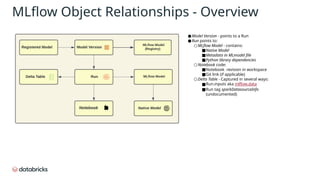
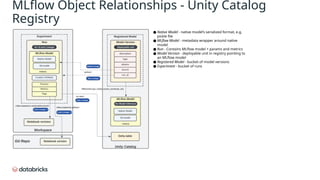
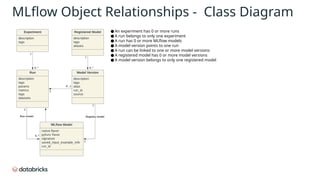
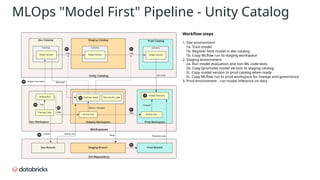
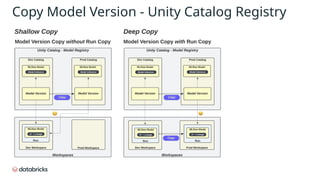
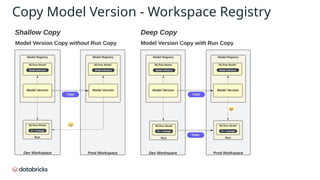
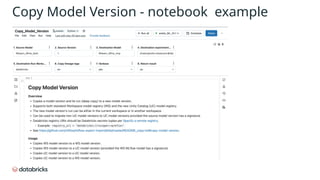
The document provides an in-depth overview of MLflow MLOps architecture, detailing the various meanings and types of models in MLflow and their relationships within the system. It outlines the workflow for managing model versions across development, staging, and production environments, emphasizing processes like model registration and version copying. Additionally, it describes the nuances of shallow and deep copying of model versions for lineage and governance tracking.



![artifact_path: model
databricks_runtime: 13.2.x-cpu-ml-scala2.12
flavors:
python_function:
env:
conda: conda.yaml
virtualenv: python_env.yaml
loader_module: mlflow.sklearn
model_path: model.pkl
predict_fn: predict
python_version: 3.10.6
sklearn:
code: null
pickled_model: model.pkl
serialization_format: cloudpickle
sklearn_version: 1.1.1
mlflow_version: 2.5.0
model_uuid: 2daecace267f4de29ec73062a10e2036
run_id: c62ccf932e0649a2b9247cc76d89b637
saved_input_example_info:
artifact_path: input_example.json
pandas_orient: split
type: dataframe
signature:
inputs: '[{"type": "double", "name": "fixed_acidity"}, {"type": "double", "name":
"volatile_acidity"}, {"type": "double", "name": "citric_acid"}, {"type": "double",
"name": "residual_sugar"}, {"type": "double", "name": "chlorides"}, {"type": "double",
"name": "free_sulfur_dioxide"}, {"type": "double", "name": "total_sulfur_dioxide"},
{"type": "double", "name": "density"}, {"type": "double", "name": "pH"}, {"type":
"double", "name": "sulphates"}, {"type": "double", "name": "alcohol"}]'
outputs: '[{"type": "tensor", "tensor-spec": {"dtype": "float64", "shape": [-1]}}]'
utc_time_created: '2023-08-11 08:40:16.227603'
MLflow Model - MLmodel metadata file
● Always has a Pyfunc flavor - python_function
● Most often has a native flavor, e.g. sklearn
● Should have a signature defining the input and output
schemas
● Signature is required to register the run's model in the
Unity Catalog model registry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlflowmlopsarchitecture-240917024946-73e9d838/85/MLflow_MLOps_Databricks_Architecture-pptx-6-320.jpg)