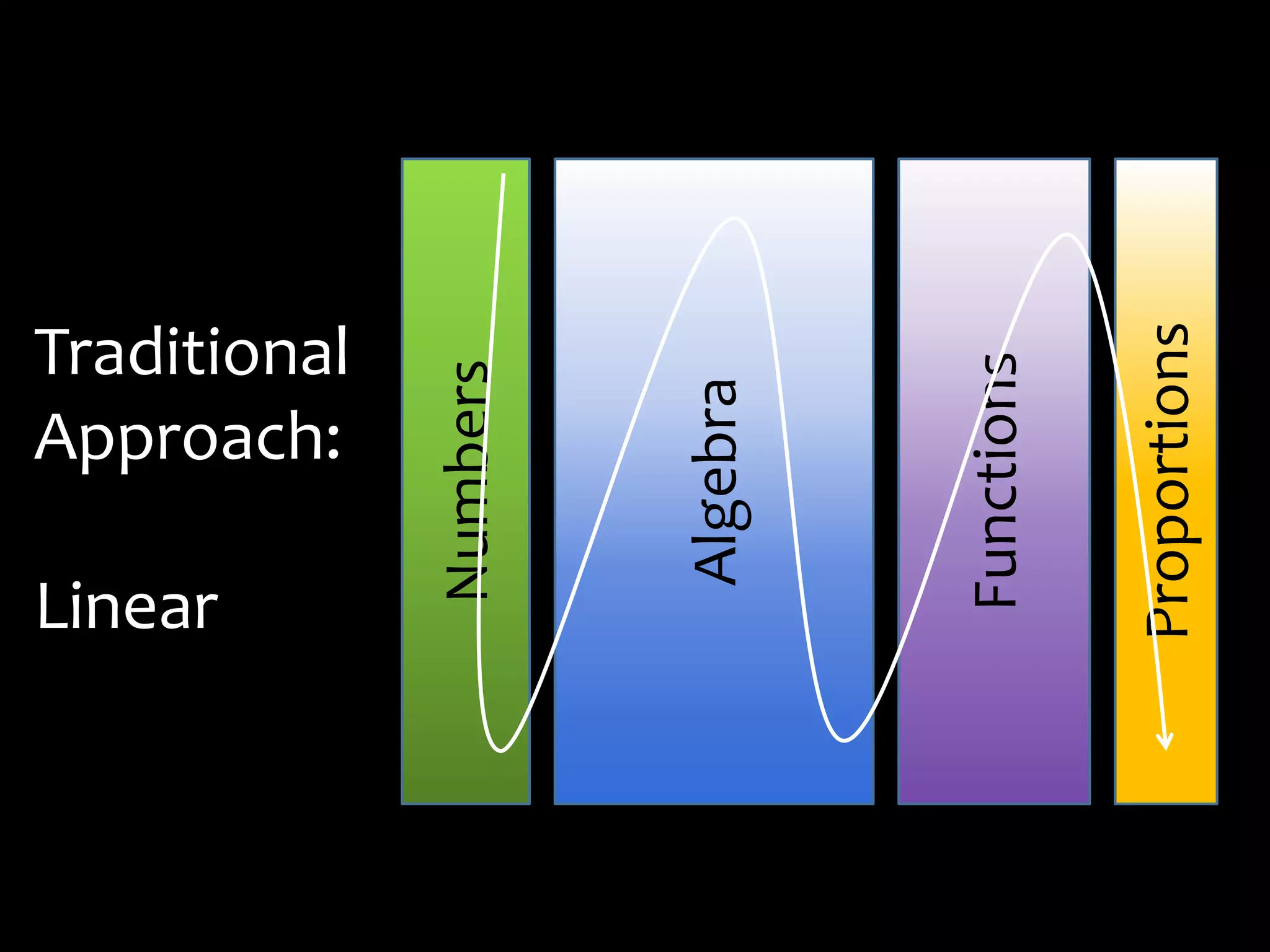
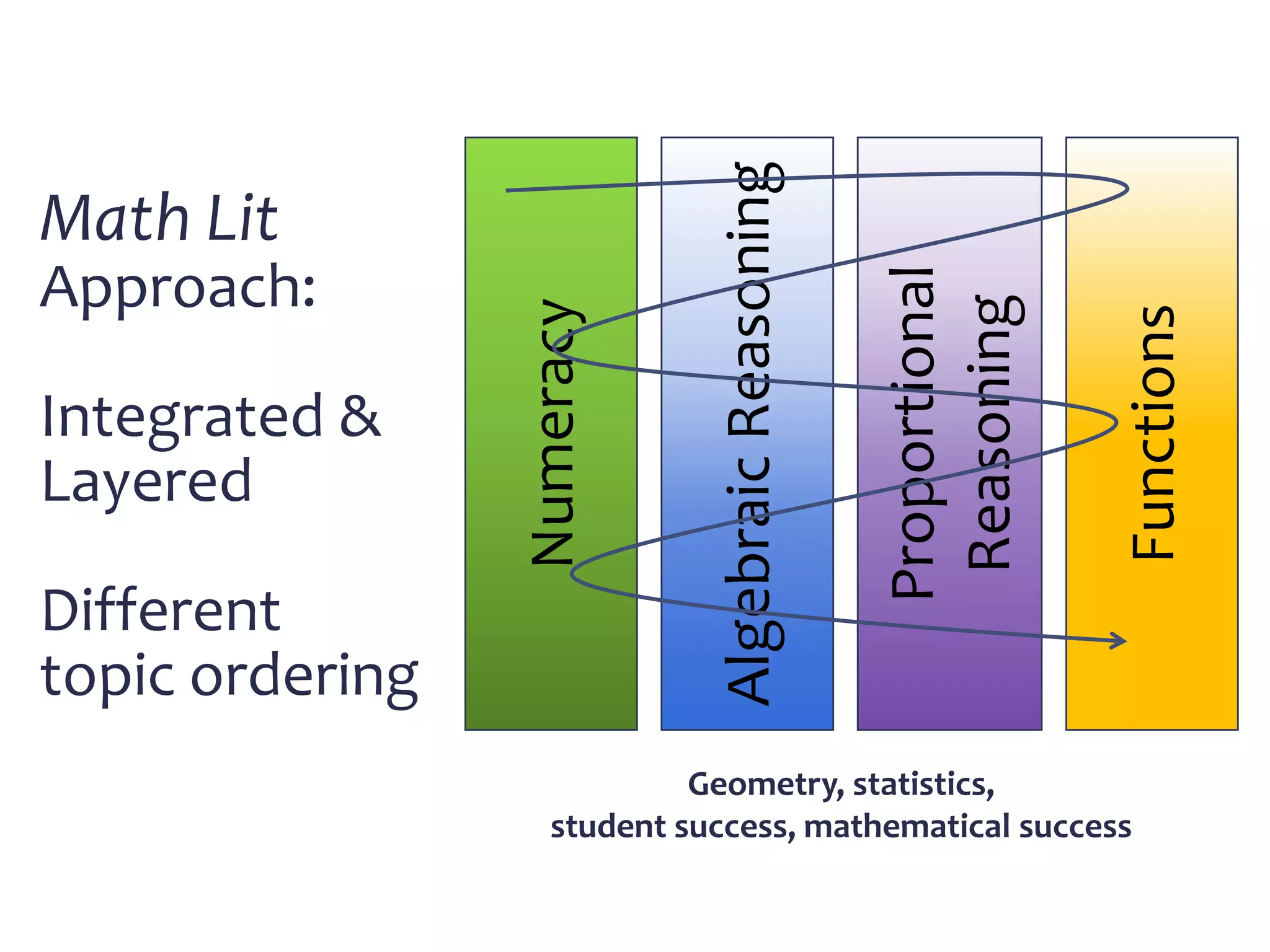
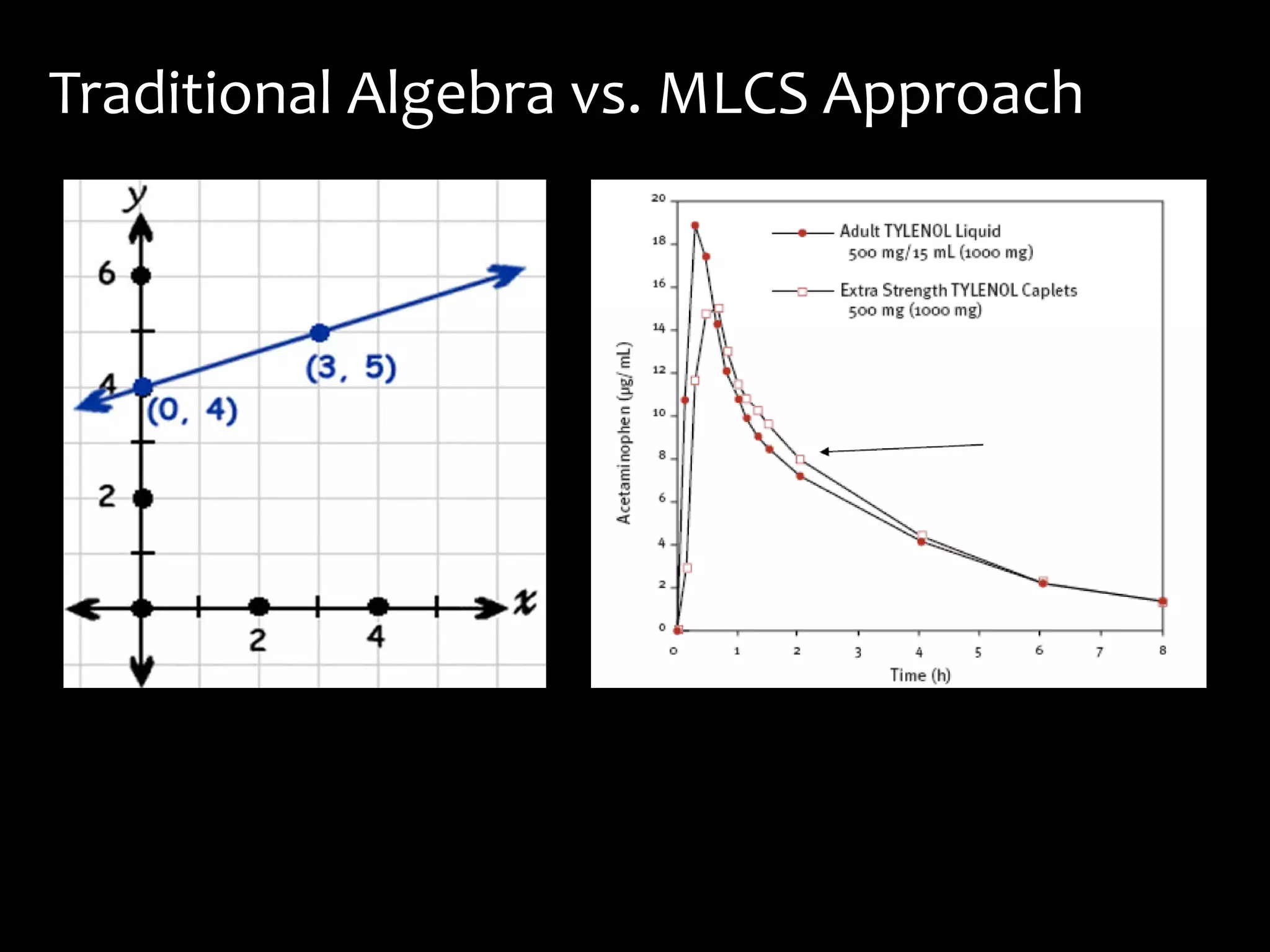
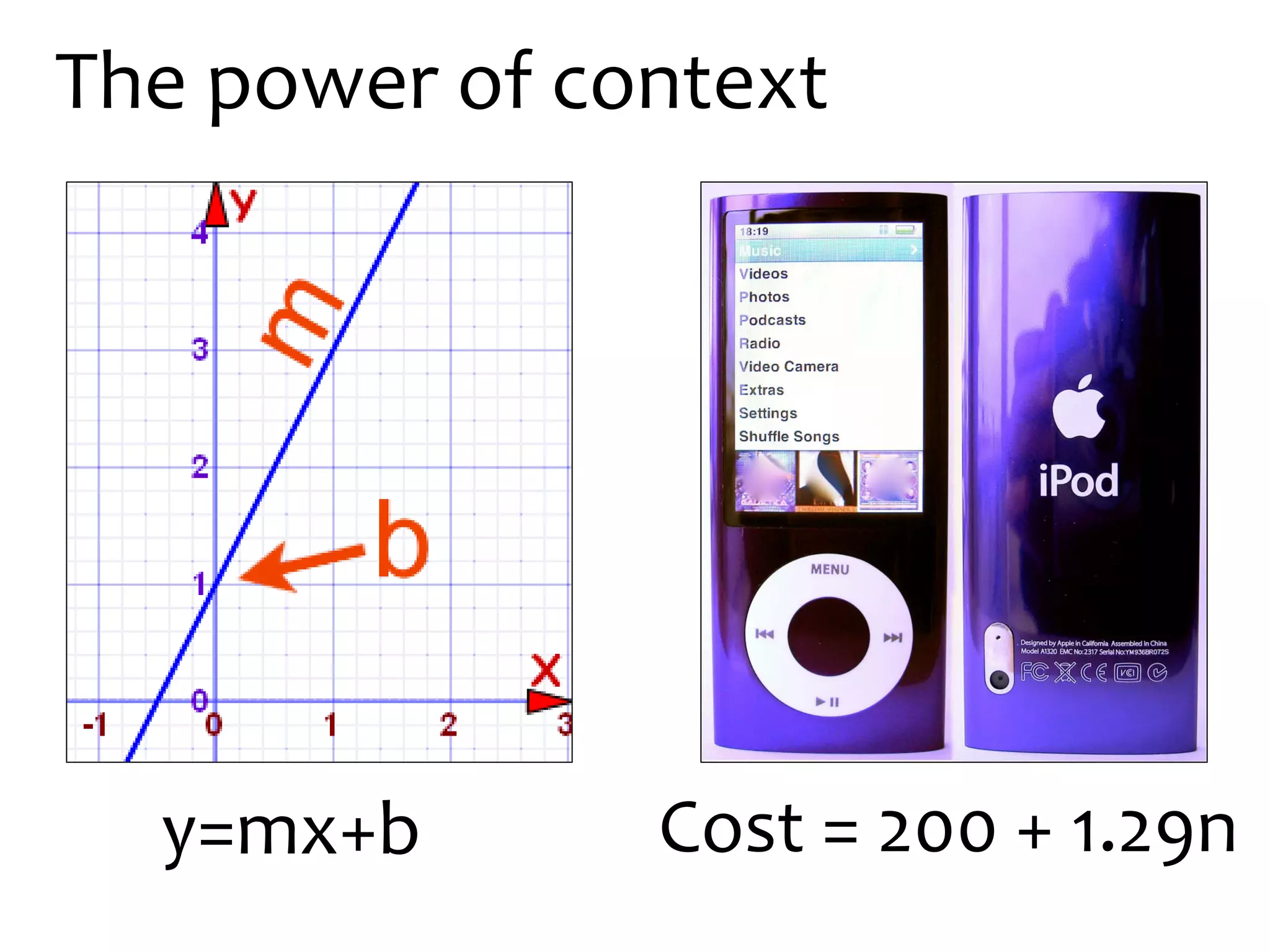
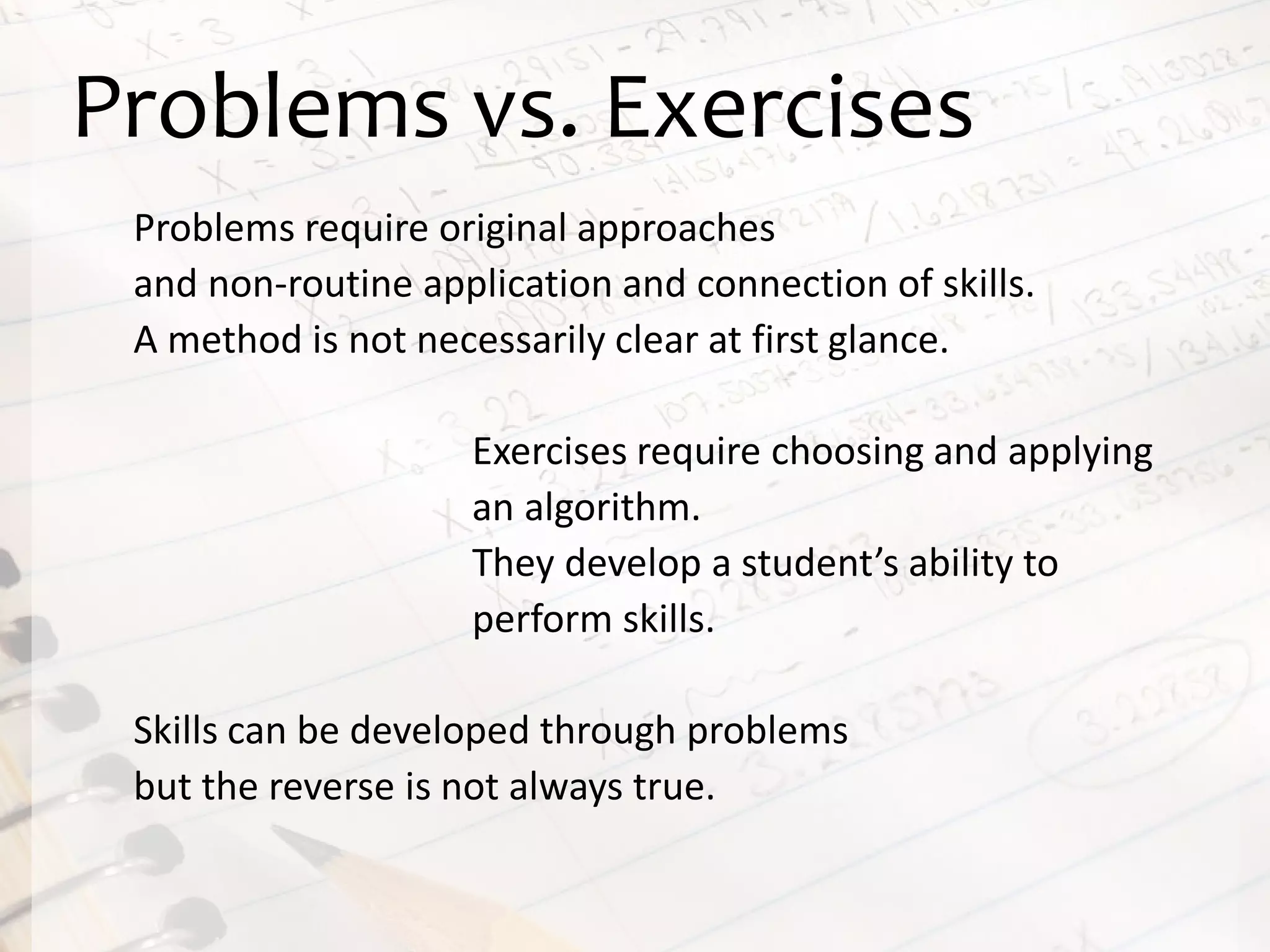
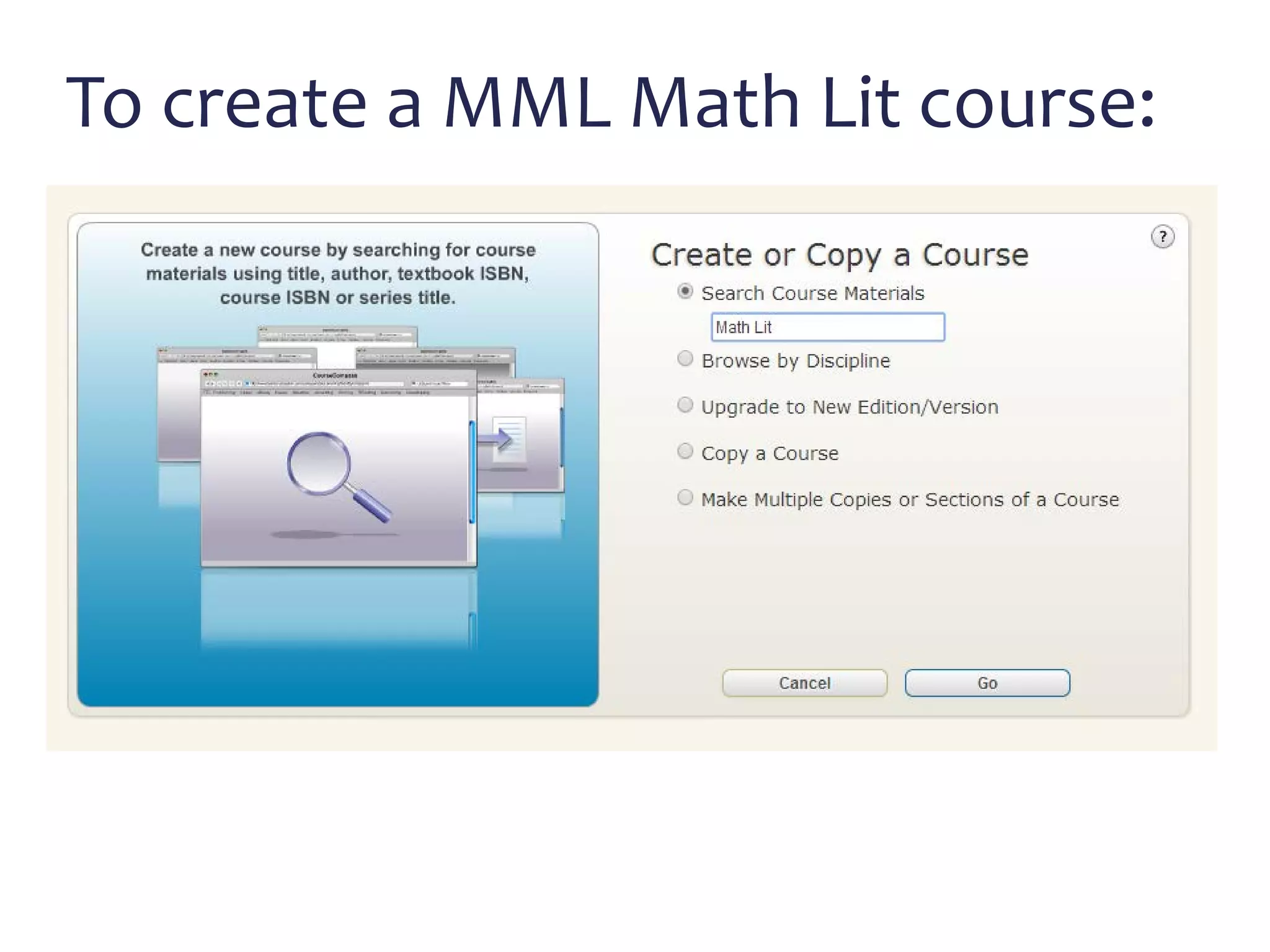
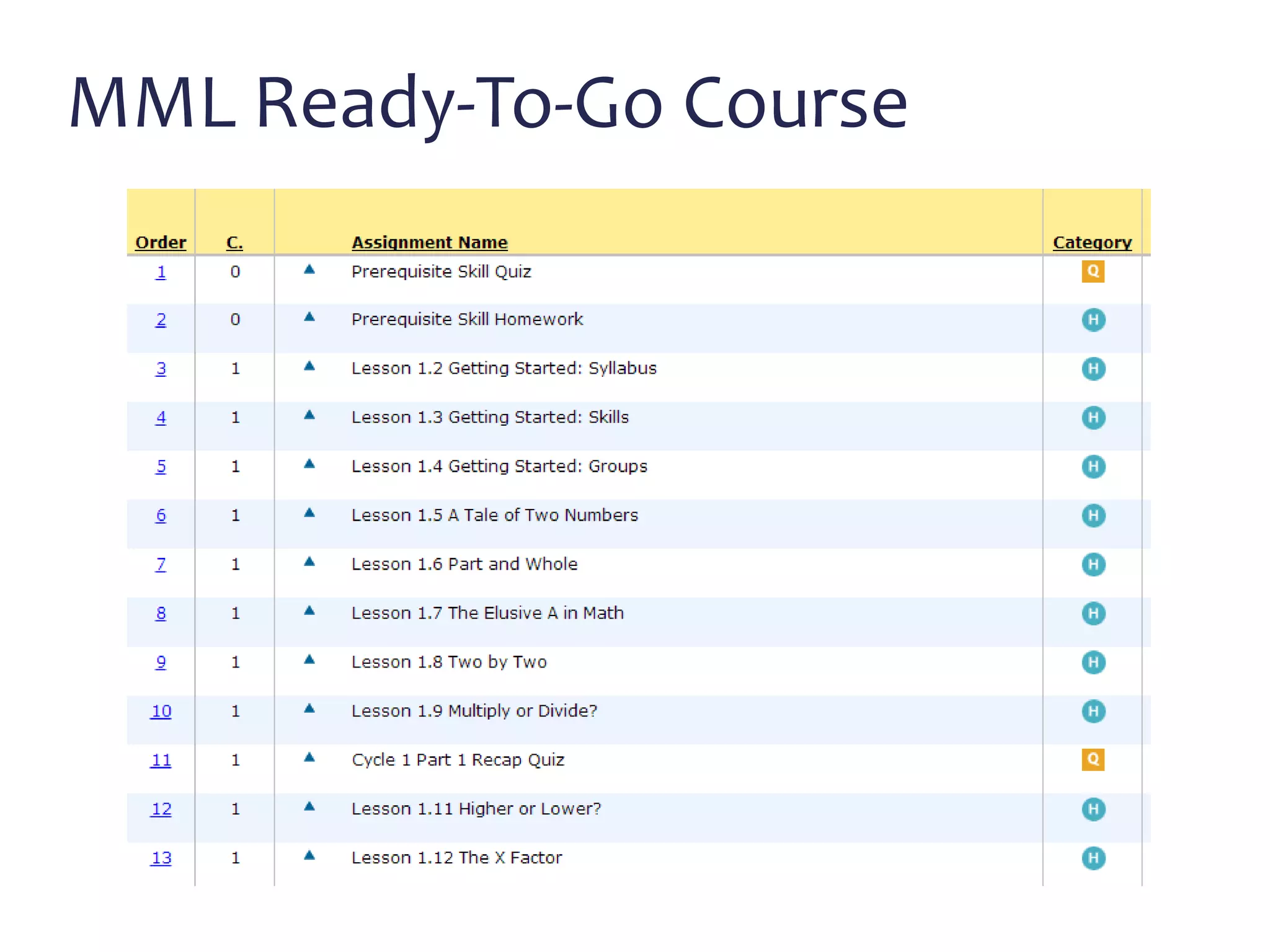
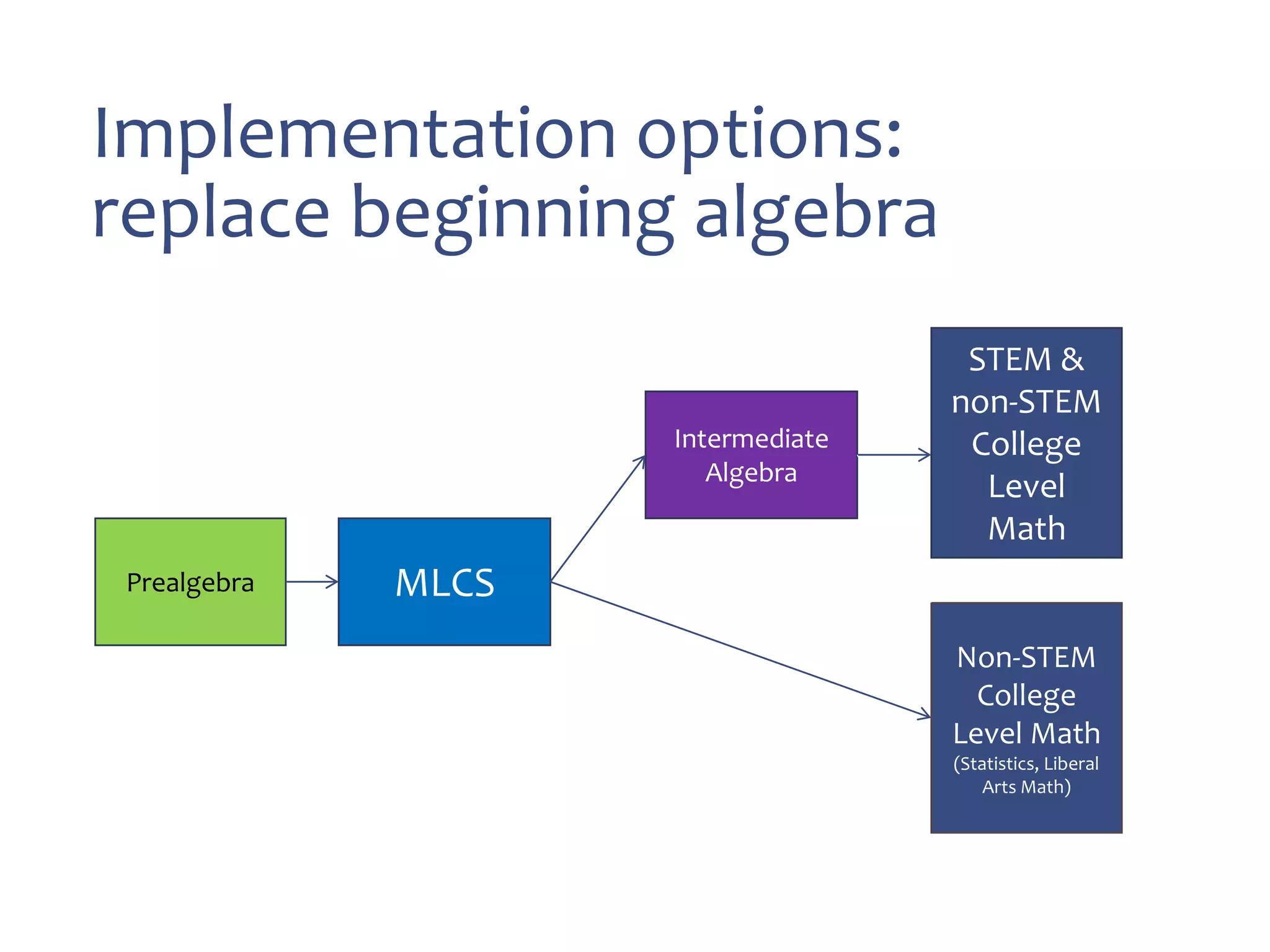
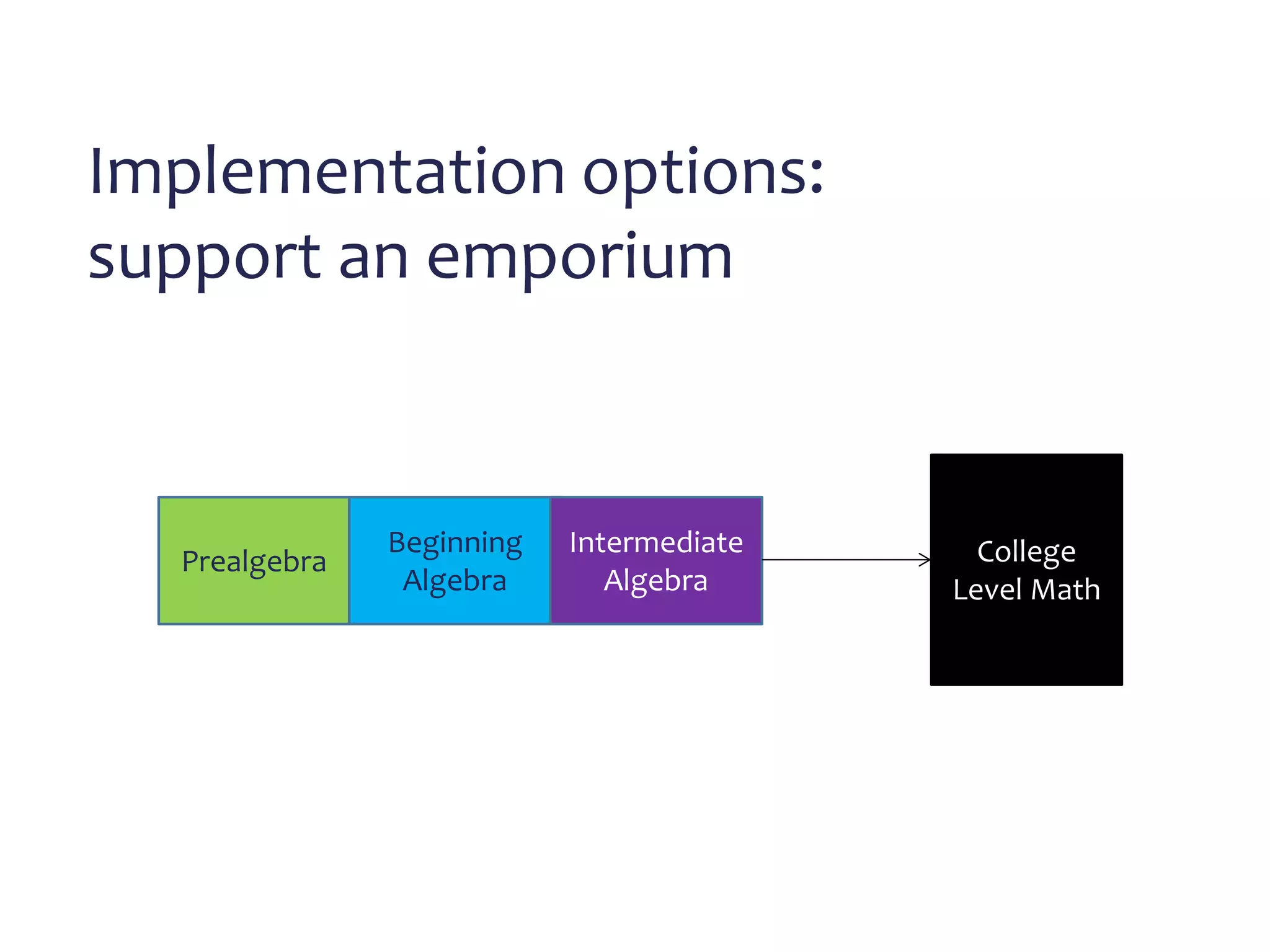
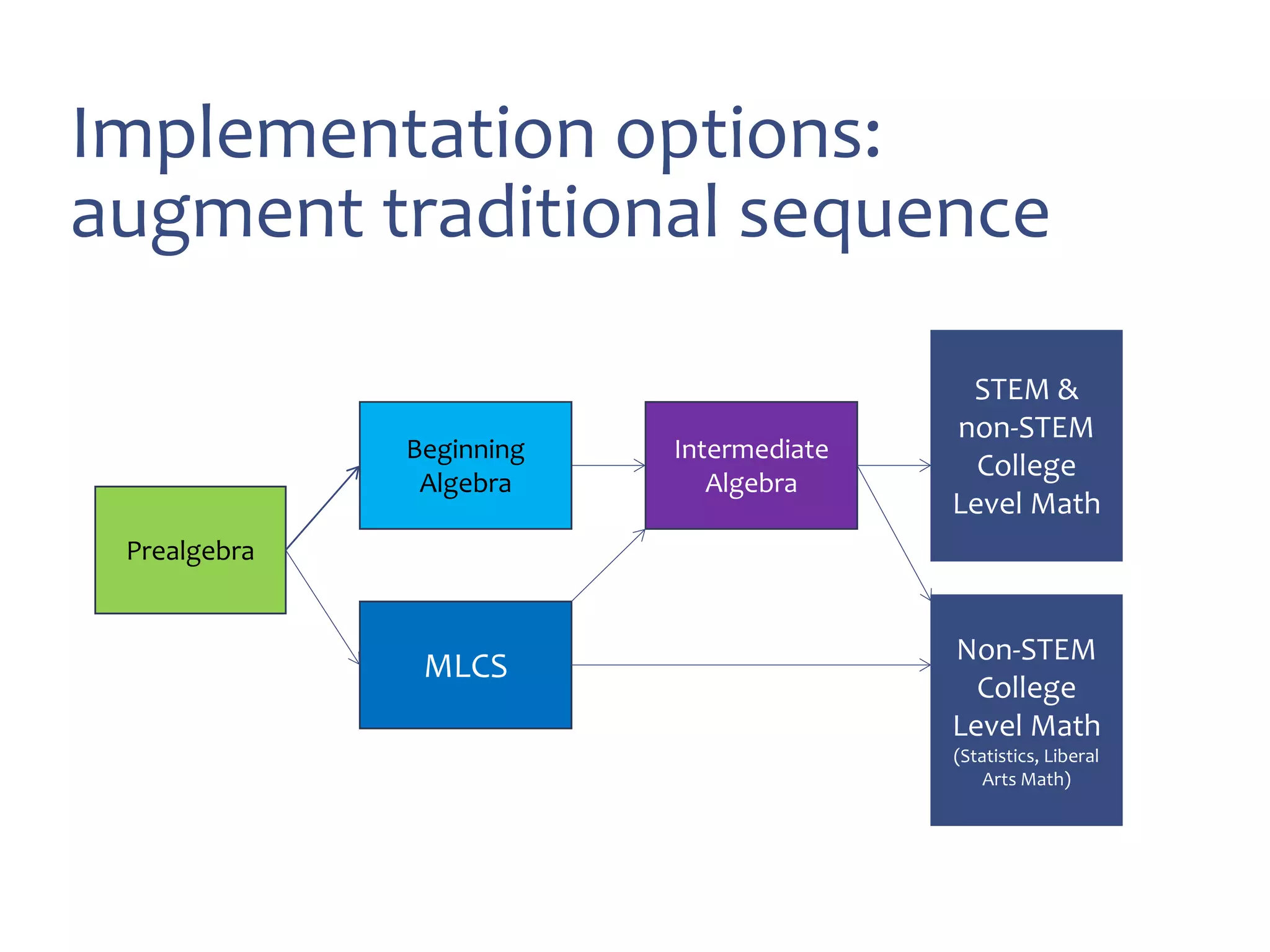
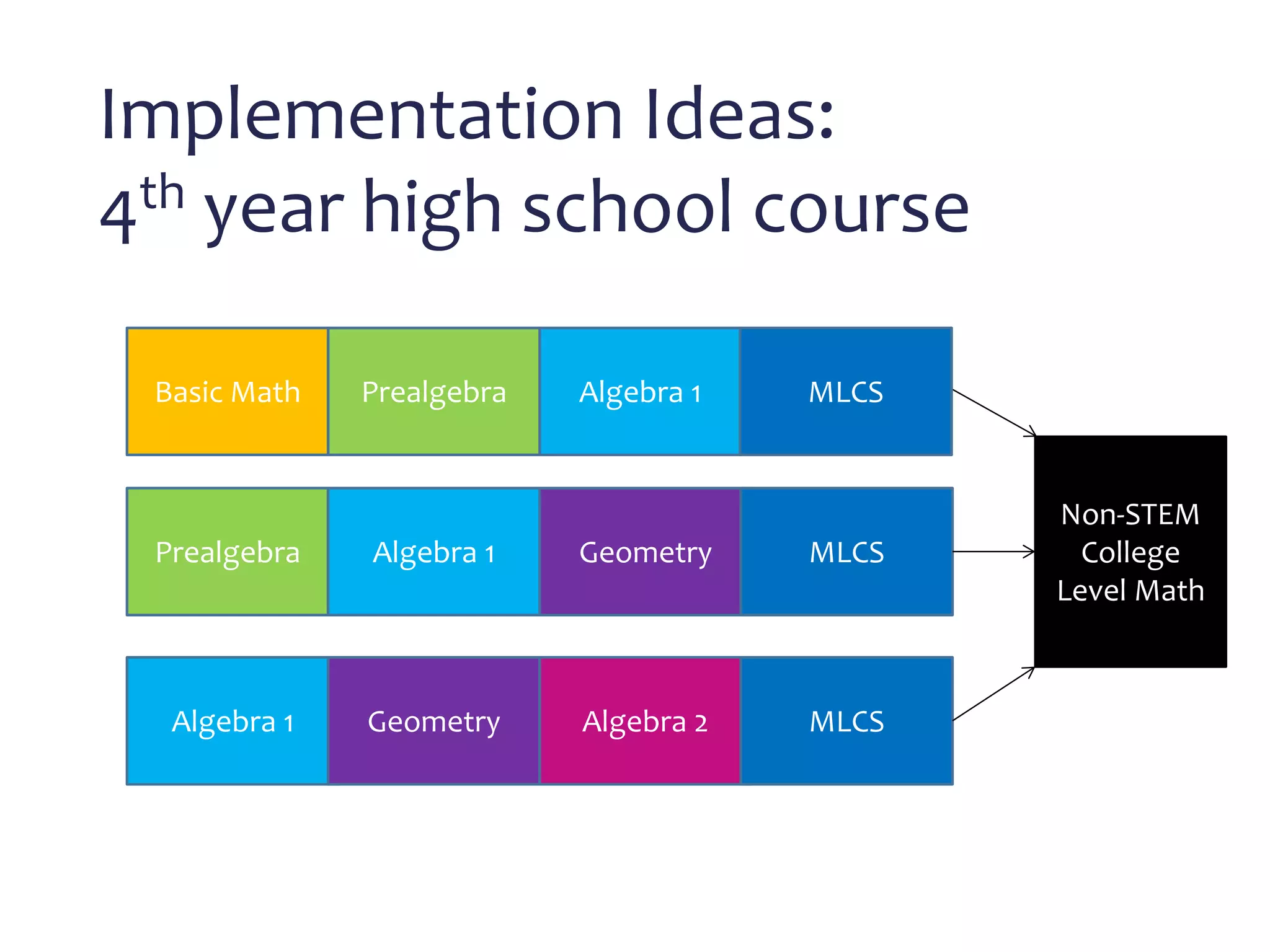
This document discusses math literacy pathways for college students, including the Math Literacy for College Students (MLCS) course. It provides an overview of the history and goals of developmental math pathways, which aim to better prepare students for non-STEM courses through contextualized learning focusing on critical thinking over deficiencies. The MLCS course covers integrated and layered math topics across one semester to give students the mathematical maturity for statistics and liberal arts math. Early outcomes indicate 60-70% pass rates for MLCS and no significant differences in subsequent gen ed math courses based on taking algebra or MLCS. The document discusses challenges and options for implementing MLCS to replace or augment traditional sequences.