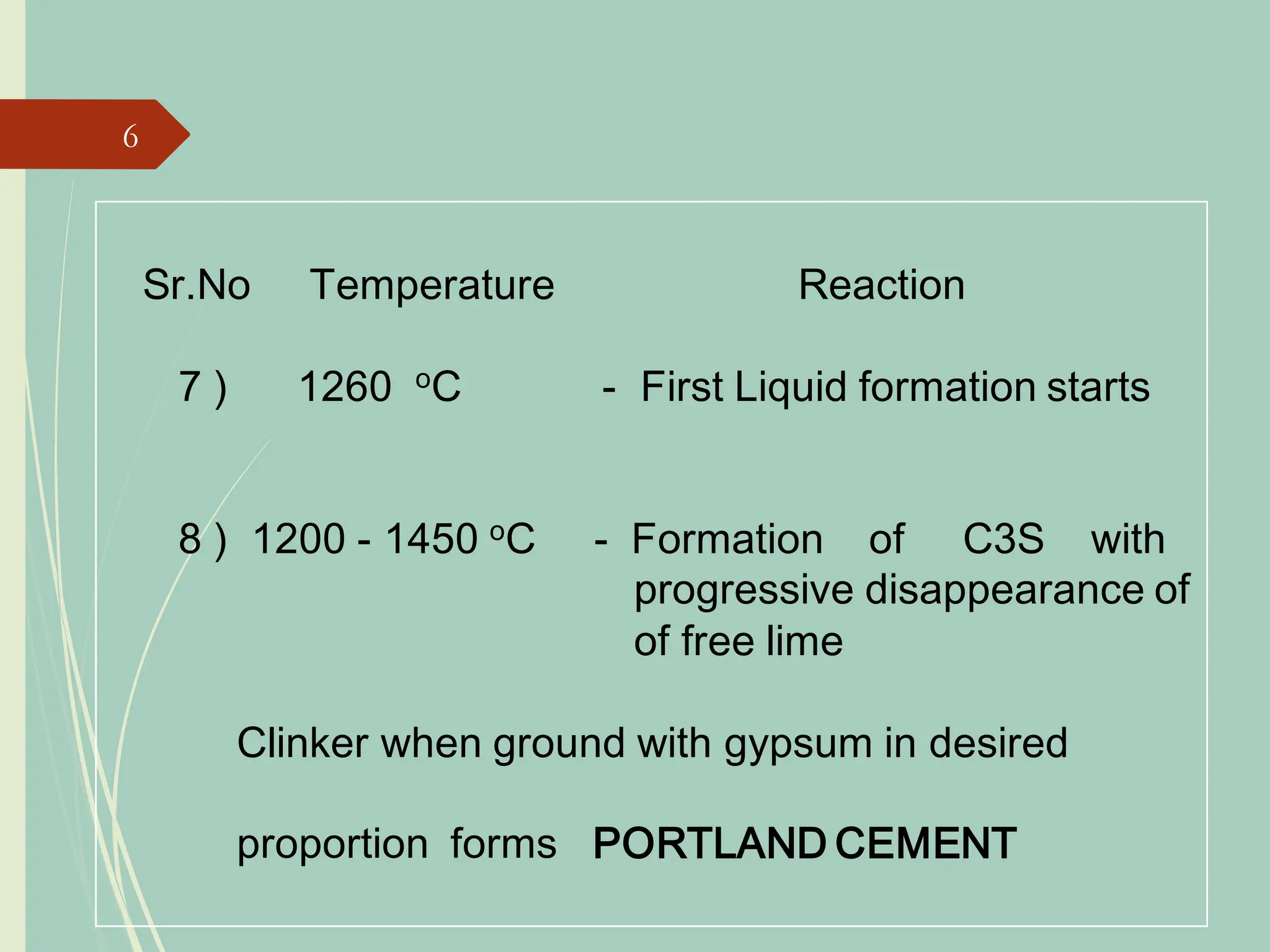
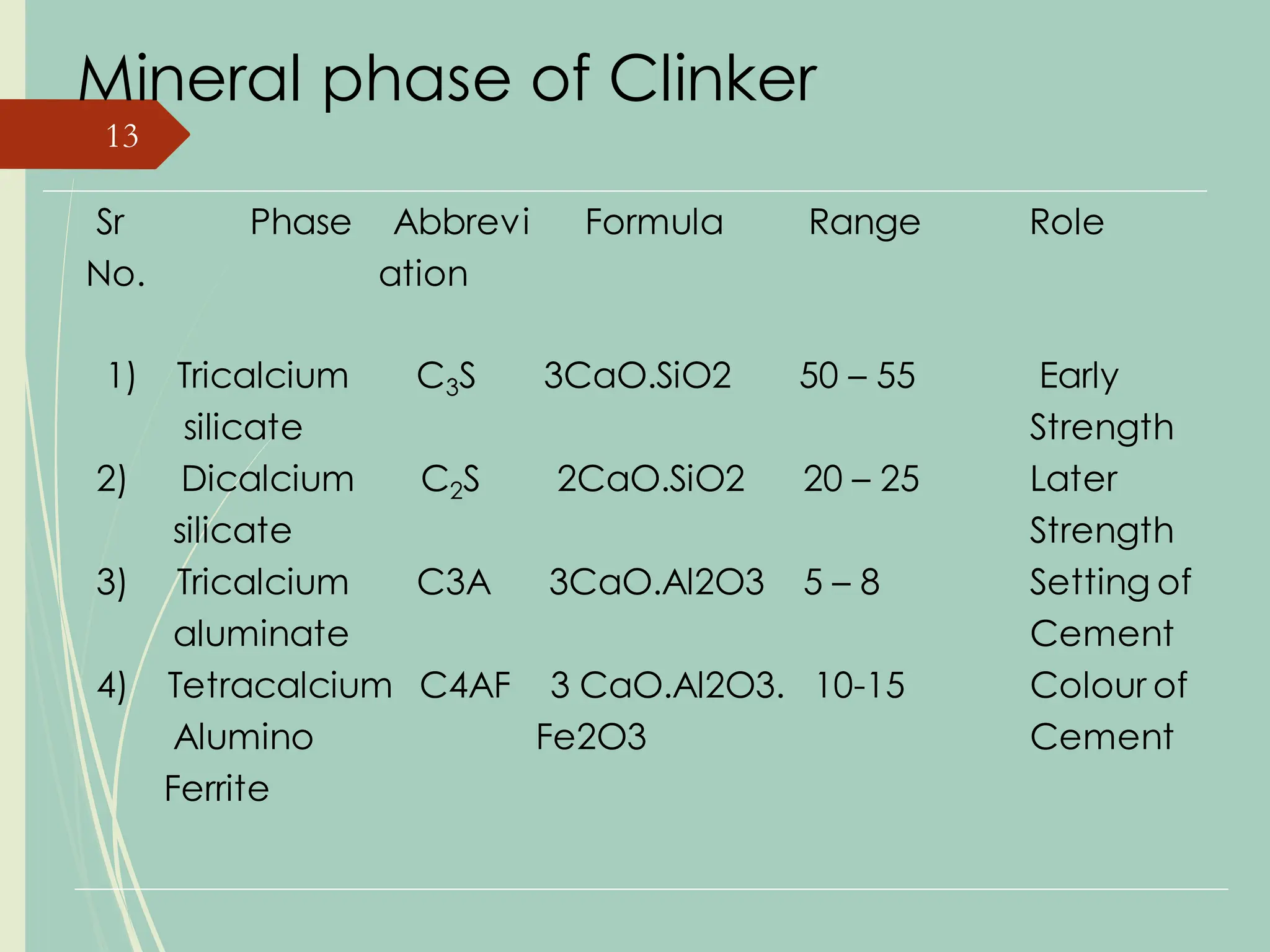
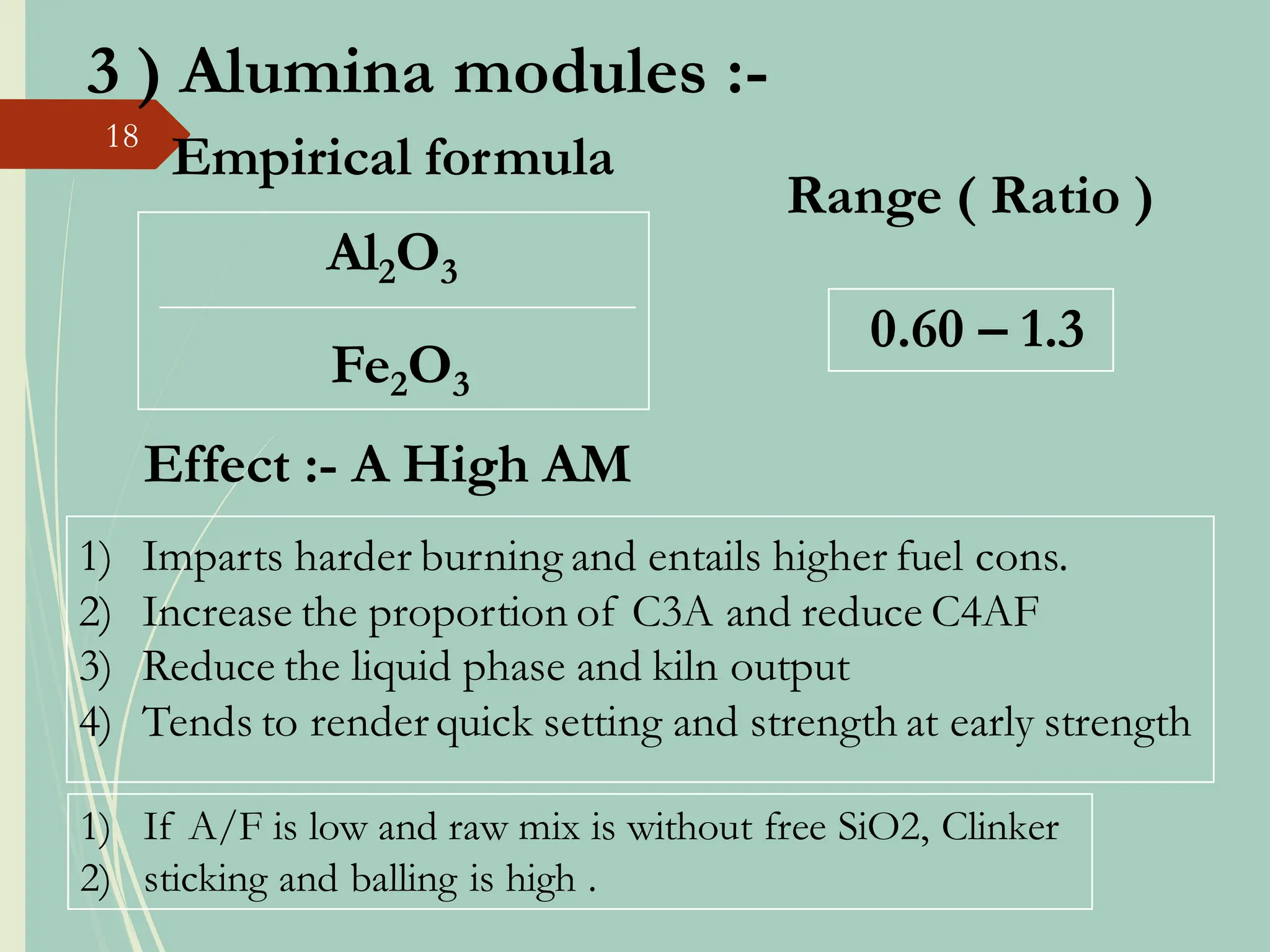
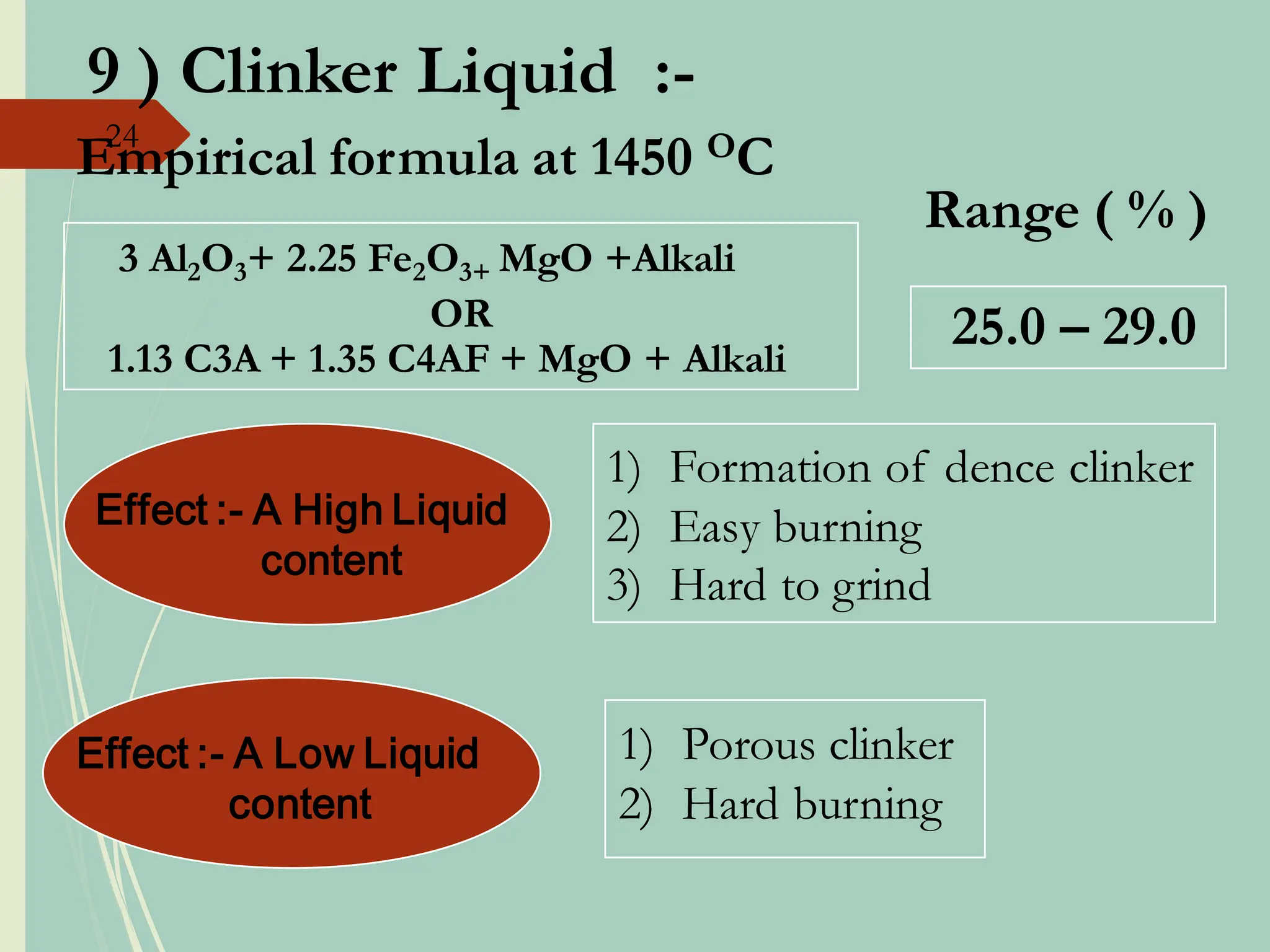
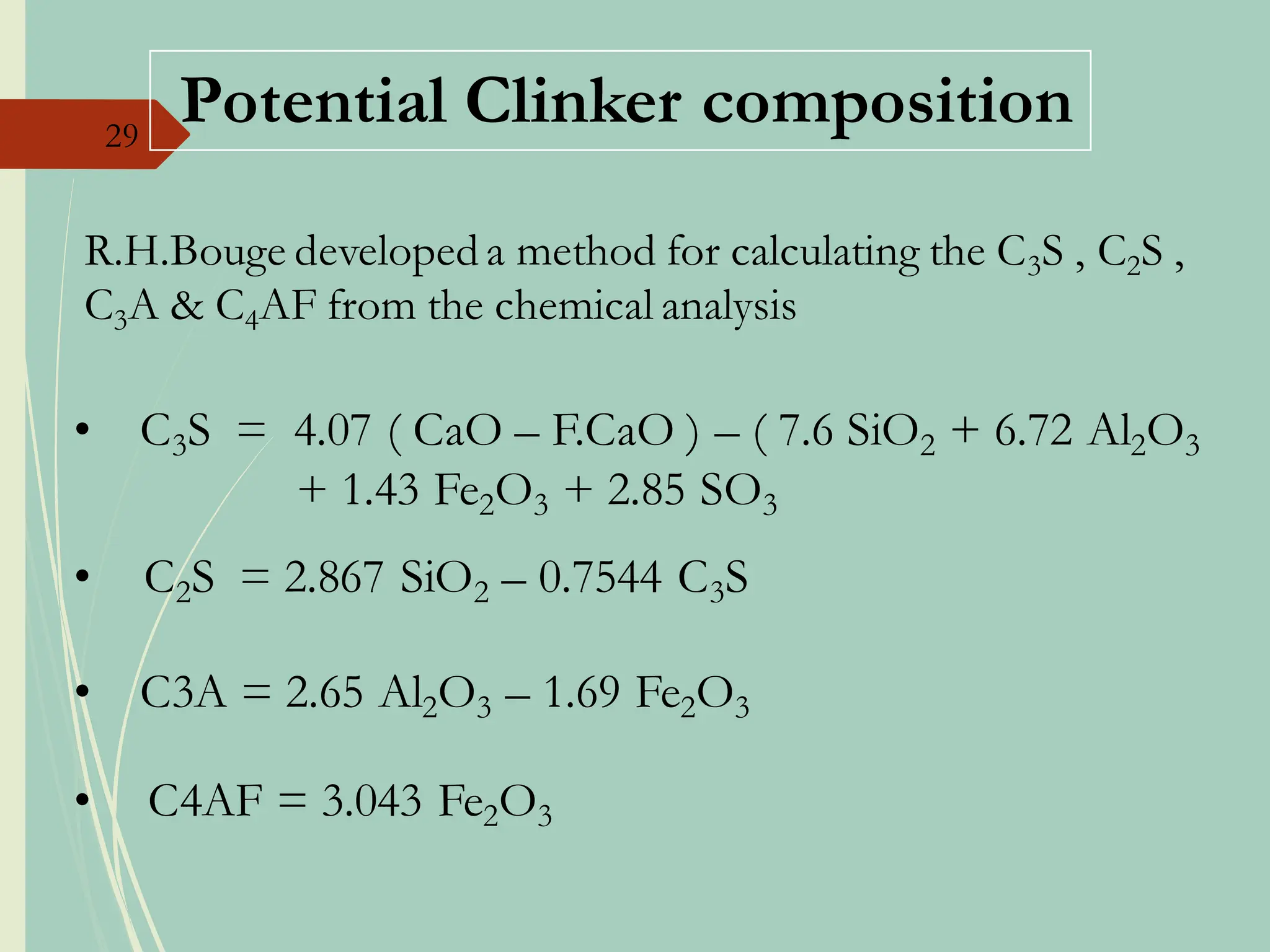
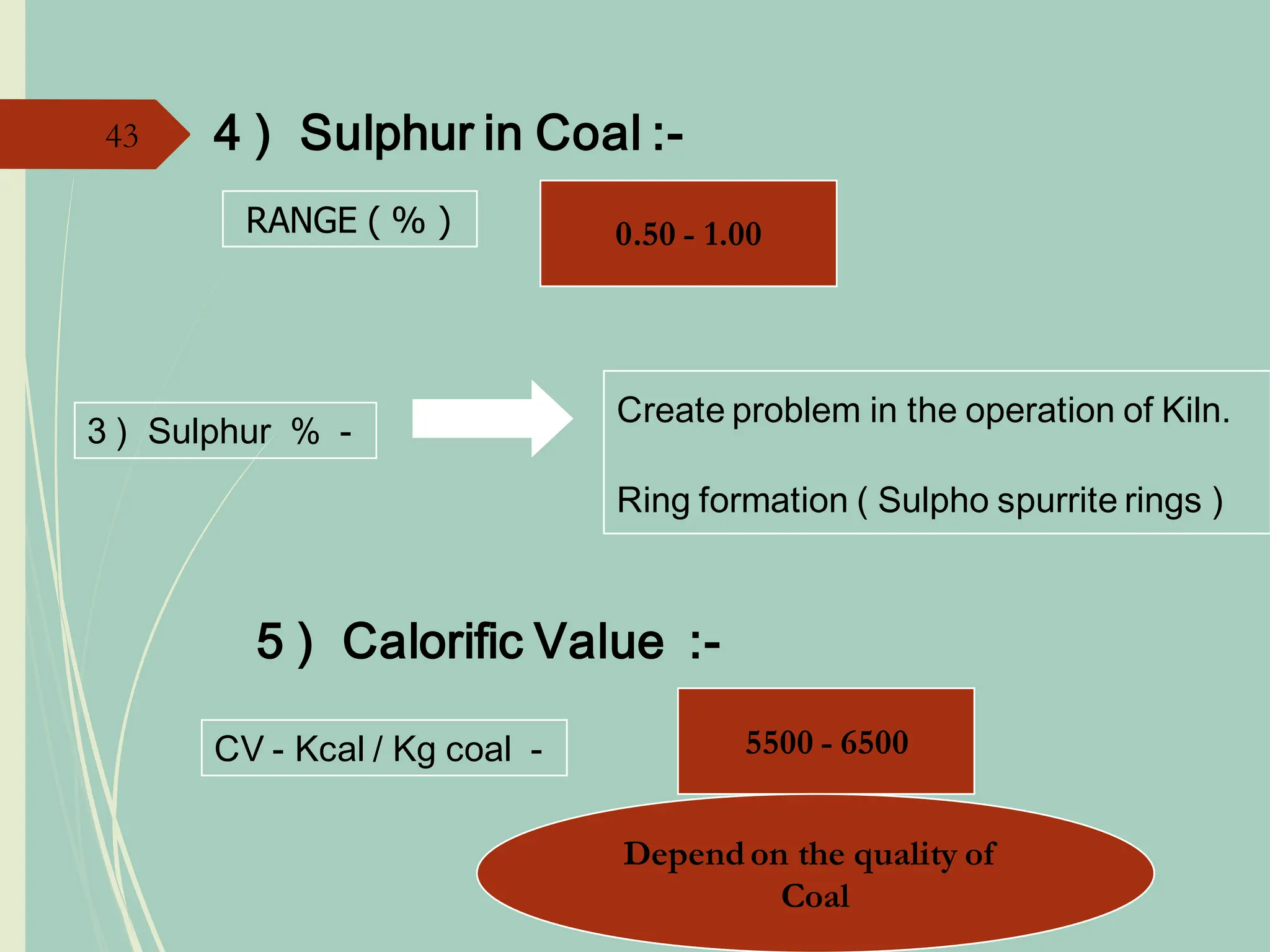
The document details the raw mix design process for clinker manufacturing, emphasizing the importance of raw material quality, proportions, and the chemical composition necessary for efficient cement production. It outlines the stages of the cement manufacturing process, including various temperature reactions in the kiln, and defines critical parameters such as lime saturation factor and silica modulus that affect clinker quality. Additionally, factors influencing the burnability of the raw mix and the impact of coal properties on production efficiency are discussed.