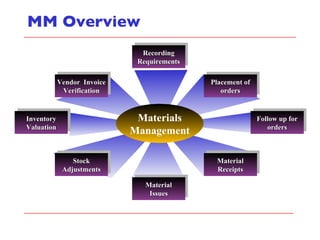
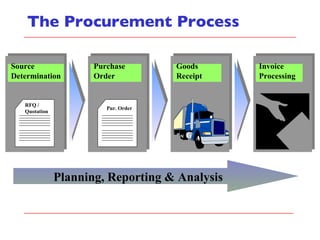
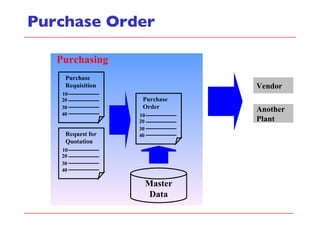
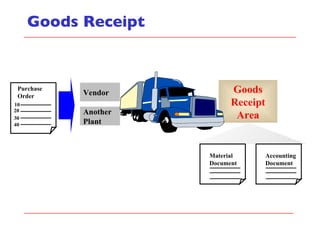
- The document discusses key concepts in materials management in SAP including procurement processes, inventory management, material master data, and material movements.
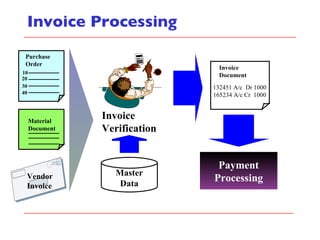
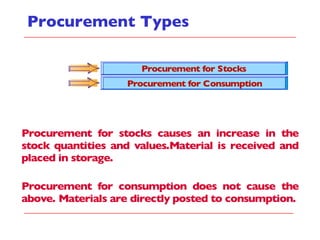
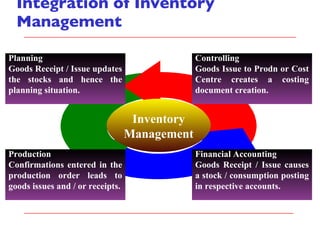
- It describes the different types of procurement including consumable materials, procurement for stock, and procurement for consumables. Inventory management integrates with modules like financial accounting, controlling, and production.
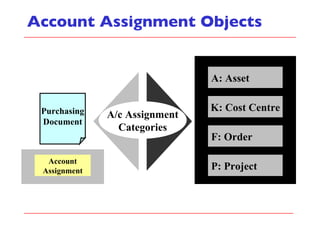
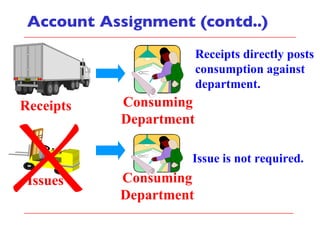
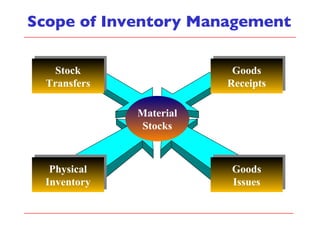
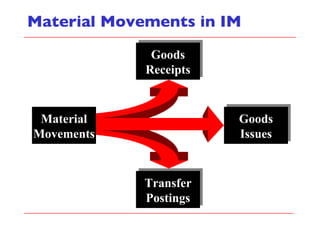
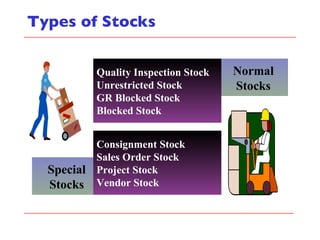
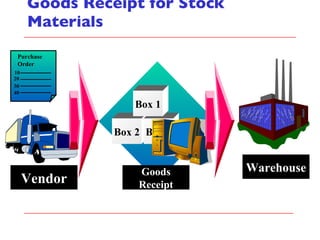
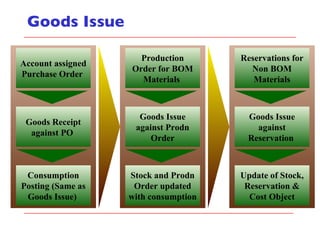
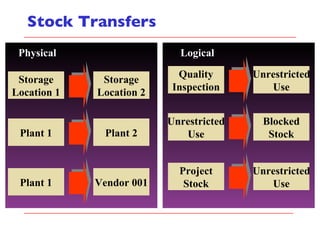
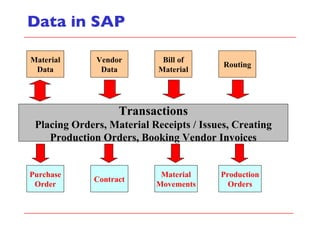
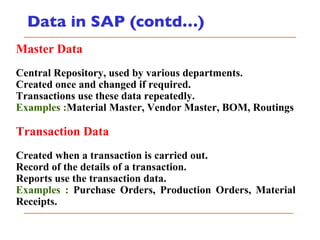
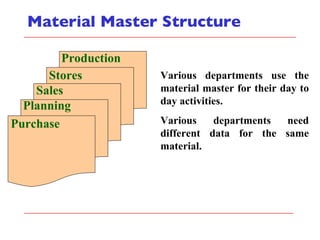
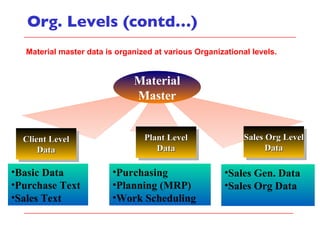
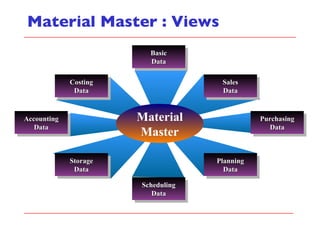
- The document outlines material movements like goods receipts, goods issues, and stock transfers and how they impact the material master, accounting, production, and inventory. Master and transactional data are also discussed.