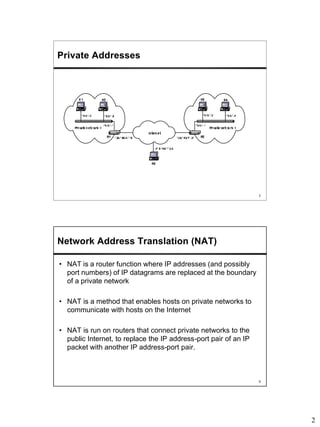
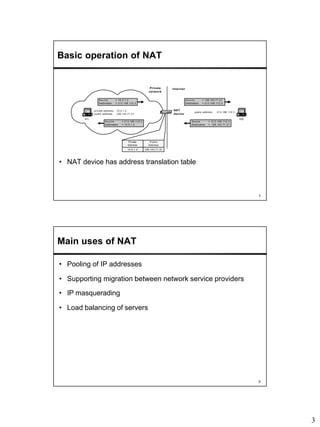
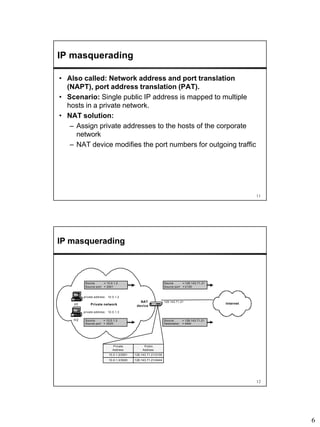
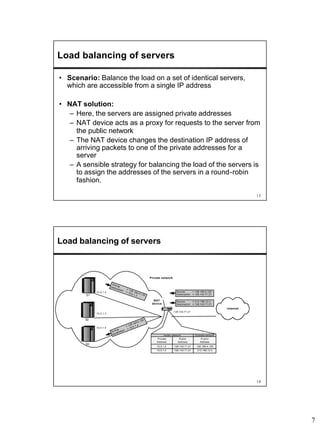
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows hosts on private networks to communicate with hosts on the public Internet. NAT is run on routers and replaces the IP address and port of packets traveling between a private network and the public Internet. The main uses of NAT are pooling IP addresses, supporting migration between ISPs, IP masquerading, and load balancing servers. NAT solves issues like IP address exhaustion but breaks the end-to-end connectivity principle and can cause problems for applications that embed IP addresses.