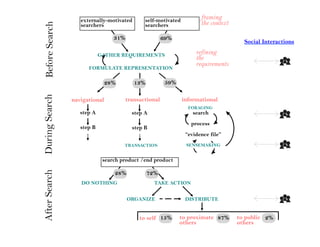
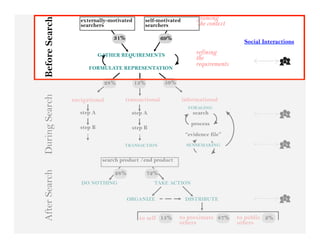
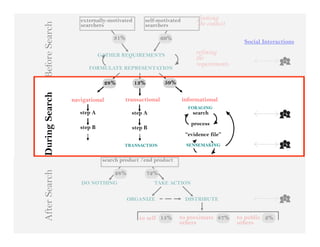
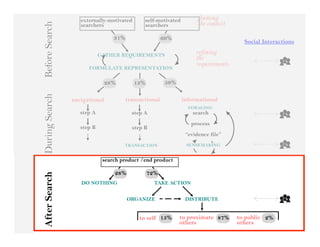
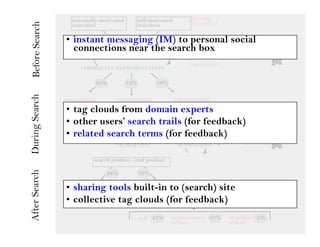
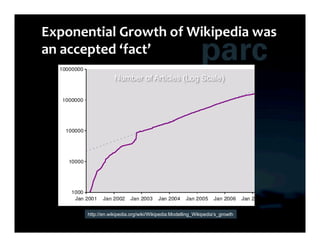
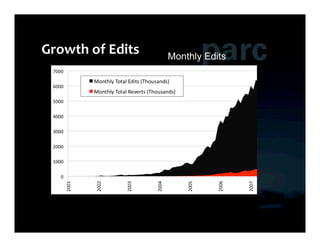
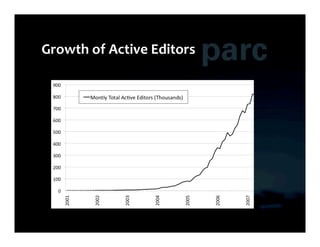
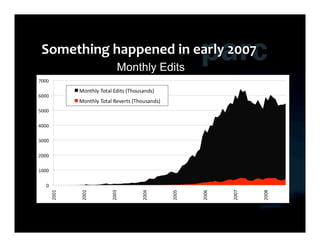
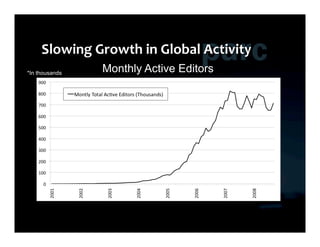
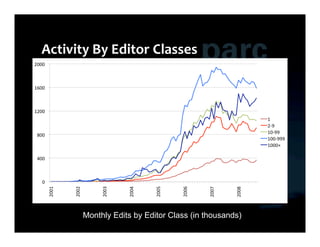
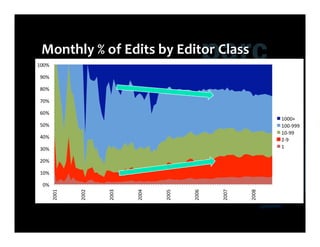
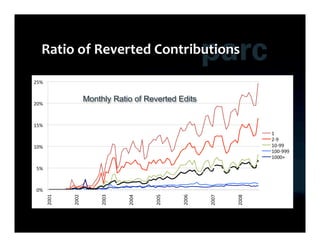
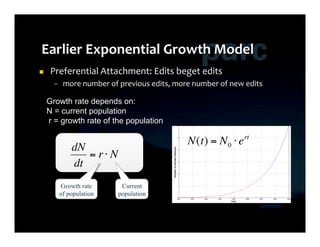
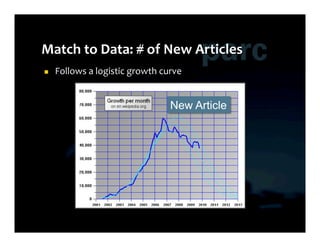
This document summarizes Ed Chi's keynote presentation on augmented social cognition at the Hypertext 2010 workshop. Chi discusses characterizing social systems using analytics, modeling social interactions and dynamics, prototyping tools to increase benefits or reduce costs, and evaluating prototypes with real users. He provides examples of models for information diffusion and Wikipedia growth. Chi also covers challenges in identifying relevant models from literature and techniques for addressing noise in social tagging like synonyms, misspellings and morphologies.




![ For
example,
for
information
diffusion,
it’s
theory
of
influentials
[Gladwell,
etc.]
– reach
a
small
group
of
influential
people,
and
you’ll
reach
everyone
else
Figure From: Kleinberg, ICWSM2009
Hypertext 2010 Keynote at MSM
2010-06-13 Workshop 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-12-social-modeling-hypertext-msmworkshop-1hr-100613234213-phpapp01/85/Model-Driven-Research-in-Social-Computing-5-320.jpg)





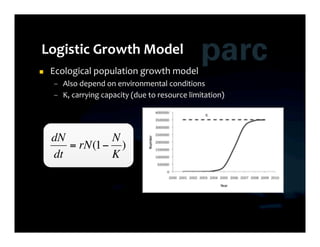


![ r-‐Strategist
– Growth
or
exploitation
dN N
– Less-‐crowded
niches
/
produce
many
= rN(1− )
offspring
dt K
K-‐Strategist
– Conservation
[Gunderson & Holling 2001]
– Strong
competitors
in
crowded
niches
/
invest
more
heavily
in
fewer
offspring
€](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-12-social-modeling-hypertext-msmworkshop-1hr-100613234213-phpapp01/85/Model-Driven-Research-in-Social-Computing-24-320.jpg)


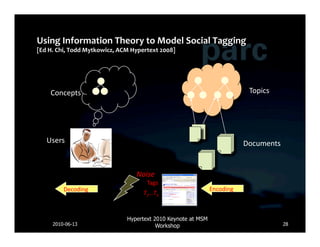
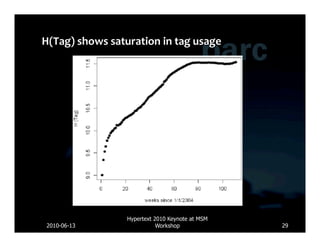
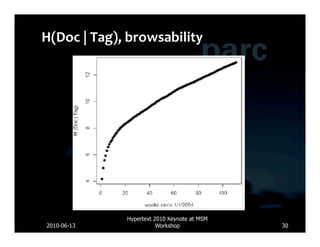


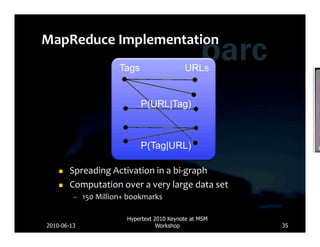
![Database Lucene
• Delicious • P(URL|Tag) • Serve up search
• Ma.gnolia • P(Tag|URL) results
• Tuples of • Pre-computed
• Other social cues bookmarks • Bayesian Network patterns in a fast • Well defined APIs
• [User, URL, Tags, Inference index
Time]
Crawling MapReduce Web Server
Web
Server
UI Search
Frontend Results
• MapReduce:
months
of
computa*on
to
a
single
day
• Development
of
novel
scoring
func*on
Hypertext 2010 Keynote at MSM
2010-06-13 Workshop 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-06-12-social-modeling-hypertext-msmworkshop-1hr-100613234213-phpapp01/85/Model-Driven-Research-in-Social-Computing-36-320.jpg)