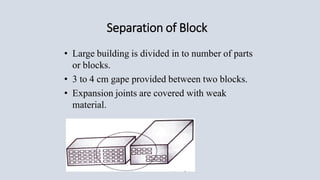
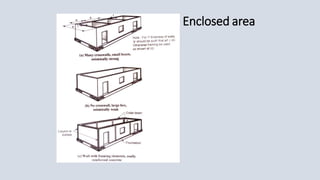
This document discusses key aspects of earthquake resistant building design. It outlines several important features such as symmetry, regularity, separation of blocks, simplicity, lightness, continuity of construction, and use of ductile materials. These features help reduce horizontal and vertical vibration during an earthquake and minimize damage to the building structure. The document emphasizes designing buildings to be simple and dividing large structures into rectangular blocks to improve earthquake resistance.