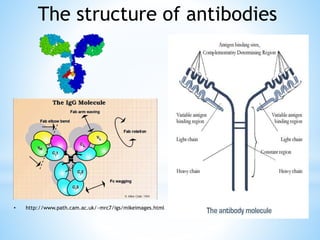
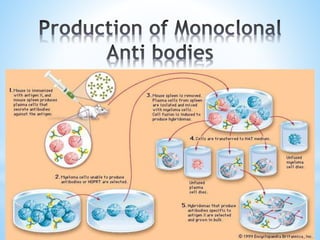
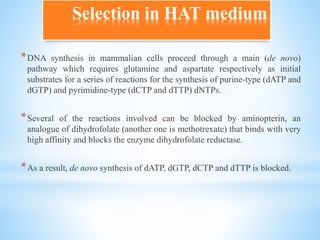
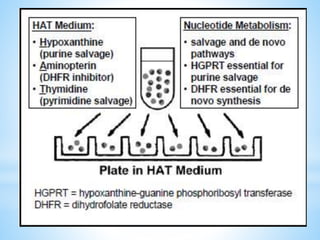
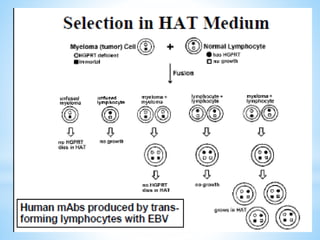
This document discusses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), including their definition, production process, structure, applications, and limitations. It describes how mAbs are produced through the fusion of immune spleen cells from immunized mice with myeloma cells, which results in hybridoma cells that can produce identical antibodies. The key steps involved are immunizing mice, screening for antibody production, preparing myeloma cells, fusing cells, cloning hybridomas, and selecting cells in HAT medium. mAbs have various analytical, preparative, and therapeutic applications, but also have limitations such as immunogenicity and production challenges.