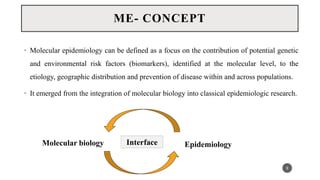
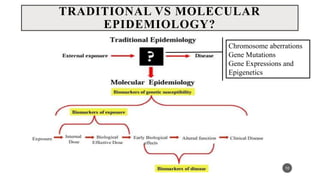
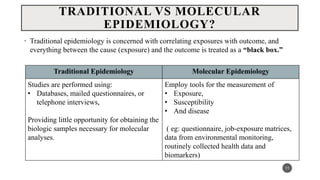
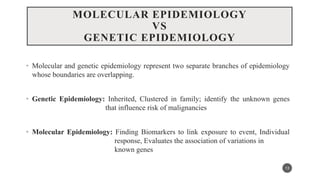
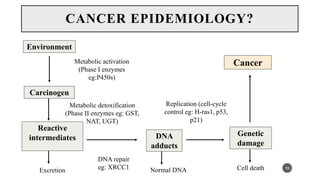
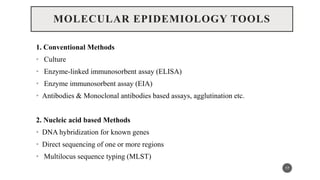
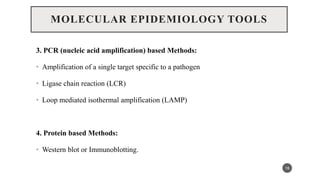
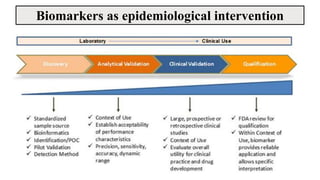
The document discusses the emergence and significance of molecular epidemiology in understanding chronic diseases and cancer risk factors by integrating molecular techniques with traditional epidemiologic methods. It highlights goals, comparison with traditional epidemiology, study designs, and various tools and biomarkers utilized in molecular epidemiology. The key takeaway is that molecular epidemiology provides insights into genetic and environmental interactions affecting disease risk, thereby aiding in better prevention strategies.