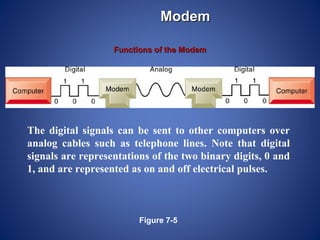
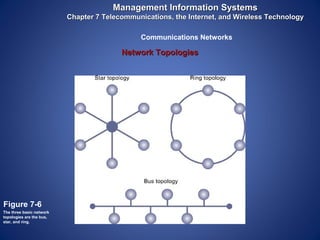
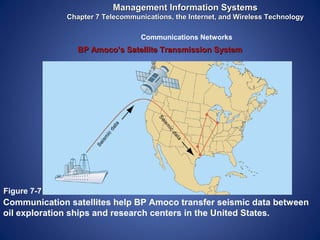
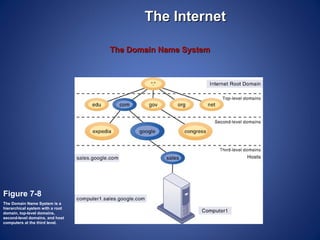
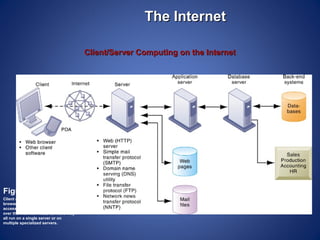
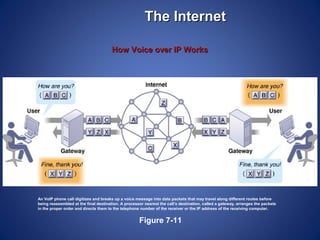
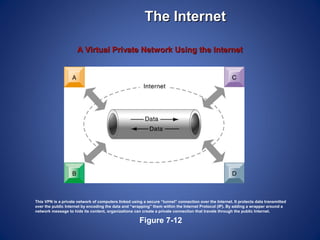
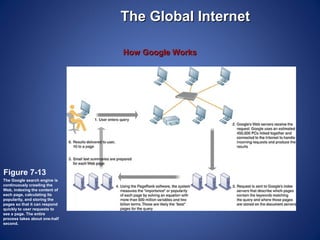
The document provides an overview of basic internet concepts including modems, types of networks, transmission media, the internet, domains, web browsers, search engines, and virtual private networks. It describes how digital signals are converted to analog and vice versa to transmit data over phone lines and fiber optics. The summary also explains how Google indexes web pages and how virtual private networks create secure connections over the public internet.