This document summarizes the physical development of infants and toddlers. It discusses the major areas of development from birth to age 2 including:
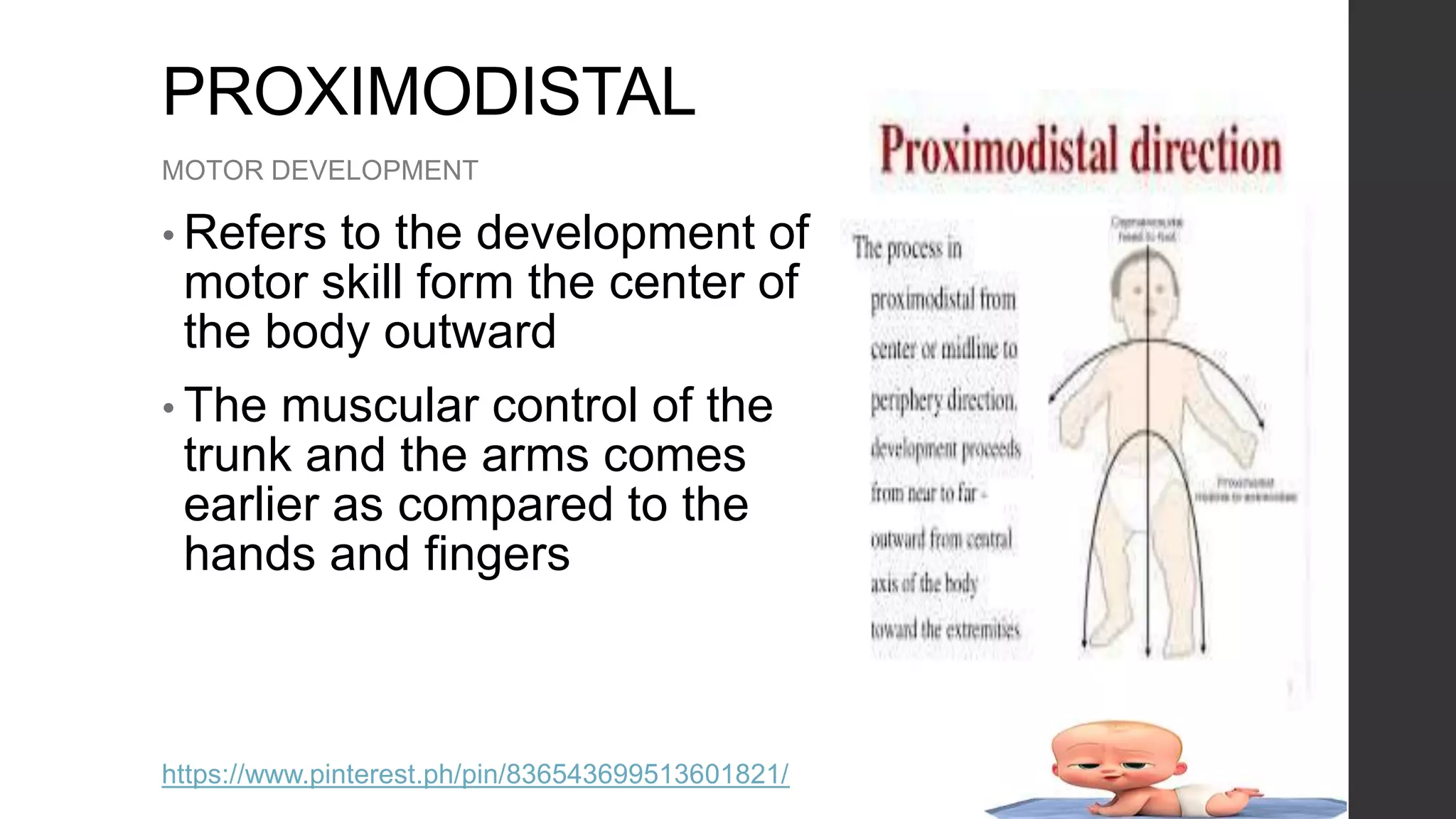
- Cephalocaudal and proximodistal motor development which describes how infants develop control of their upper body before lower body.
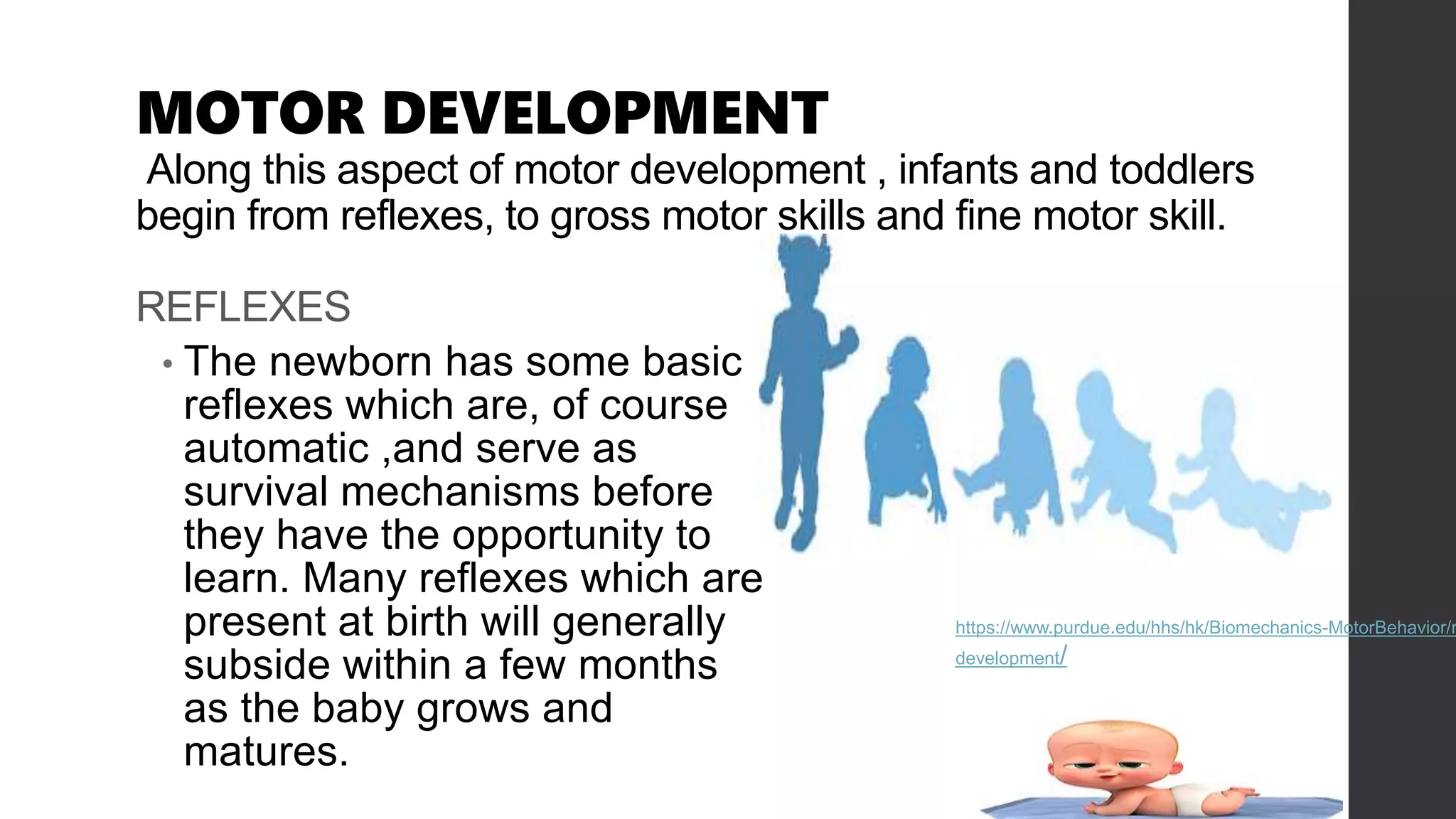
- Important milestones in gross and fine motor skills like grasping, rolling over, sitting, crawling, walking and hand-eye coordination.
- Rapid brain development and myelination which increases neural connections and speed of information processing.
- Emergence of reflexes in newborns and their purpose in survival before voluntary control.
The document outlines physical, sensory, language and cognitive skills infants and toddlers typically acquire at