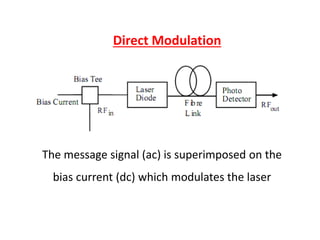
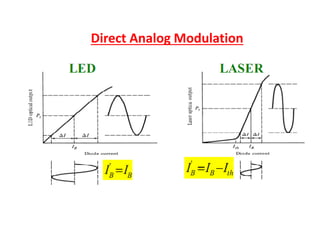
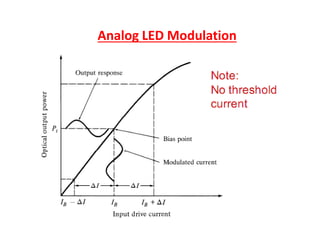
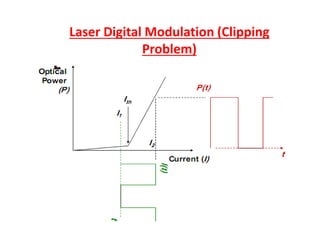
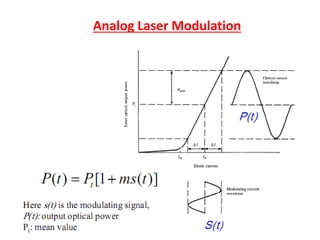
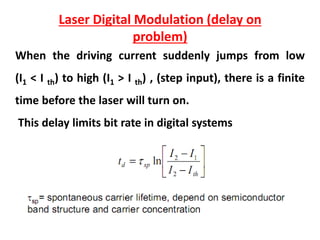
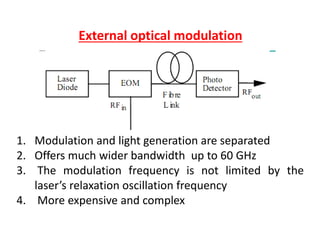
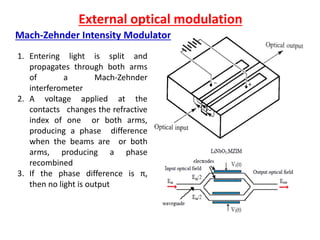
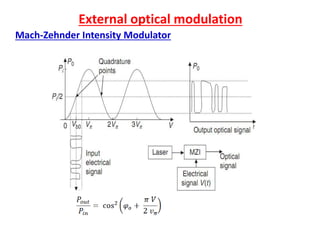
Optical modulation can be done directly by modulating the driving current of the light source, or externally by modulating light in the fiber. Direct modulation has limitations including turn-on delay and nonlinear distortions that limit modulation speed. External modulation using a Mach-Zehnder interferometer separates modulation and light generation, allowing wider bandwidth up to 60 GHz without limitations from the laser's properties.