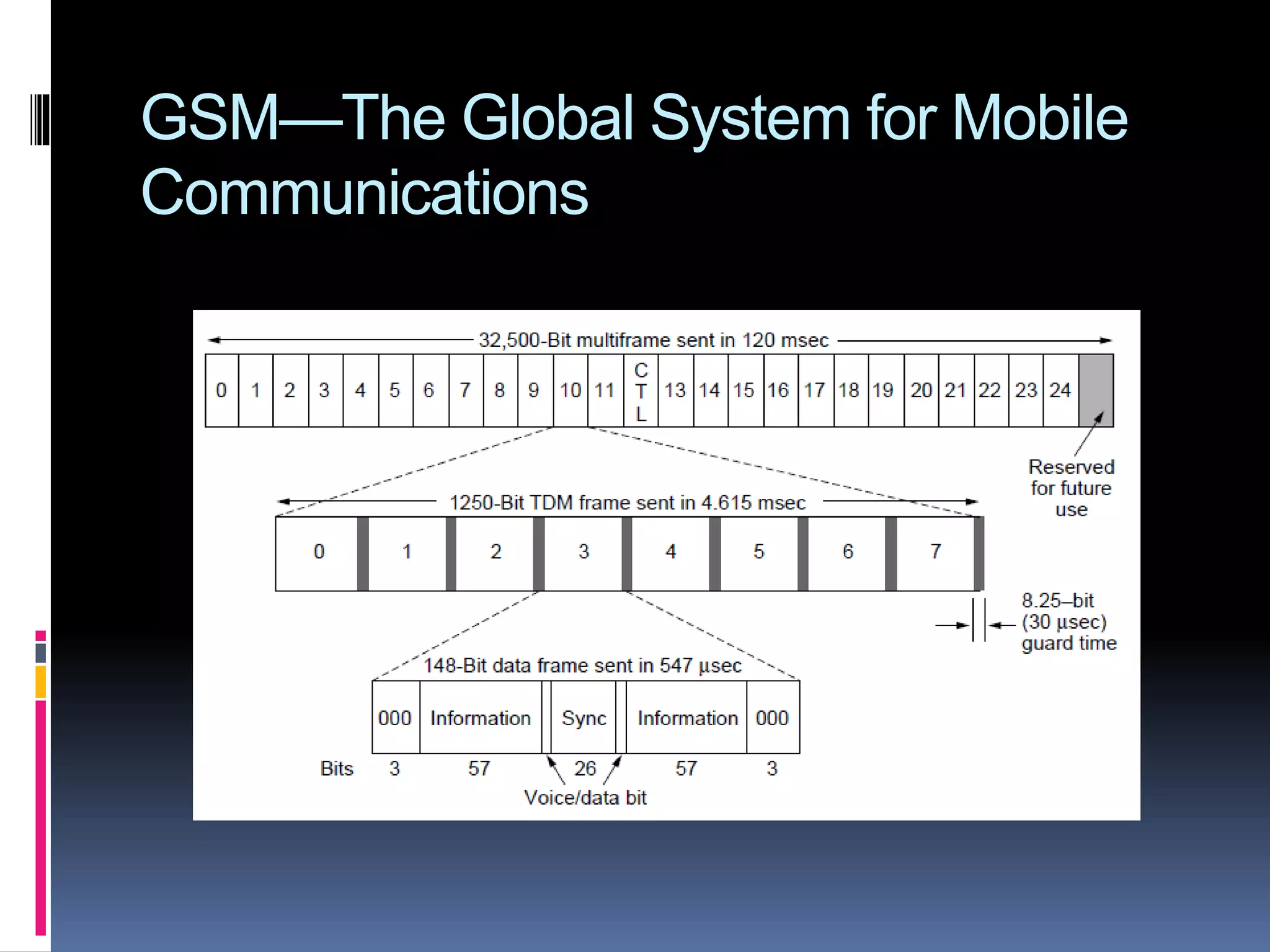
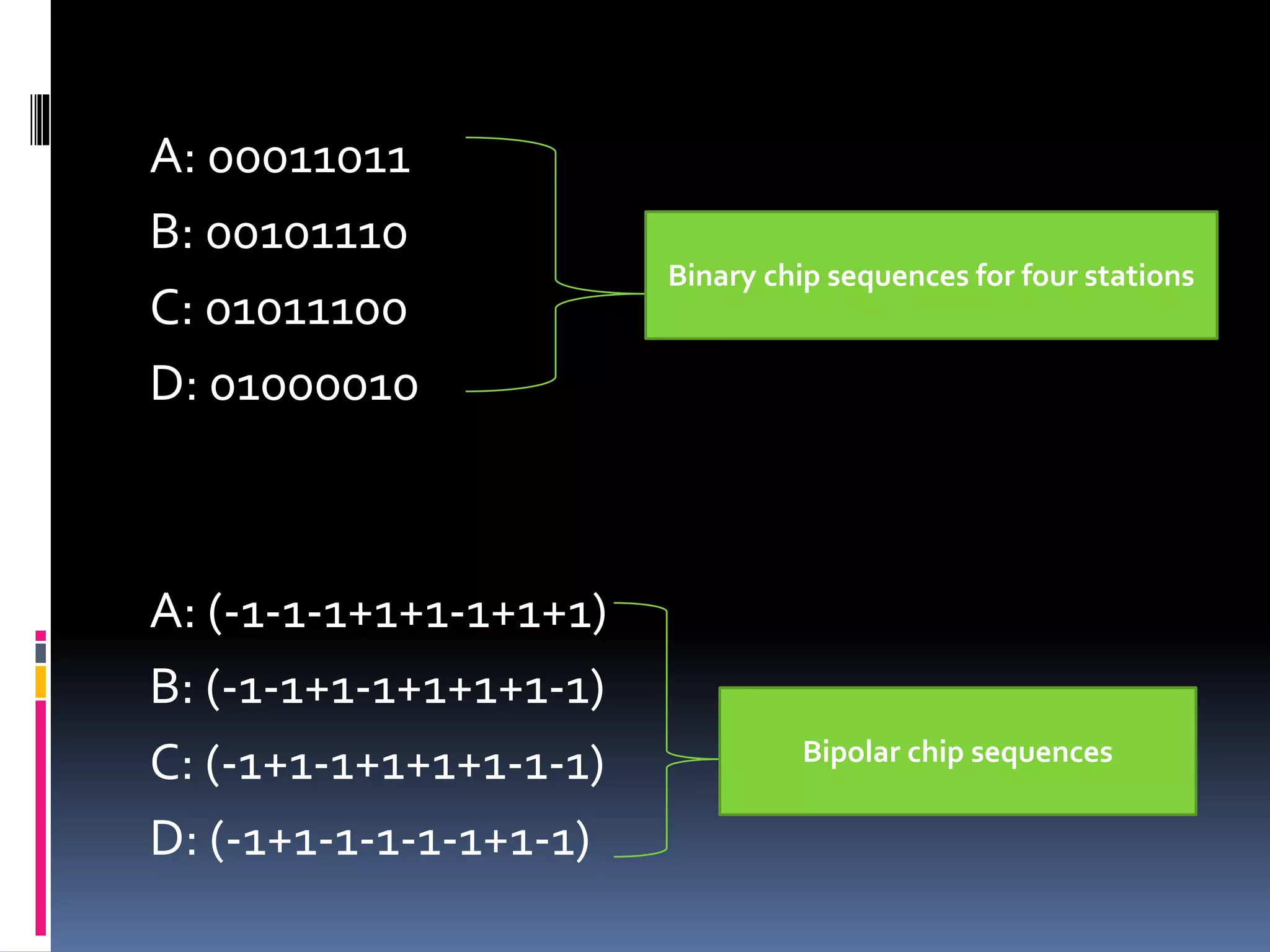
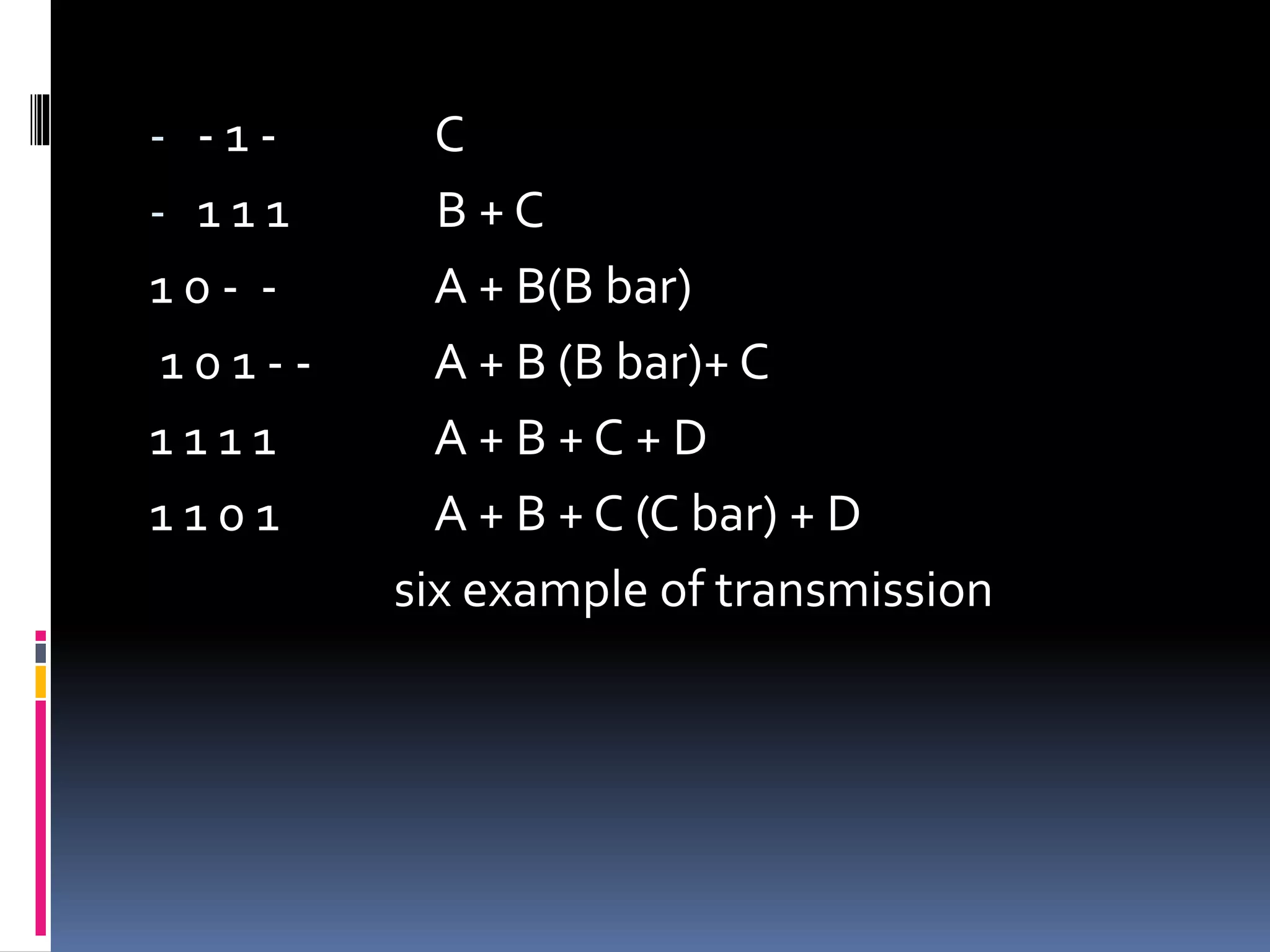
The document summarizes the evolution of mobile telephone systems from analog to digital technologies. It describes early analog systems like Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) and its features. It then discusses the transition to digital with Digital AMPS (D-AMPS) and the widespread adoption of Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) as the dominant 2G standard. It also provides a brief overview of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) technology and 3G standards like W-CDMA and CDMA2000.