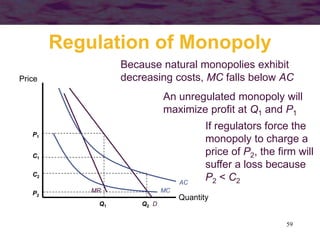
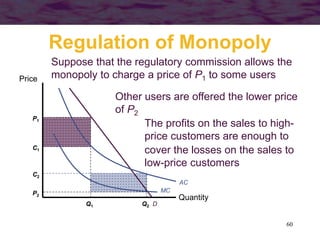
Regulation of Monopoly
• Suppose that s is constrained by
regulation to be equal to s0, then the
firm’s problem is to maximize profits
= pf (k,l) – wl – vk
subject to this constraint
• The Lagrangian for this problem is
L = pf (k,l) – wl – vk + [wl + s0k – pf (k,l)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch13-200823133743/85/Ch13-63-320.jpg)








