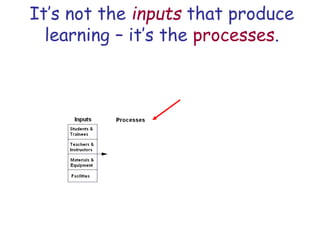
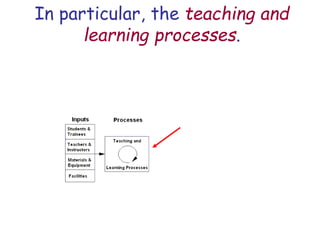
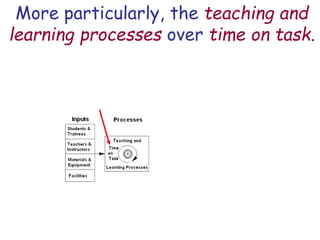
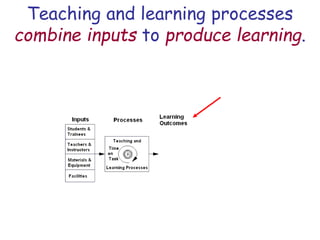
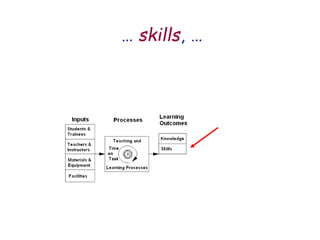
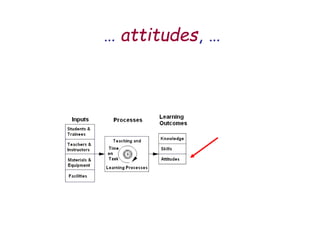
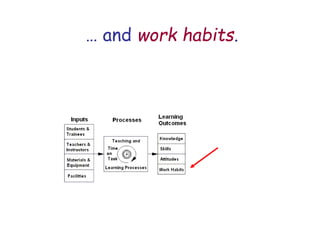
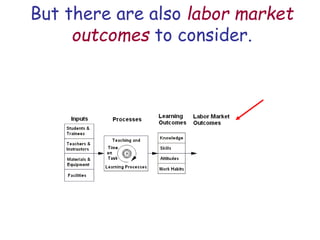
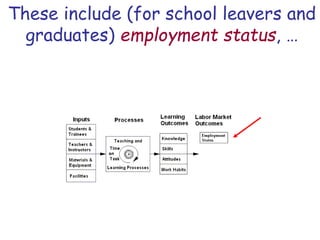
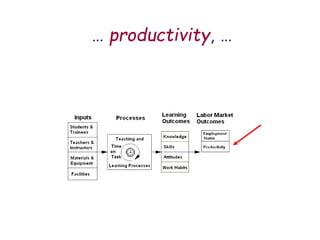
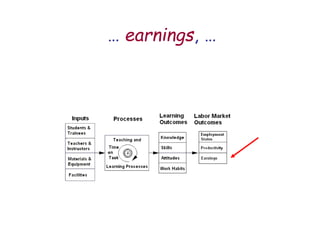
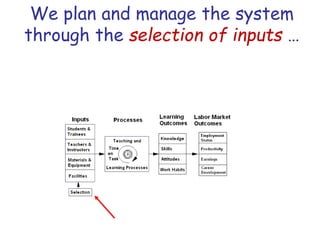
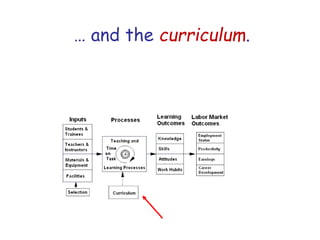
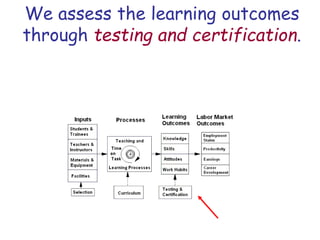
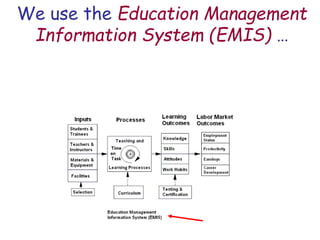
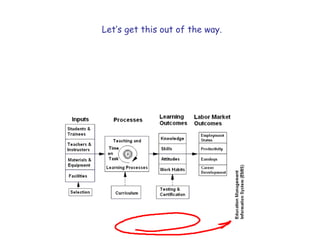
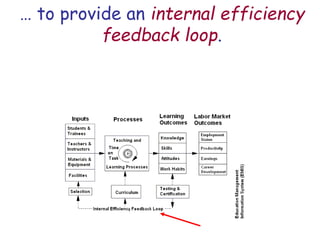
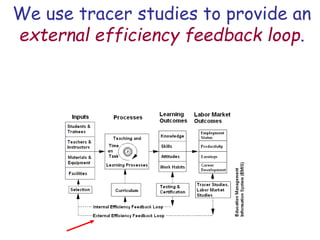
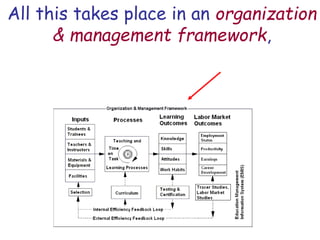
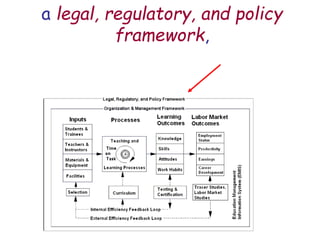
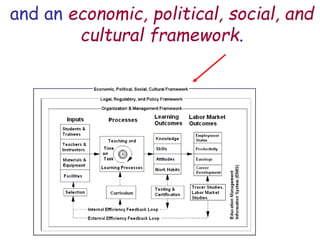
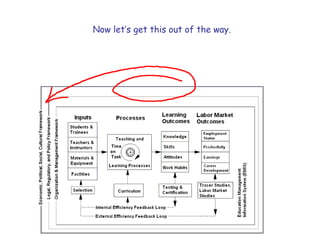
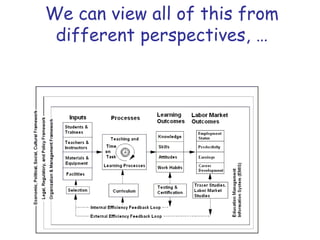
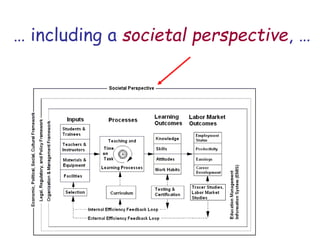
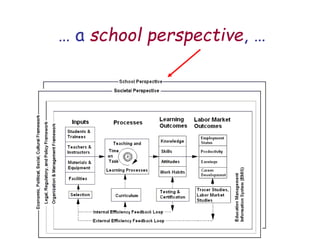
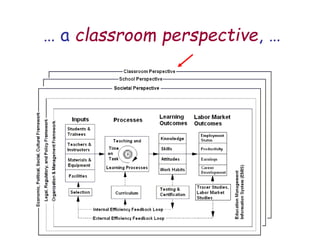
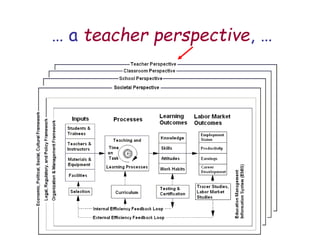
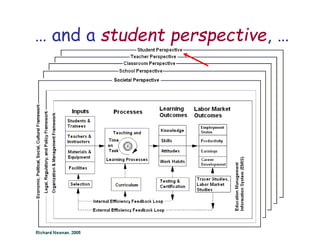
The document presents a model for monitoring and evaluating school systems, emphasizing the roles of inputs like students and teachers, and processes that lead to learning outcomes and labor market results. It highlights the importance of feedback loops to assess efficiency and cautions against confusing correlation with causation in educational contexts. The model aims to aid in planning, management, and development while acknowledging the complex frameworks surrounding education systems.