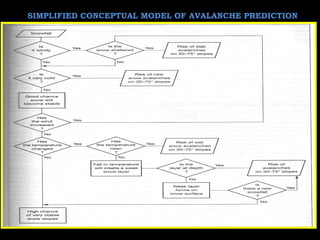
This document discusses different types of models used for modeling spatial processes in GIS for decision support. It describes natural and scale analogue models which use real-world events or objects as analogues. Conceptual models represent processes visually using diagrams. Mathematical models include deterministic, stochastic, and optimization models. Deterministic models show direct relationships while stochastic models use probabilities. Optimization models maximize or minimize outputs. The document argues that combining different modeling techniques in GIS allows for complex spatial process modeling to support decisions.