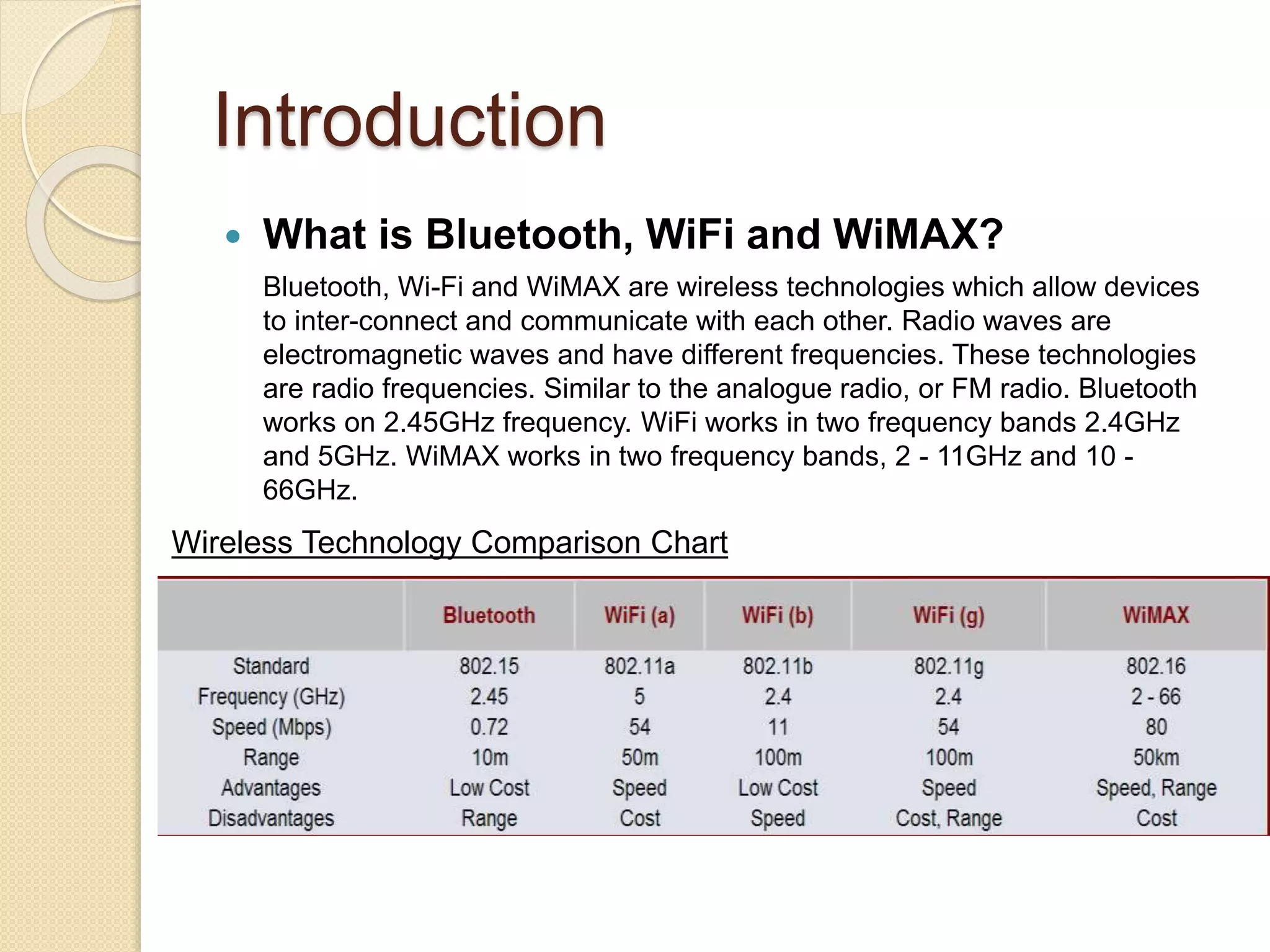
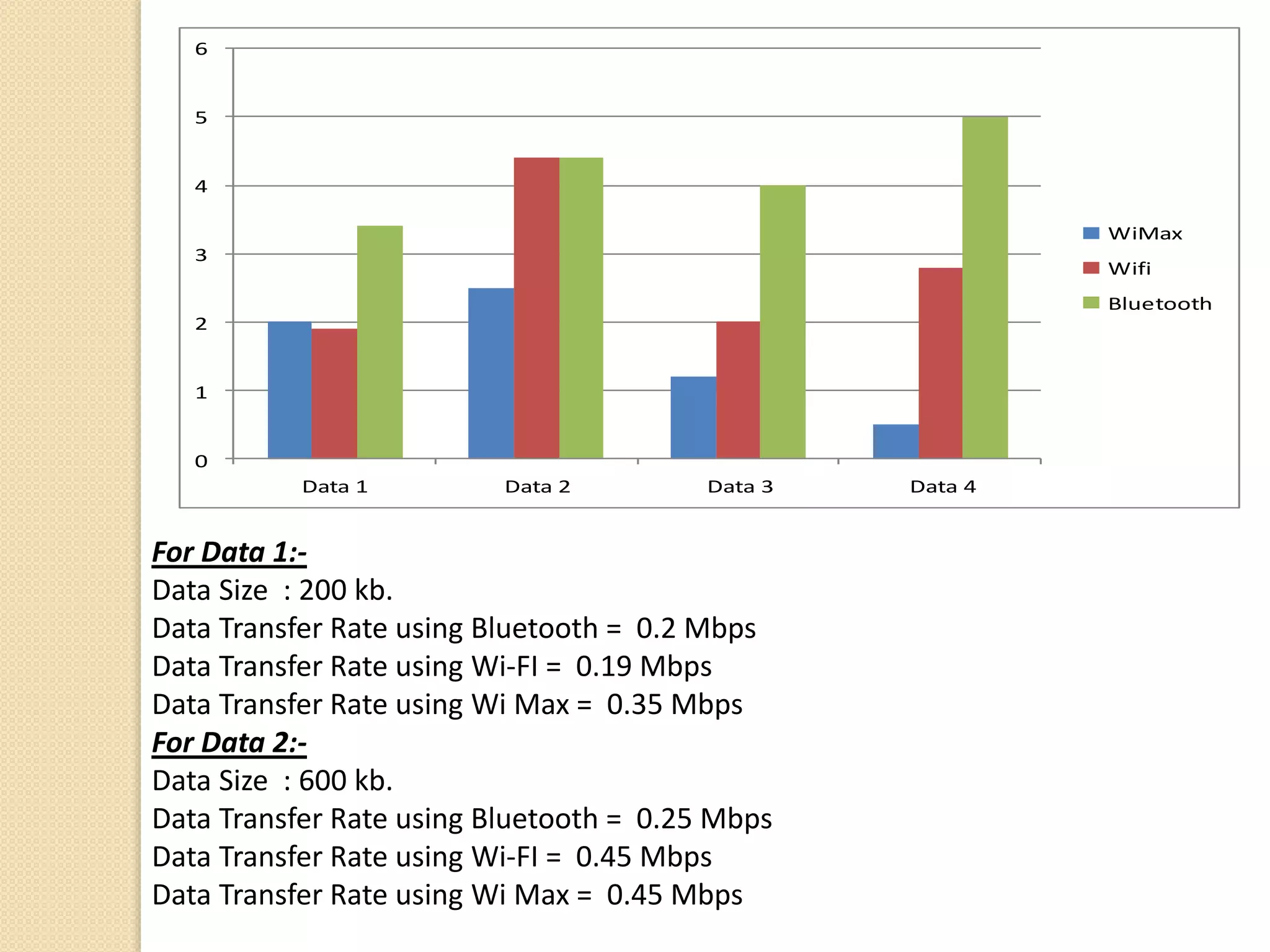
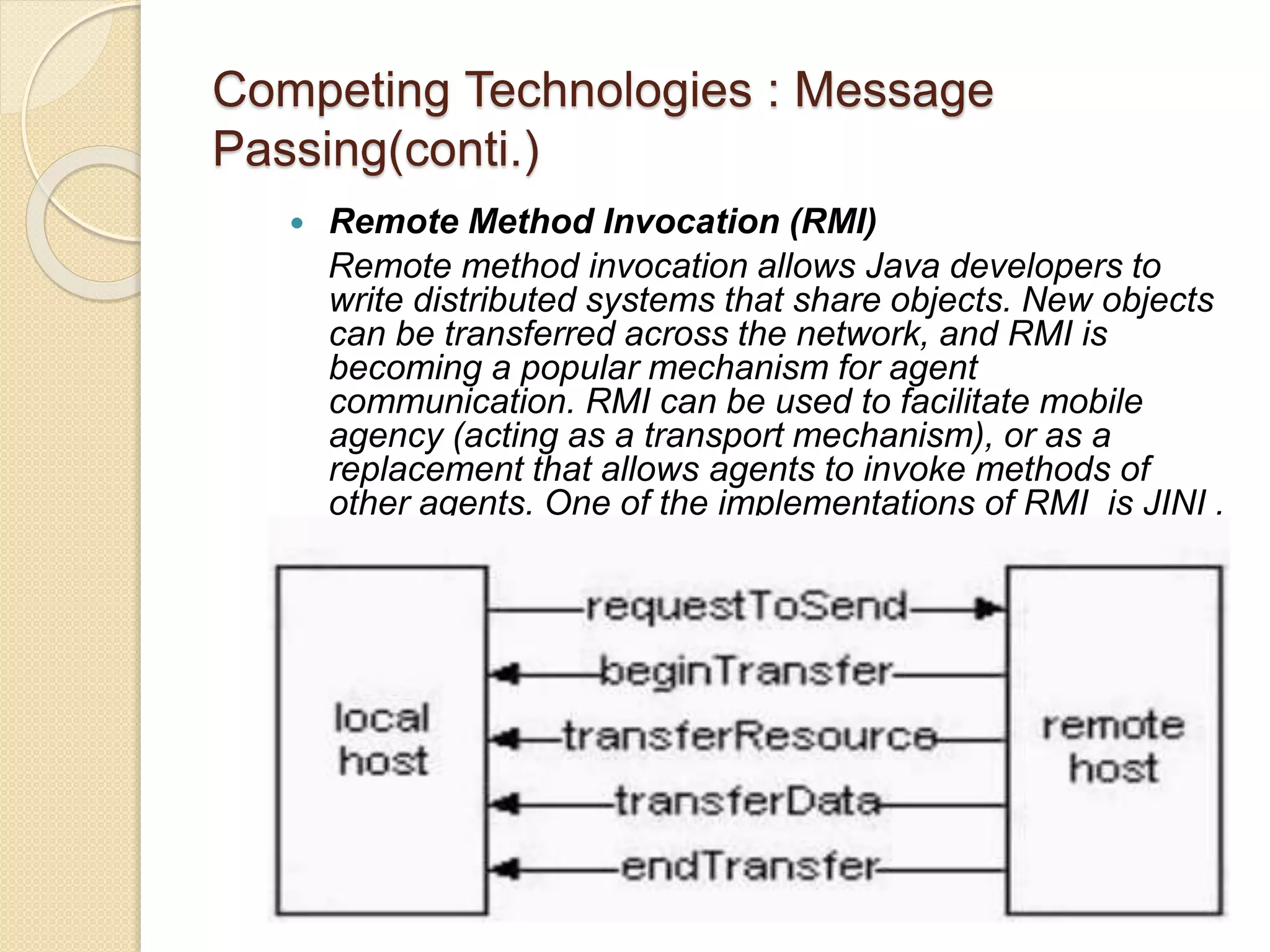
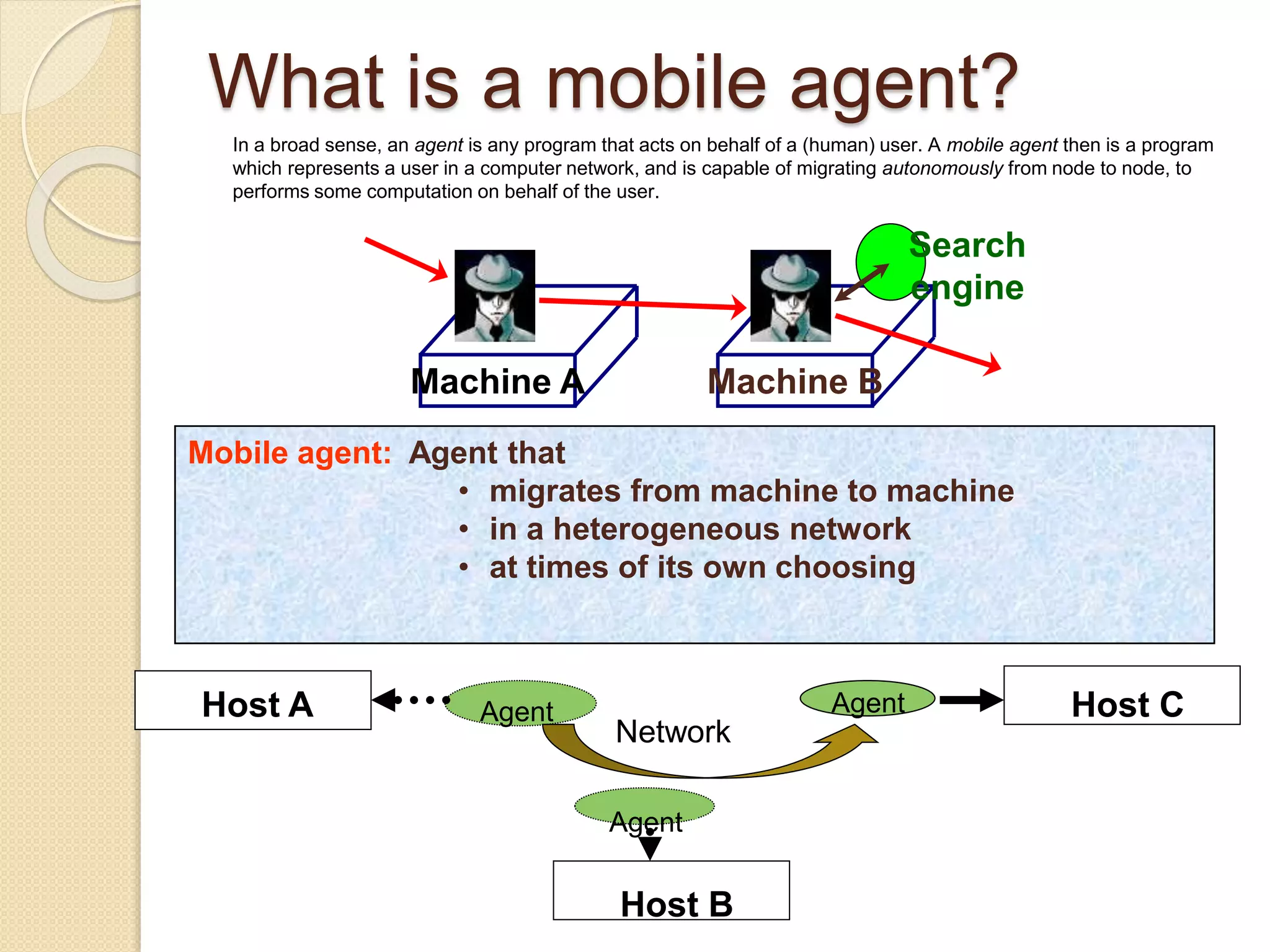
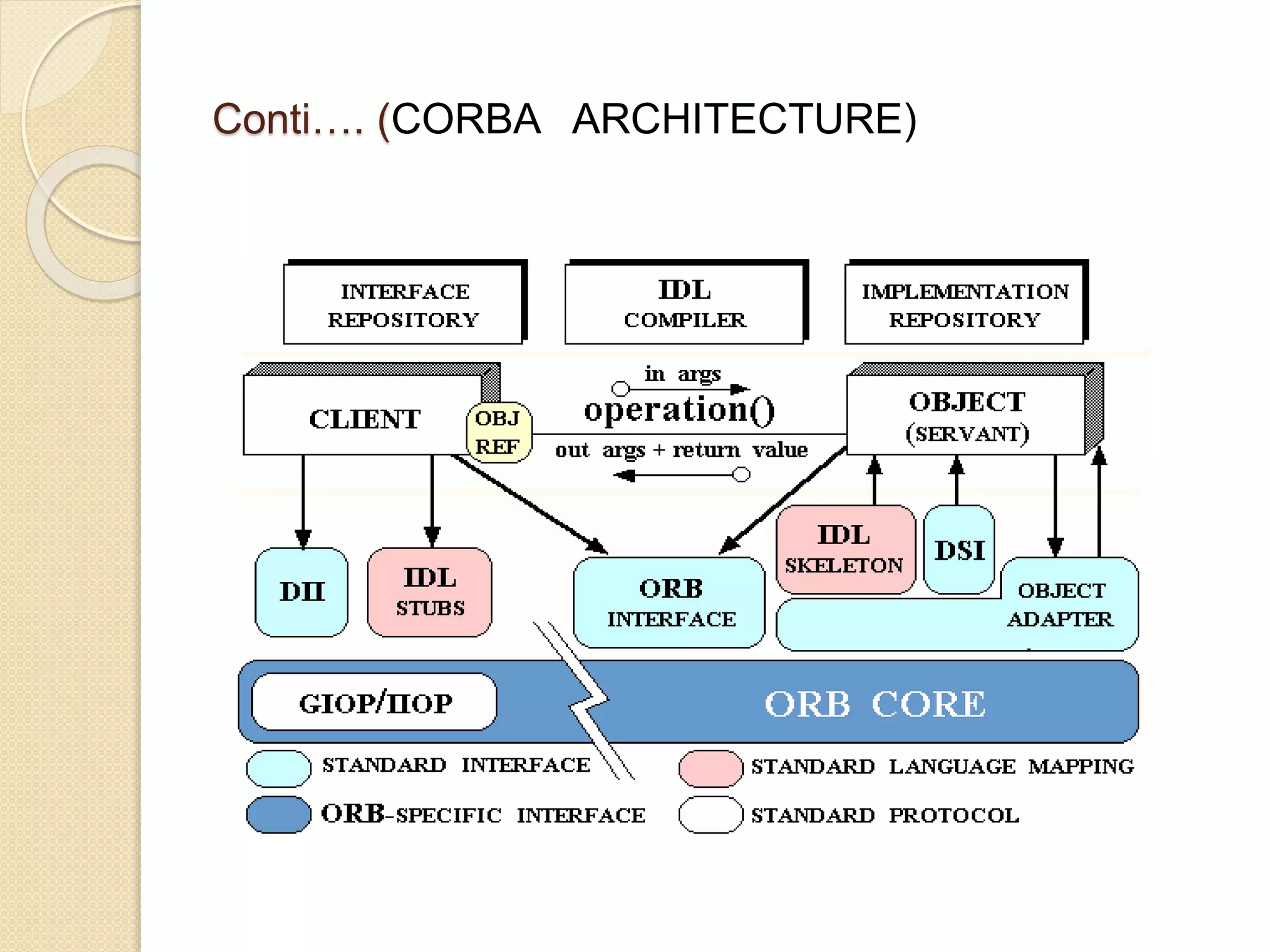
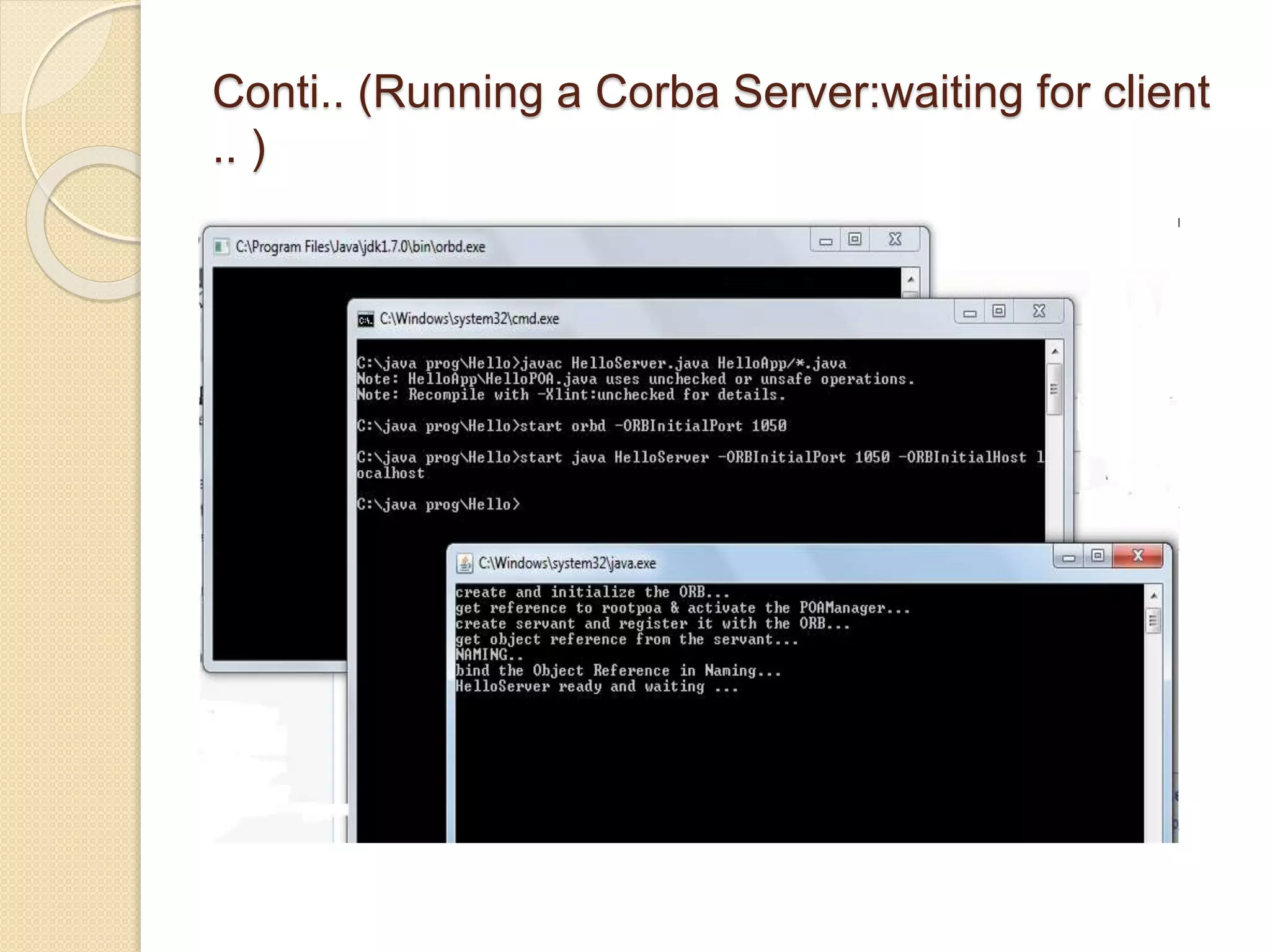
This document examines various wireless data streaming technologies, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and WiMAX, emphasizing their comparative speeds, behaviors in different environments, and the role of mobile agents in data transfer. It discusses mobile ad hoc networks, peer-to-peer systems, and mobile agent frameworks like CORBA and Aglets, highlighting the benefits and challenges associated with mobile agent deployment. The paper concludes that while mobile agent technology shows promise for mobile environments, real-world applications remain limited due to design constraints and security concerns.