Embed presentation
Download to read offline






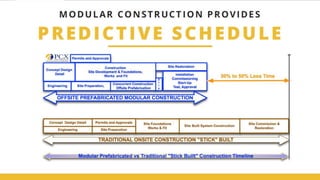

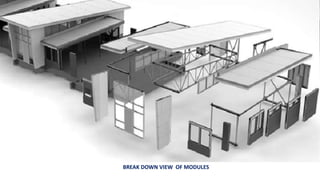
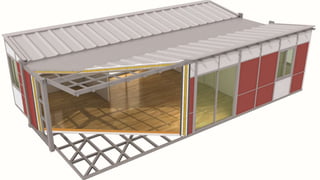










Modular buildings consist of prefabricated rooms or sections that are constructed off-site and assembled on-site. They offer advantages like less waste, lower costs, safer construction, and shorter build times compared to conventional methods. The Dean 461 apartment building in Brooklyn is an example of a modular high-rise consisting of 32 stories and 363 pre-fab apartment blocks. While modular construction has advantages, it also has some disadvantages such as potential transport difficulties with large modules and an unconventional aesthetic.



















