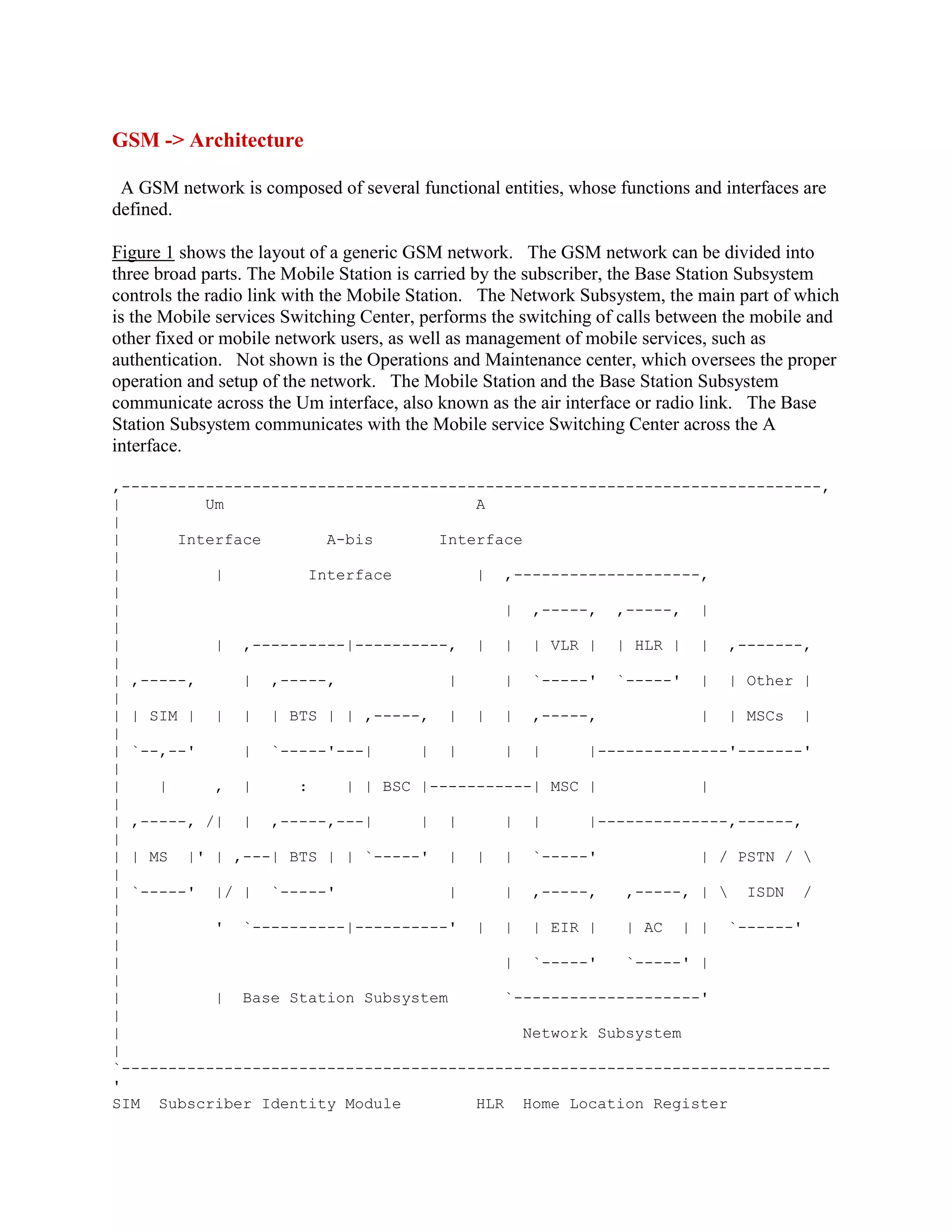
The document summarizes the architecture of a GSM network. It is composed of mobile stations, a base station subsystem, and a network subsystem. The base station subsystem controls radio links with mobile stations and communicates with the network subsystem. The network subsystem performs switching functions and manages services like authentication. It connects to other networks and contains functional elements like HLRs, VLRs, and an MSC that route calls and provide subscriber information.