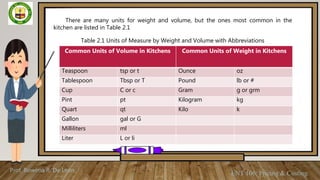
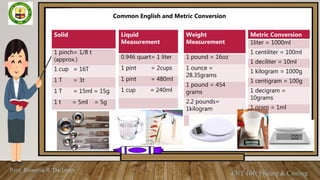
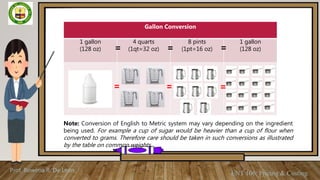
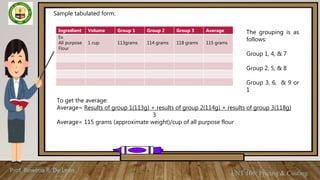
This document discusses weights and measures used in food production. It defines weights as a measurement of mass using units like ounces and grams, while measures refer to volumes using cups, teaspoons, etc. Common units of weight and volume with abbreviations are presented in a table. Conversion tables show equivalents between English and metric units for solid, liquid and weight measurements. Students are asked to memorize the units and practice converting amounts. Accurate measurement is important for food quality, cost control and consistency. Group activities involve measuring and weighing sample ingredients to calculate averages.