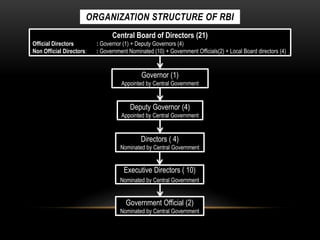
The document provides information about the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which is India's central bank. It was established in 1934 and frames monetary policy. Some key points:
- RBI is among the top 10 most influential central banks globally based on GDP and other economic factors.
- It aims to maintain price stability and promote growth. The RBI Governor and committee determine the repo rate to influence monetary conditions.
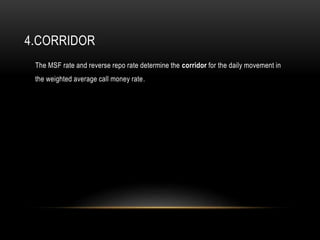
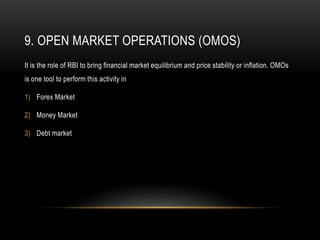
- Tools include repo rate, CRR, OMOs and more to target inflation and ensure adequate credit in the economy.