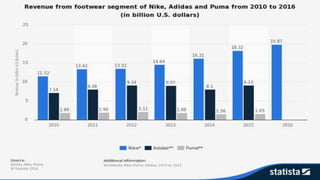
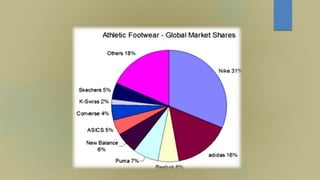
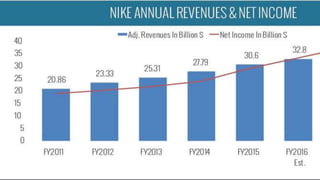
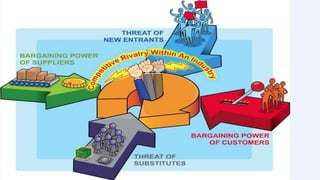
This document discusses Nike, the leading sportswear brand. It provides an overview of Nike, including its founding in 1964, iconic swoosh logo, core business units of footwear and apparel, and marketing strategies such as celebrity endorsements. It also discusses opportunities and threats in the sports apparel industry, Nike's response to controversies over labor practices, and a five forces analysis of the competitive landscape. The key learnings are the importance of customer satisfaction, maintaining values, effective marketing, and business ethics.