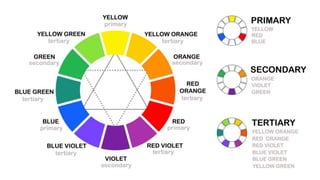
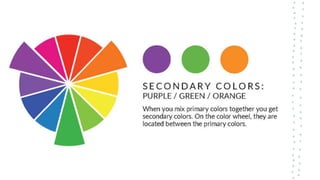
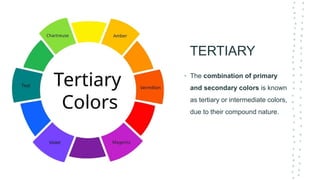
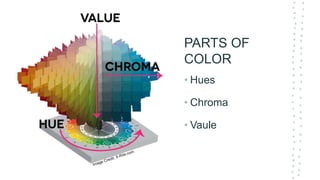
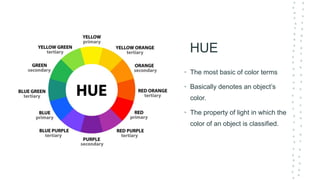
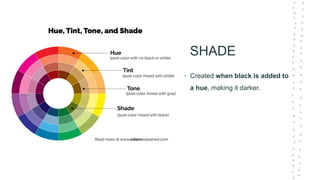
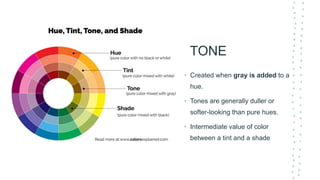
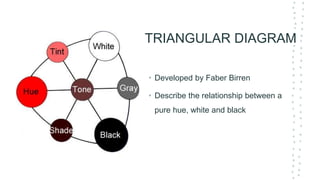
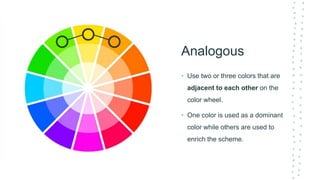
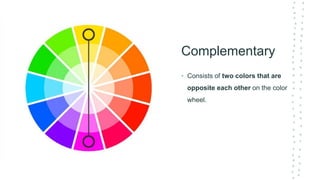
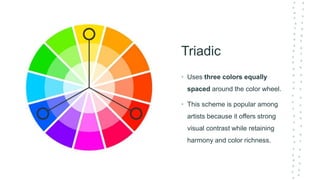
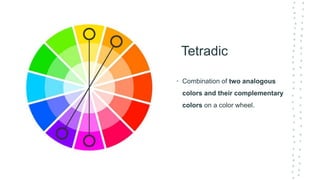
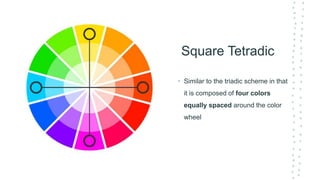
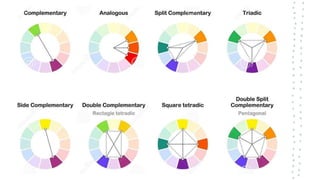
This document discusses color theory and its application in architectural design. It begins by defining key terms like chromatic, energy, hue, value, and saturation. It then explores color psychology and how different hues can impact moods. The document outlines several color schemes architects may use, such as monochromatic, analogous, complementary, split complementary, and triadic. It closes by emphasizing the importance of understanding color theory to properly apply color in architectural works and create desired psychological effects.