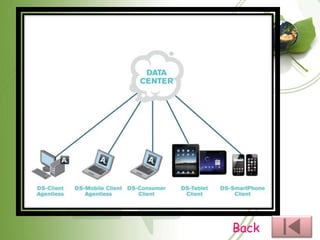
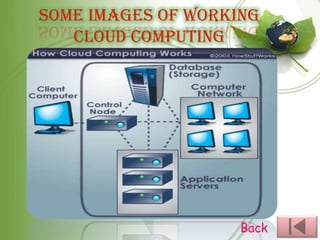
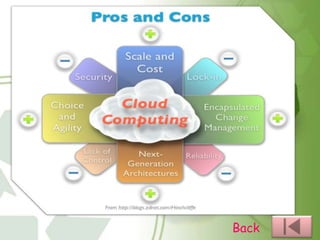
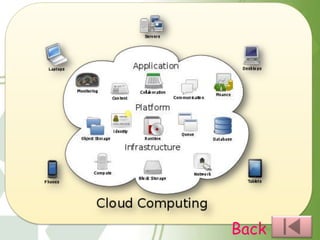
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including the different types (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, etc.), how it works by hosting information on remote servers accessed over the internet, the benefits of scalability and reduced costs, and the risks around loss of control and dependency on cloud providers. It also discusses cloud clients, examples of cloud applications, and storage as a service.





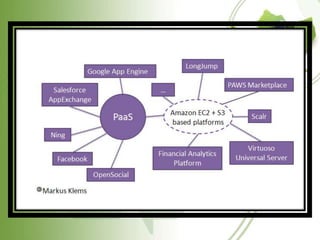
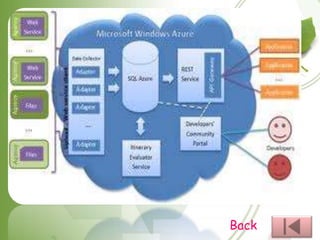
![IaaS (Infrastructure
as a Service)
Delivers utility computing capability, typically as raw virtual
servers, on demand that customers configure and manage. Here
Cloud Computing provides grids or clusters or virtualized servers,
networks, storage and systems software, usually (but not always) in
a multitenant architecture.
IaaS is designed to augment or replace the functions of an entire
data center. This saves cost (time and expense) of capital equipment
deployment but does not reduce cost of configuration,
integration or management and these tasks must be performed
remotely.
Vendors would include Amazon.com (Elastic Compute Cloud [EC2]
and Simple Storage), IBM and other traditional IT vendors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingjayanth-120826011039-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-jayanth-10-320.jpg)
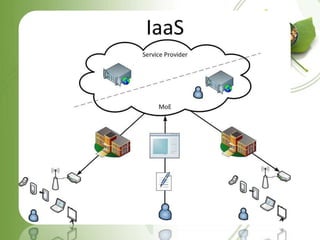

![BUSINESS PROCESS AS A
SERVICE (BPAAS)
Business process as a service (BPaaS) pronounced [bē-păss] is
an application delivered as a service that is used by business
process service-provider personnel, who are performing activities
on behalf of the service recipient. It's a service that combines
the Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) with theSoftware as a
Service (SaaS) models. BPaaS is a model for businesses
outsource traditional business services. The difference with
BPaaS over BPO is that BPaaS emphases on the end results versus
operational activities. Where typical BPO programs will have the
client focusing on daily operational tasks to deliver the outcome,
BPaaS focuses on service level agreements (SLA) and Key
Performance Indicators (KPI) as the measure of operational
service and success.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingjayanth-120826011039-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-jayanth-14-320.jpg)
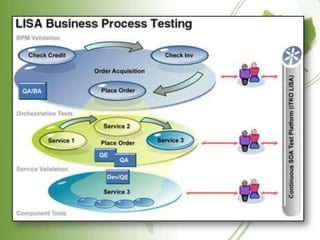
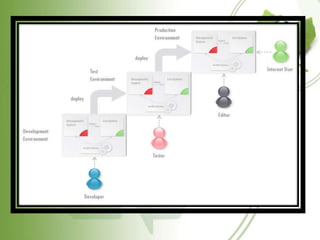
![TEST ENVIRONMENT AS A
SERVICE (TEAAS)
Test Environment as a service (TEaaS,
typically pronounced [teæs]), sometimes
referred to as "on-demand test environment,"
is a test environment delivery model in which
software and its
associated data are hosted centrally (typically
in the (Internet) cloud) and are typically
accessed by users using a thin client, normally
using a web browser over the Internet.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingjayanth-120826011039-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-jayanth-16-320.jpg)