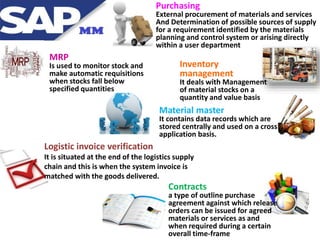
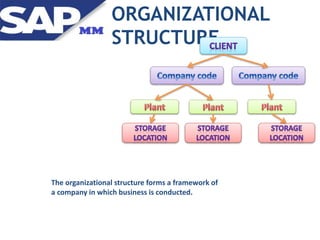
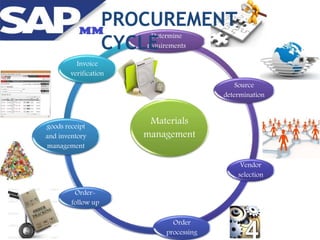
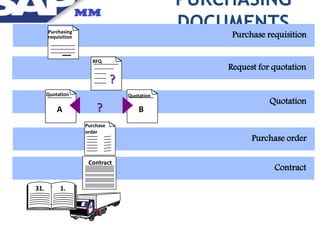
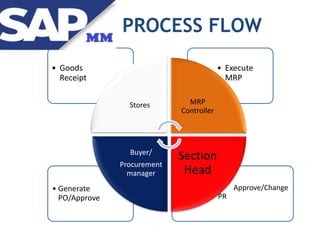
Materials management ensures adequate supply of materials through procurement and inventory management. It aims to have the right quality and quantity of supplies at the right time, place, and cost. The key functions include purchasing, inventory management, master data, and MRP. Purchasing involves acquiring external goods and services. Inventory management deals with stock levels. Master data contains item and supplier information. MRP monitors stock levels and triggers automatic requisitions. Other areas like contracts, purchasing documents, the procurement cycle, and integration with other SAP modules are also covered.