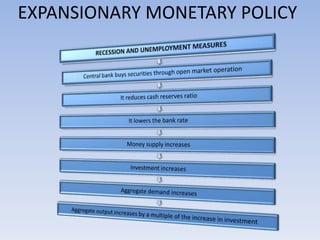
The document discusses monetary policy and fiscal policy in India. It defines monetary policy as actions by the Reserve Bank of India to regulate money supply and credit availability in order to achieve socio-economic objectives. It discusses the RBI's tools of monetary policy including bank rate, open market operations, cash reserve ratio, and statutory liquidity ratio. The document also defines fiscal policy as the government's taxing and spending policies and discusses the fiscal policy tools of public expenditure, taxation, and public debt management.