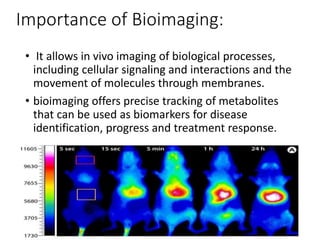
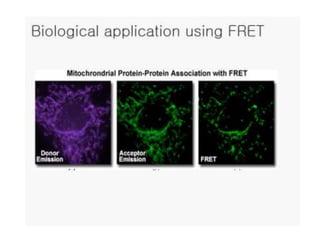
Molecular bioimaging allows visualization of biological processes in vivo through techniques like fluorescence imaging. It has four broad categories including molecular bioimaging, biomedical imaging, drug discovery applications, and computational bioimaging. Some key methods discussed are green fluorescent protein labeling, fluorescence in situ hybridization for detecting DNA sequences, the GUS reporter system for visualizing gene expression, and fluorescence resonance energy transfer for measuring molecular interactions. Bioimaging provides precise tracking of disease biomarkers but current limitations include inability to quantify tumor response to drugs or distinguish benign from malignant tumors.