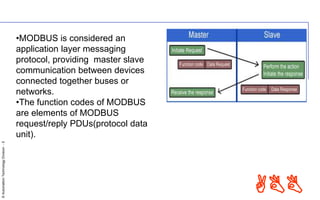
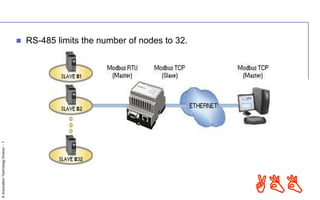
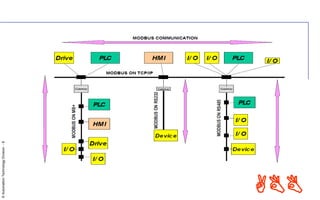
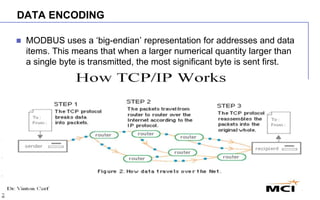
MODBUS is a serial communication protocol used for industrial automation. There are different versions, including MODBUS RTU which uses serial communication over RS-232 or RS-485, and MODBUS TCP/IP which uses TCP/IP for communication over an intranet or internet. MODBUS RTU uses a master-slave architecture and simple messages with CRC checksums to ensure reliability over serial communication. MODBUS TCP/IP allows for more connections than MODBUS RTU and uses the TCP/IP network protocol stack. Both versions are open, royalty-free protocols that enable communication between industrial devices.