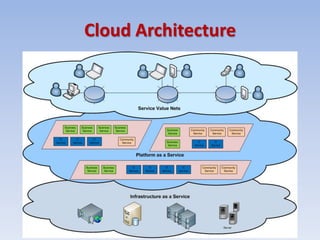
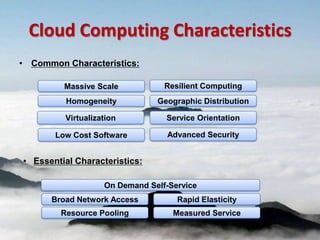
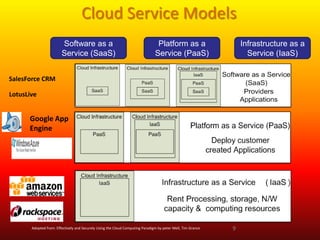
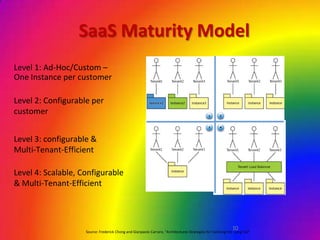
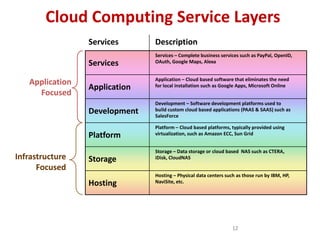
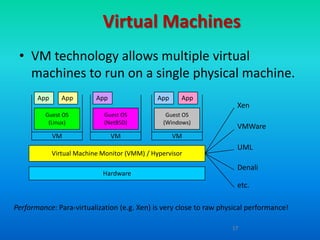
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services over the internet. It has characteristics like massive scale, resilience, virtualization, and low cost software. Common service models include Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. Cloud computing enables companies to save costs by using infrastructure on demand rather than owning their own data centers and servers. Commercial cloud offerings provide services like storage, computing resources, and platforms.