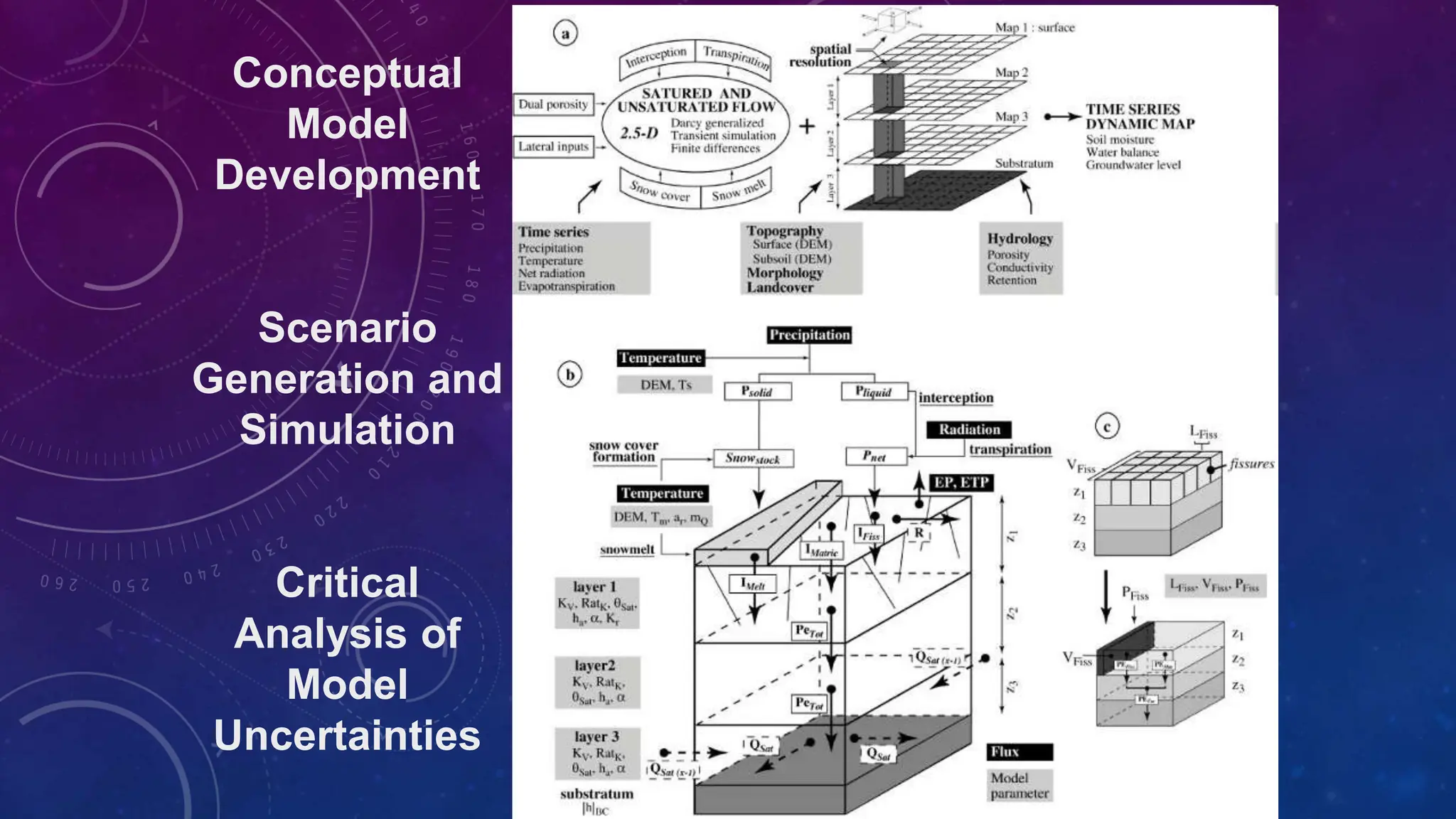
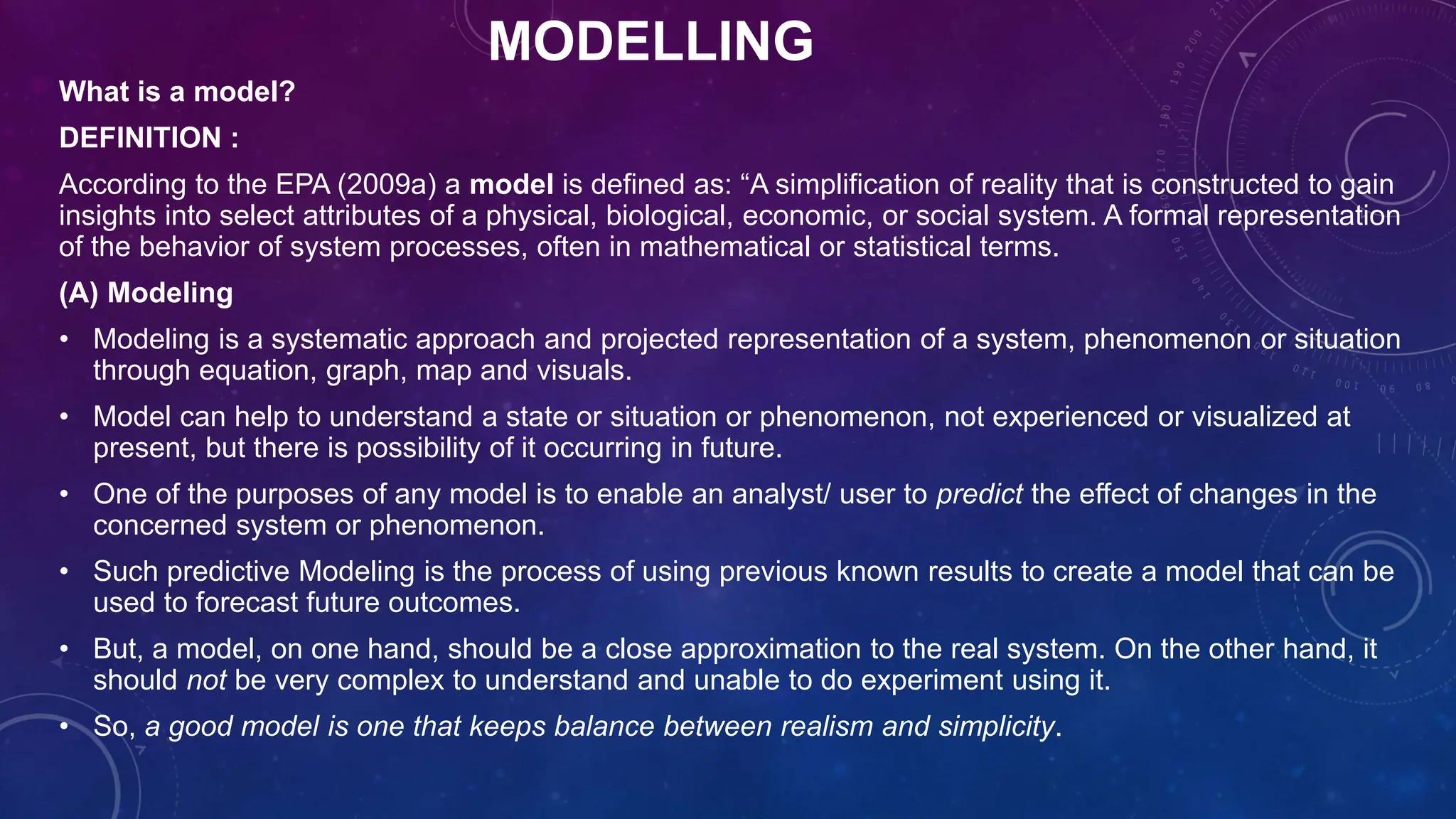
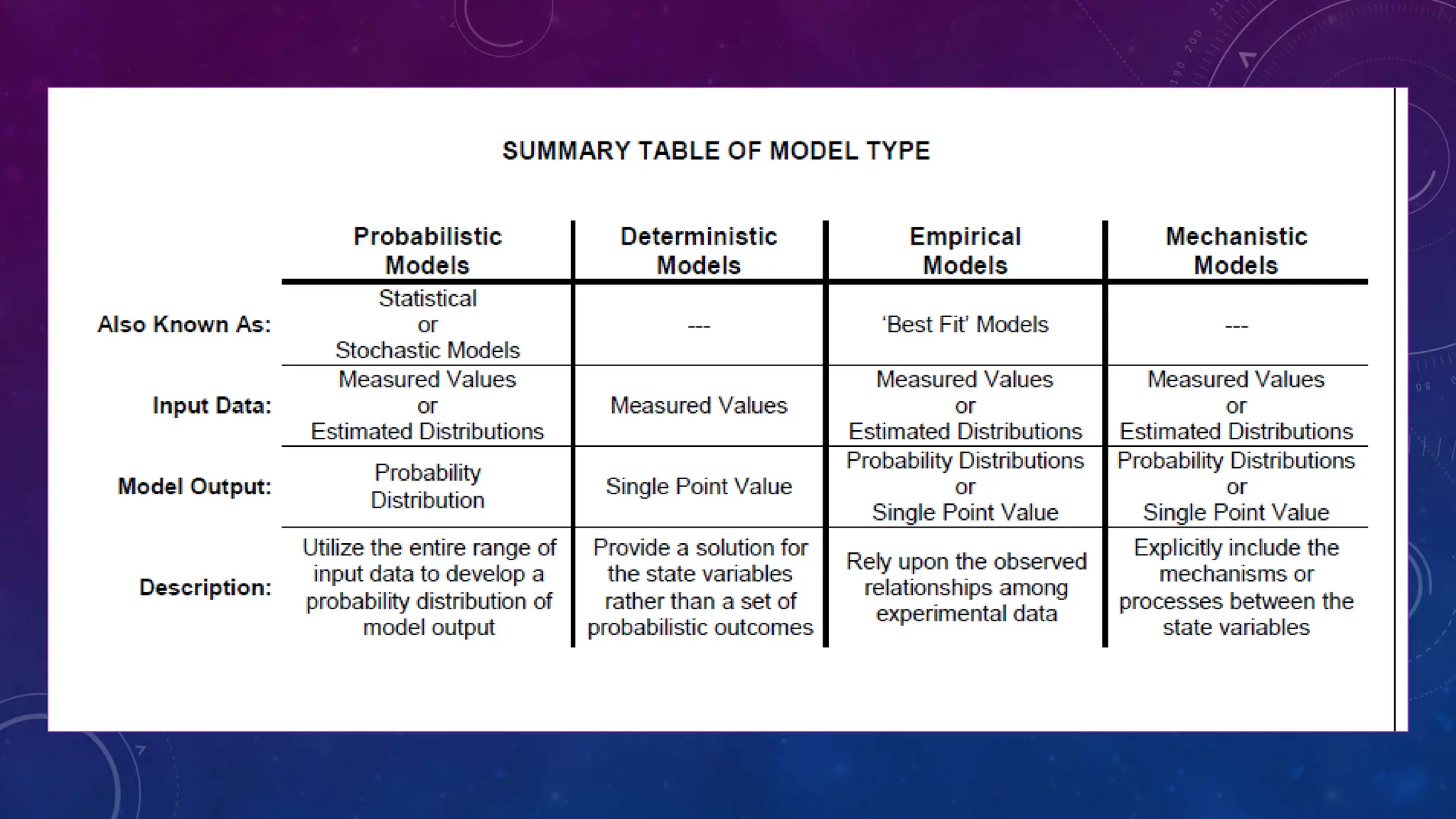
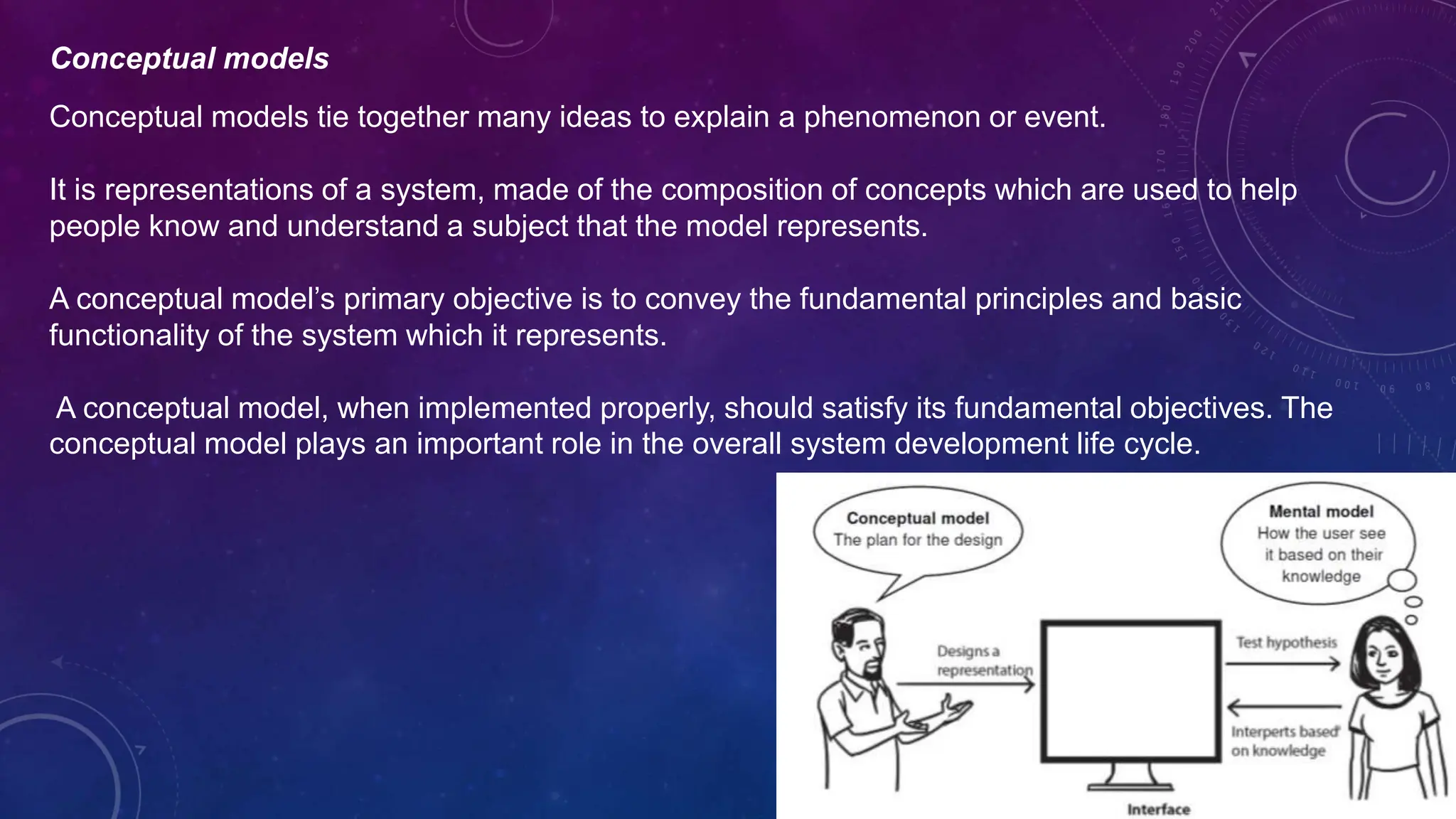
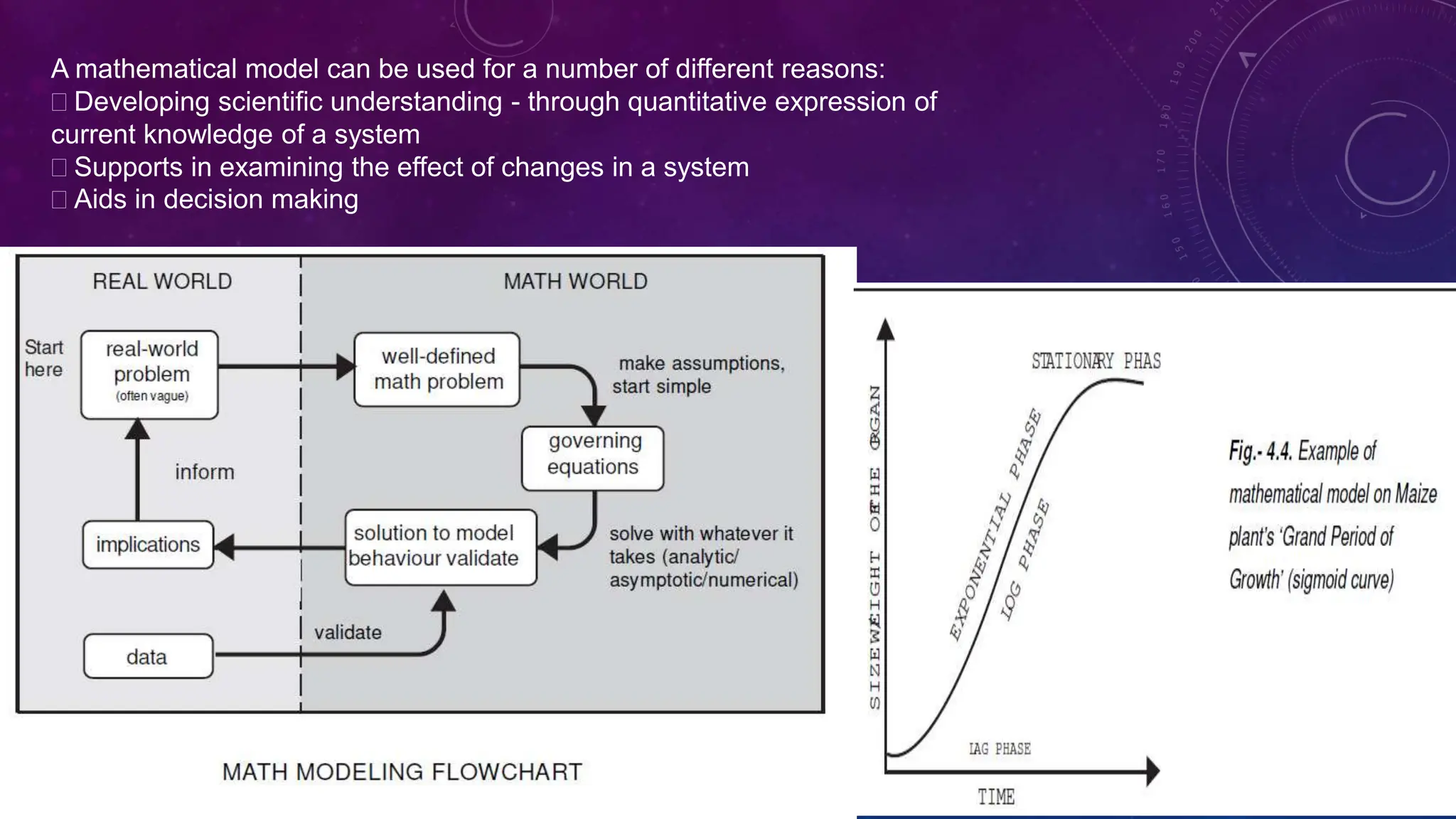
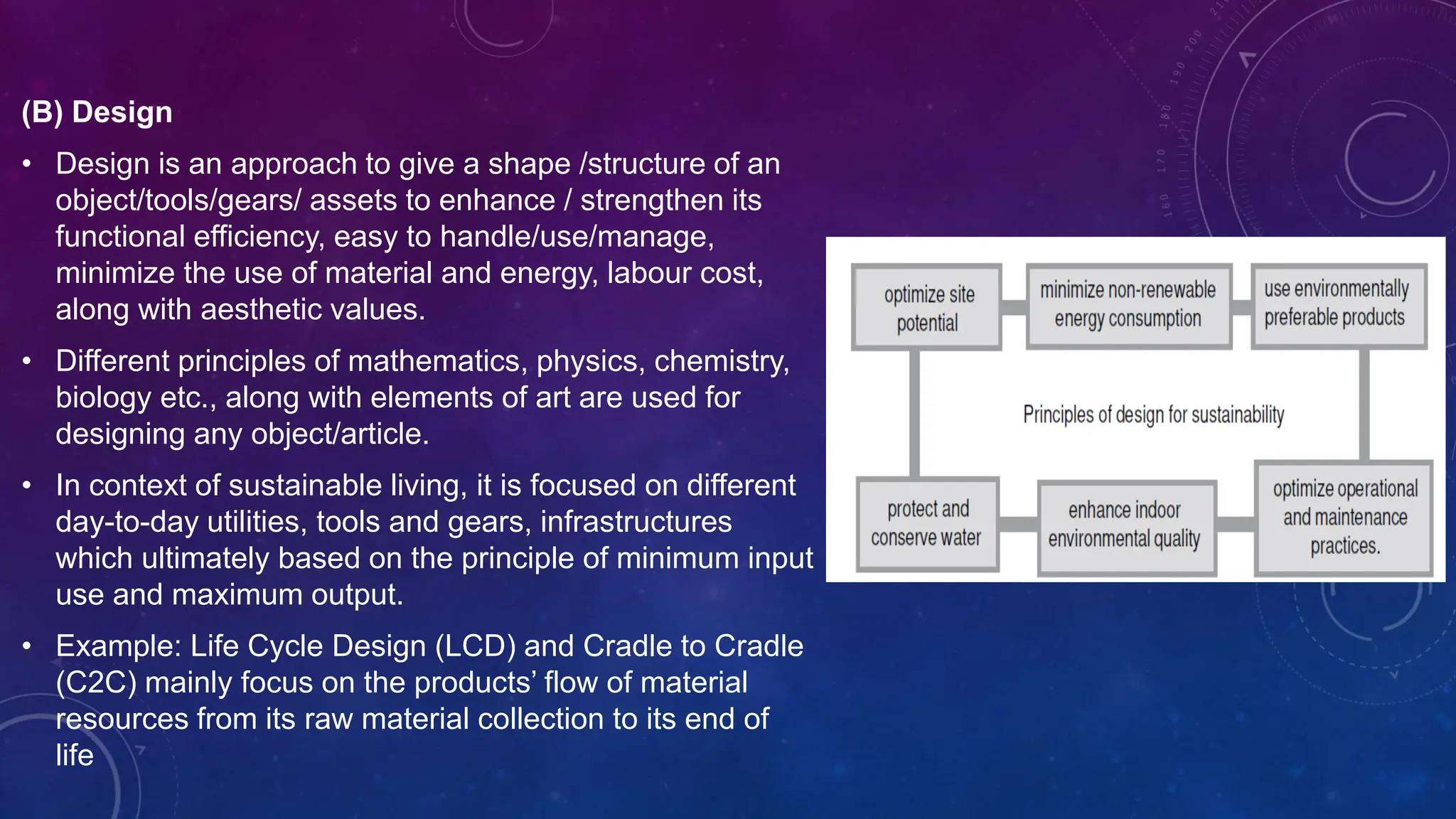
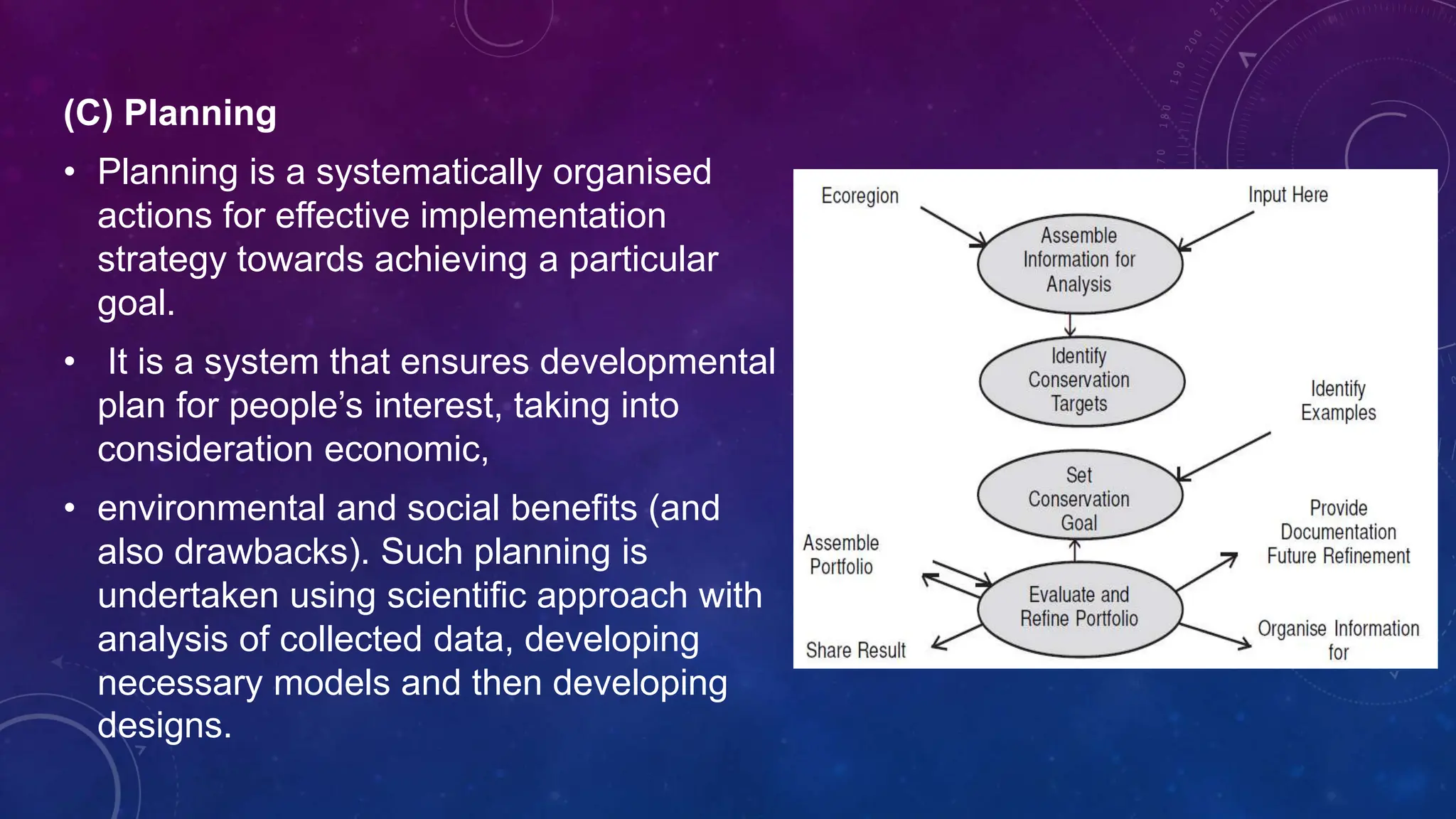
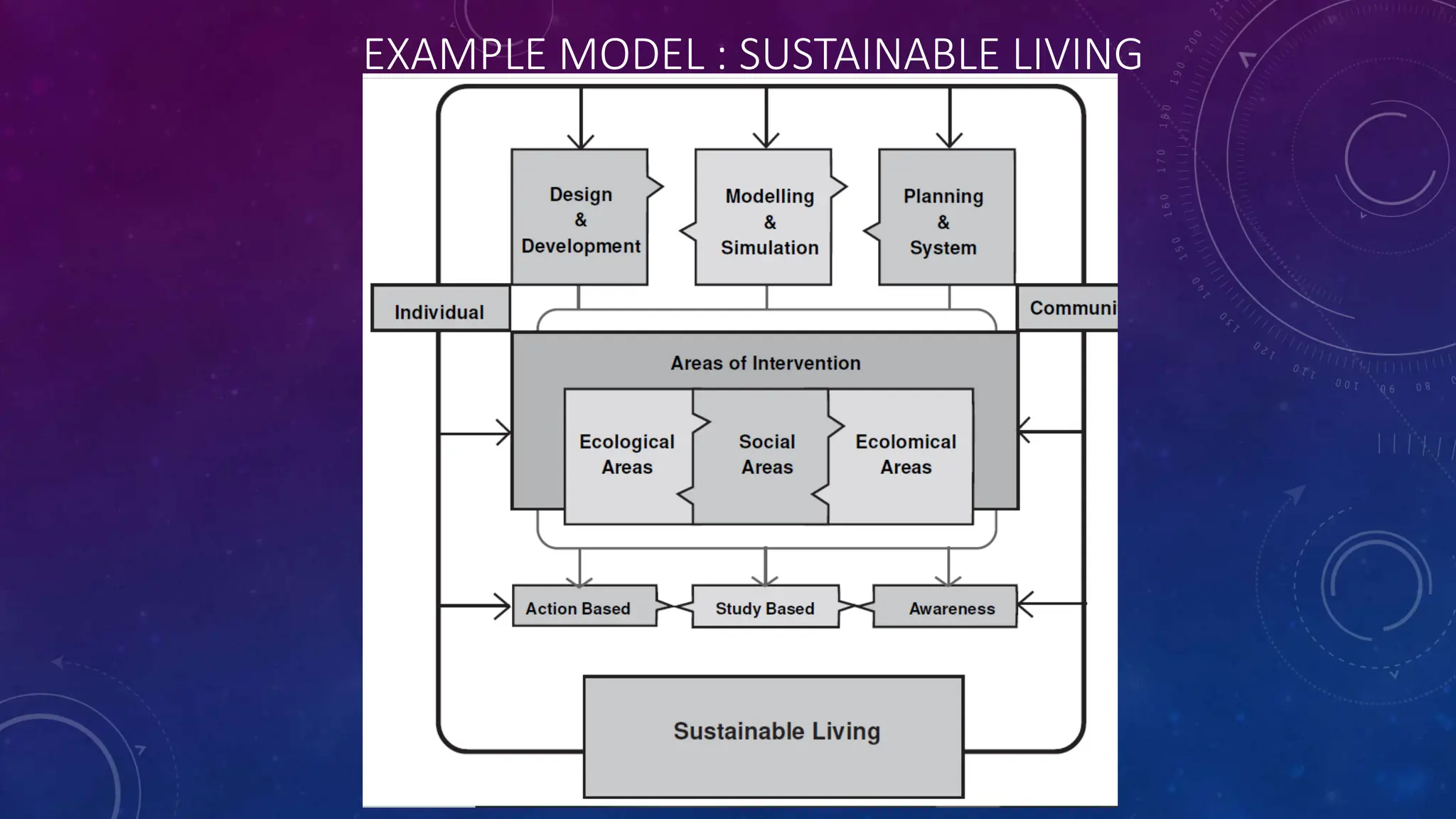
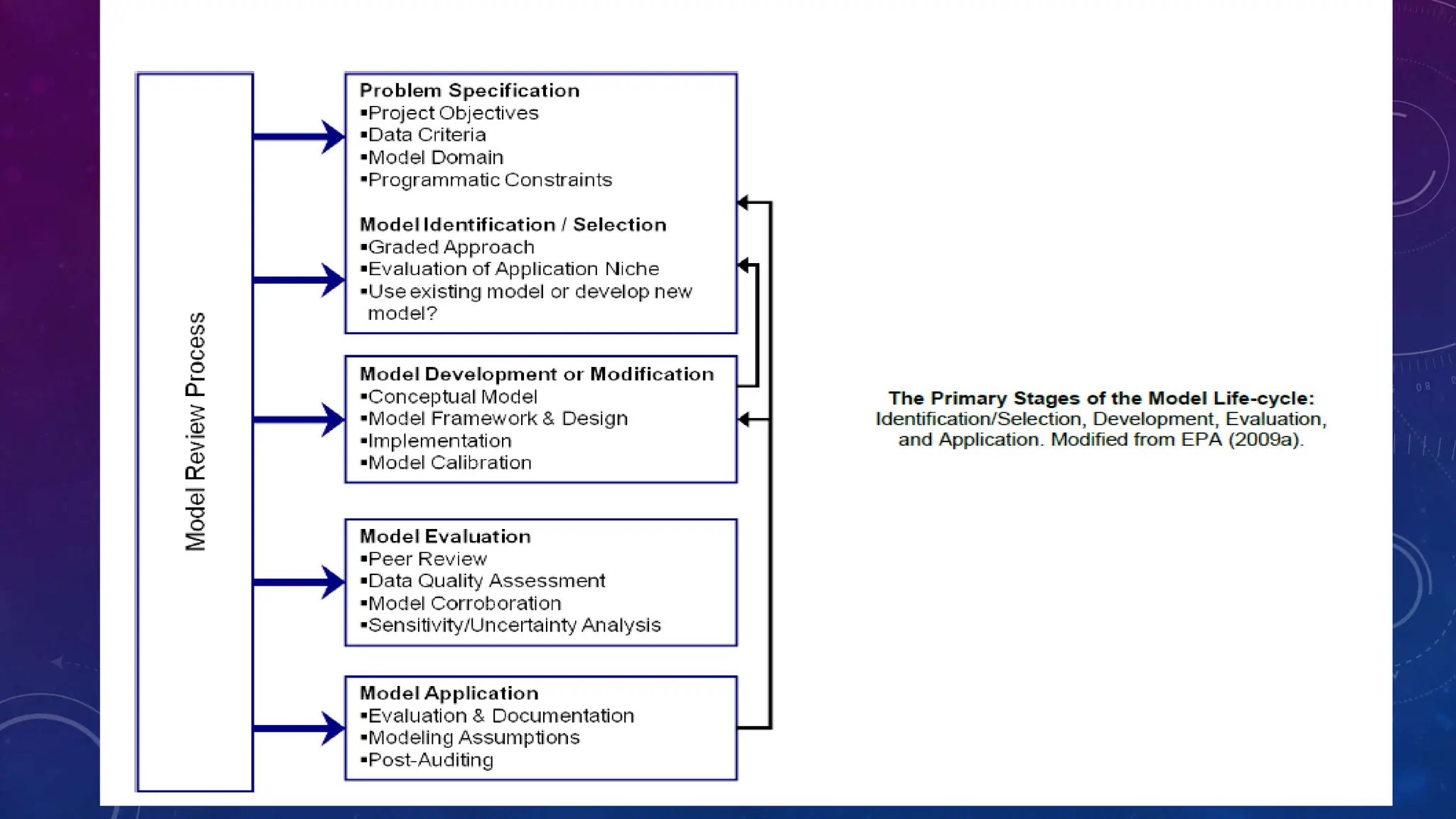
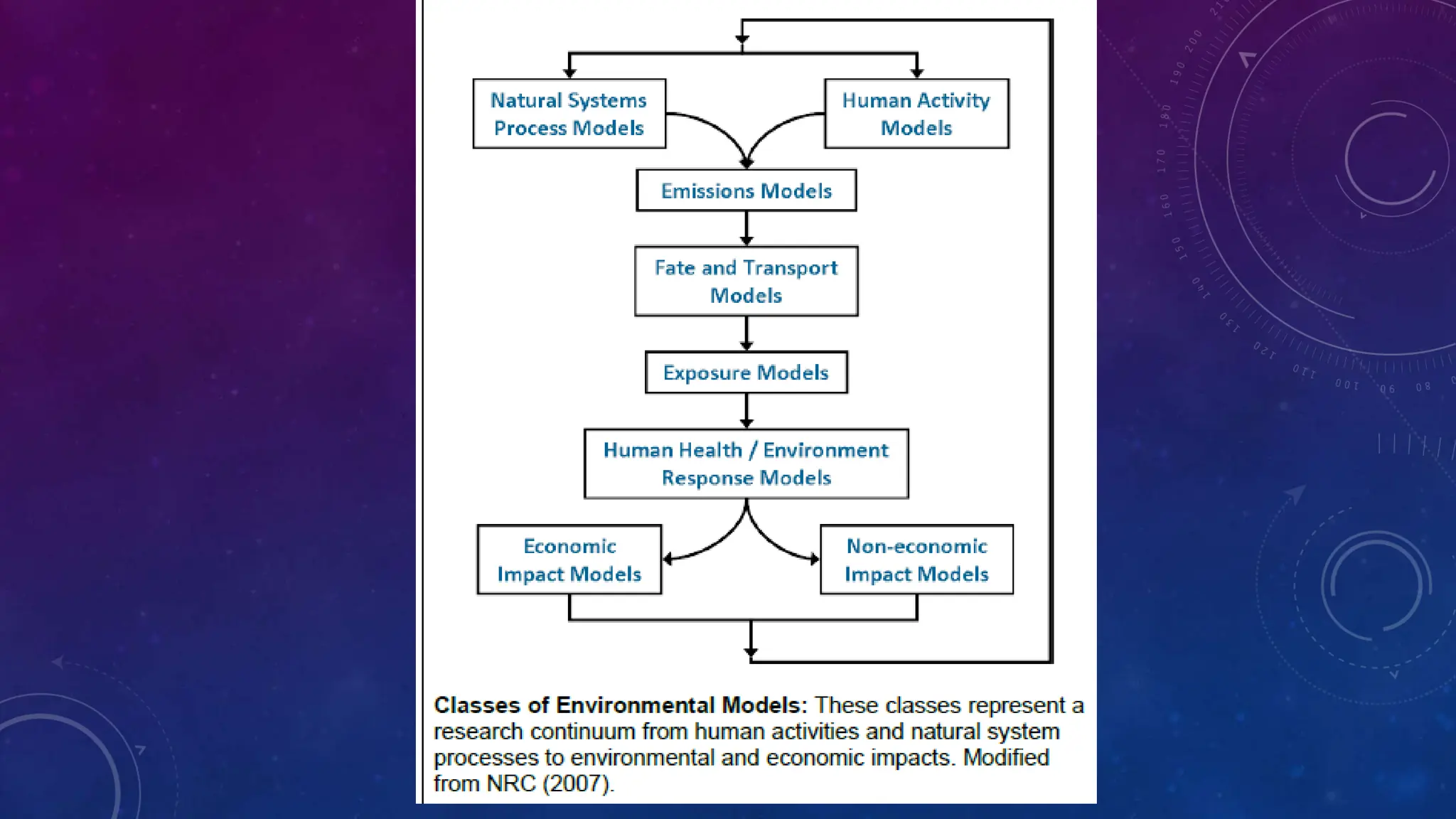
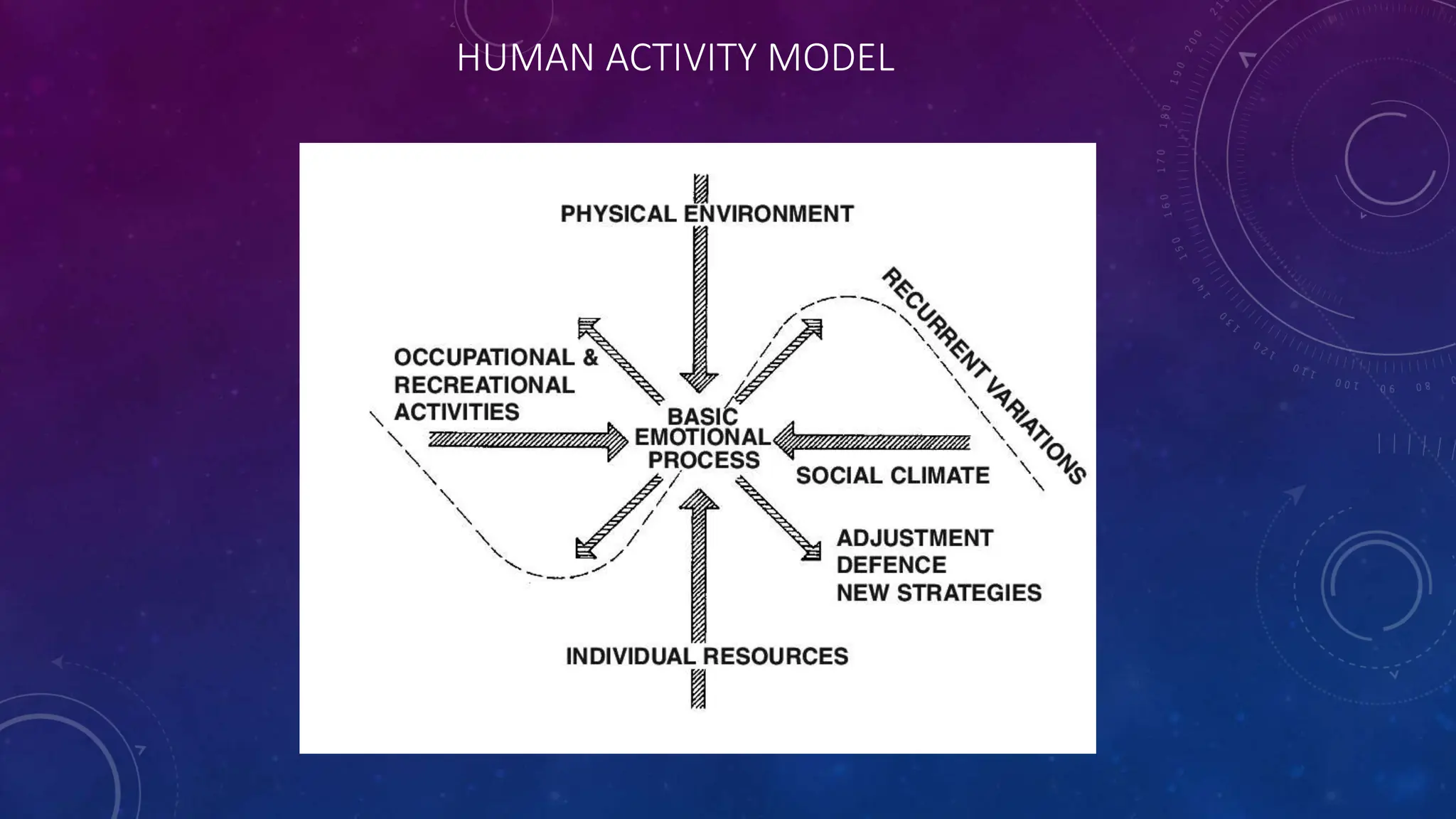
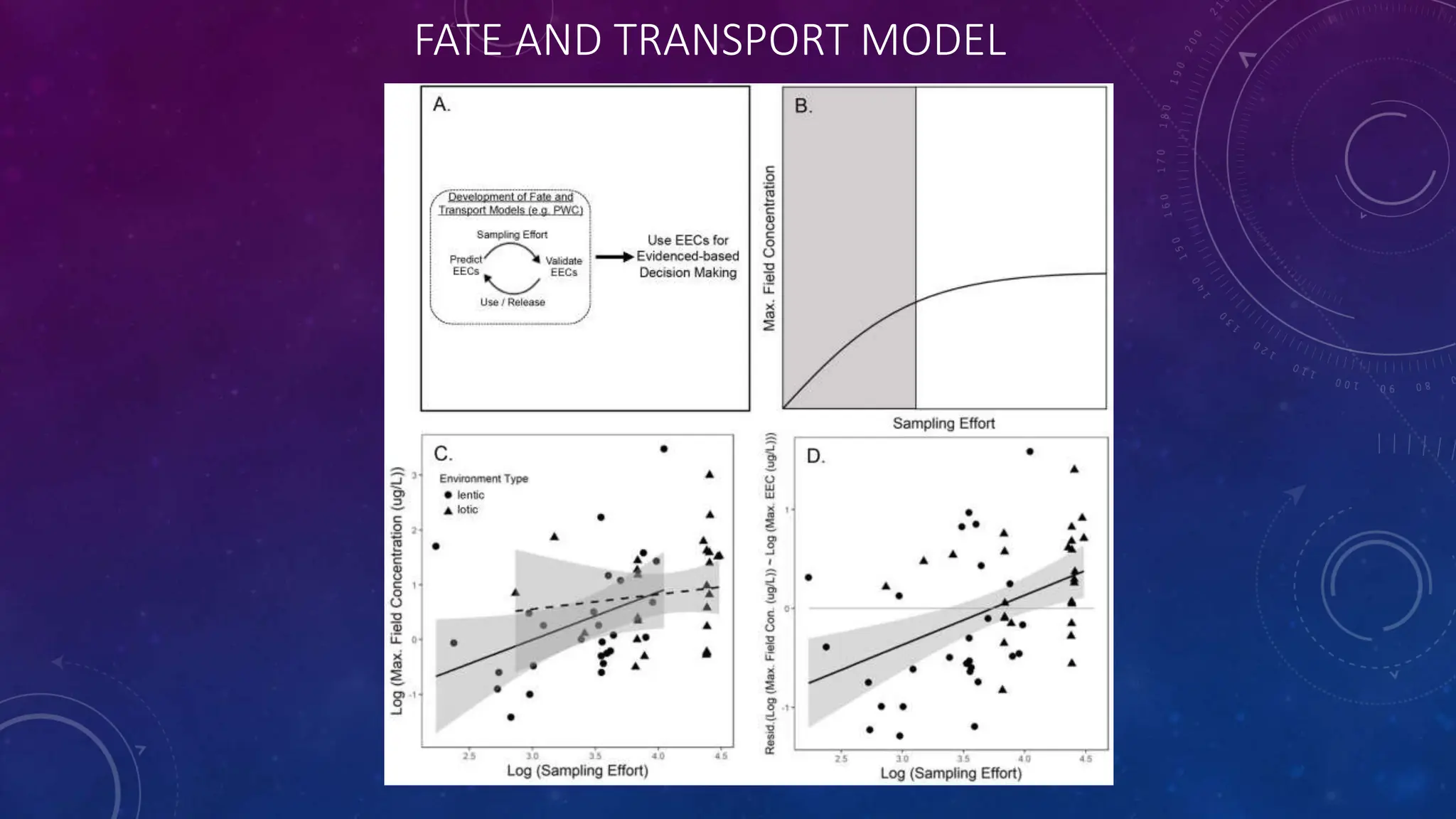
Environmental systems are complex arrangements of interacting biological, physical, chemical, social, and economic components within the Earth's environment. They are characterized by nonlinear interactions between components, heterogeneous features that vary over small spatial and temporal scales, and incompatible scales between components. Additionally, many system processes are inaccessible or unobservable. There are three main types of models used to model environmental systems: empirical, conceptual, and process-based models, which differ in complexity. Models are used to understand, diagnose, and forecast environmental systems and issues.