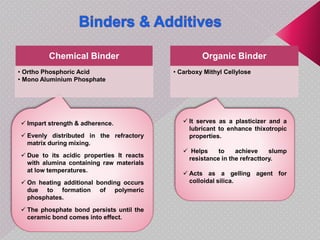
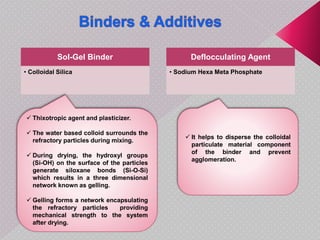
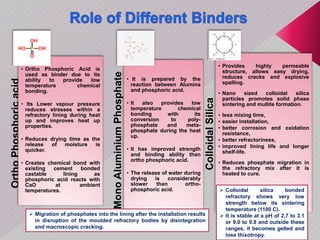
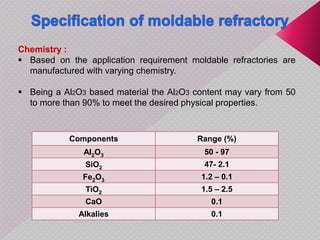
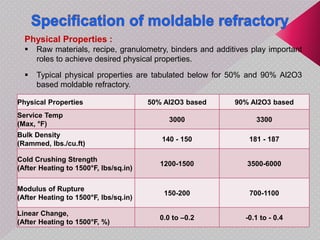
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on monolithic refractories. It discusses the introduction and history of monolithic and moldable refractories. It describes the types of moldable refractories based on setting and form. It covers the raw materials, particle size distribution, binders, additives and their roles in moldable refractories. It provides details on the typical specifications and properties of moldable refractories. Finally, it discusses the applications of moldable refractories in iron and steel, aluminum and other industries.