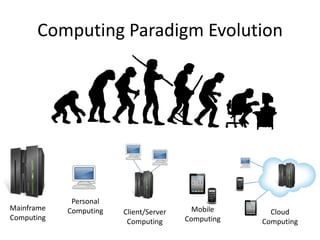
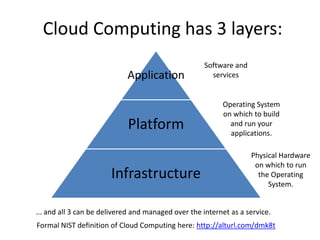
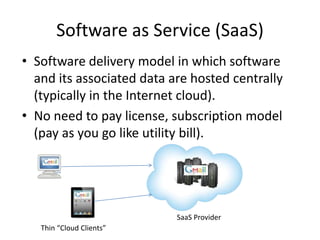
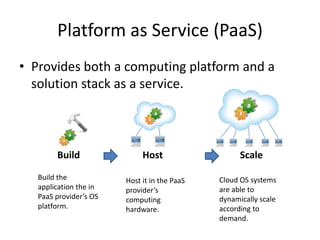
The document discusses the evolution and components of cloud computing, highlighting three primary layers: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It explains the target audiences and examples for each layer, illustrating how these services are delivered and managed over the internet. Additionally, it addresses barriers to cloud adoption, including security concerns, governance, and potential vendor lock-in.