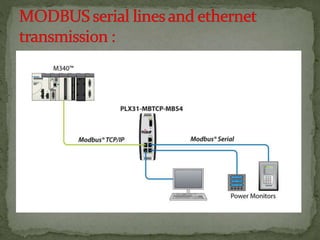
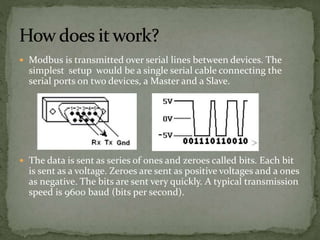
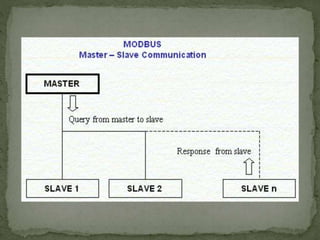
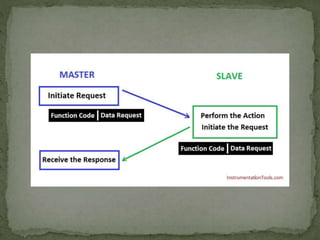
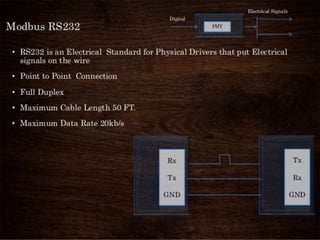
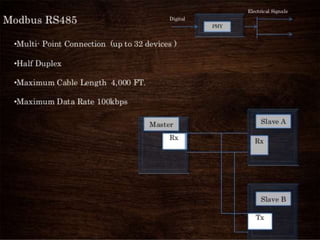
Modbus is a serial communications protocol originally developed for use in industrial applications with programmable logic controllers. It allows for communication between industrial electronic devices using a master-slave technique with one master device initiating data requests from slave devices. Modbus supports common data types used in industrial I/O and can transmit data over serial lines or Ethernet using different protocol versions. It is commonly used in SCADA systems to transmit sensor measurements and device signals back to a main controller.