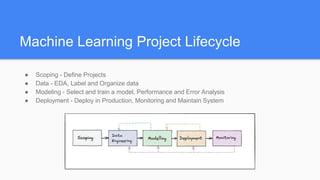
MLOps is the process of taking machine learning models into production and maintaining and monitoring them. It addresses issues like lack of reproducibility, inability to identify new trends, and lack of scalability that can occur without proper processes. The machine learning lifecycle includes scoping a project, collecting and preparing data, developing and evaluating models, deploying models into production, and ongoing monitoring. MLOps aims to operationalize this lifecycle to ensure models can be deployed and updated efficiently and reliably at scale.