Here are the steps to solve this problem:1) The points given are (4, 1175) and (8, 2175)2) Find the slope: m = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1) = (2175 - 1175)/(8 - 4) = 1000/4 = 2503) Write the equation in slope-intercept form: y = 250x + b4) Substitute a point: 1175 = 250(4) + b 5) Solve for b: 1175 = 1000 + b; b = 1756) The equation is: y = 250x + 175Therefore, the linear model for the cost of attending the college based
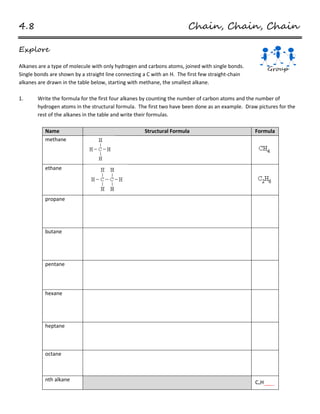
- 1. 4.8 Chain, Chain, Chain Explore Alkanes are a type of molecule with only hydrogen and carbons atoms, joined with single bonds. Single bonds are shown by a straight line connecting a C with an H. The first few straight-chain alkanes are drawn in the table below, starting with methane, the smallest alkane. 1. Write the formula for the first four alkanes by counting the number of carbon atoms and the number of hydrogen atoms in the structural formula. The first two have been done as an example. Draw pictures for the rest of the alkanes in the table and write their formulas. Name Structural Formula Formula methane ethane propane butane pentane hexane heptane octane nth alkane CnH______
- 2. 2. Since the number of hydrogen atoms increases by _ every time the number of carbon atoms increases by 1, there is a __________ relationship between the number of hydrogen atoms and the number of carbon atoms. 3. To represent the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the number of hydrogen atoms as a linear equation, write the information in the table in the form of ordered pairs. Name Number of carbon Number of Ordered Pair atoms (C) hydrogen atoms (H) (C, H) methane ethane propane butane pentane hexane heptane 4. Find the slope of the line representing this data and interpret it in words. Discover Since this data is linear, we can write a linear model that gives the number of hydrogen atoms for a given number of carbon atoms. To date, we have used inductive reasoning to find a relationship between two variables. While this does not require a lot of math, it can be time consuming and frustrating. Let’s develop a procedure to write a linear model from data. 5. a. What is the form of an equation for a linear model? b. Rewrite the formula for a linear model in terms of H and C. Use the table to determine which variable will be independent and which will be dependent. H = the number of H atoms and C = the number of C atoms c. Substitute the value of the slope for m. d. To complete the model, we need to find a value for b. One way to do this is to substitute an ordered pair into the equation and solve for b. We can do this using the first ordered pair (1, 4). After substituting in C = 1 and H = 4, we have: e. Solve this equation to find the value of b: f. Write the completed linear model:
- 3. 6. Explain the meaning of the y-intercept in the model, if possible. 7. On the following grid, create a graph that shows the ordered pairs and the linear model. 8. Use the model for straight-chain alkanes to answer the following questions. a. If an alkane has 10 carbon atoms, how many hydrogen atoms does it have? b. If an alkane has 14 hydrogen atoms, how many carbon atoms does it have? c. Is it possible to have a straight-chain alkane with an odd number of hydrogen atoms?
- 4. How it works To write the equation of a line: 1. Find the slope of the line. If it is not provided, use the table, graph, or points provided to find the slope of the line connecting them. 2. Write the slope-intercept form of a line: y = mx + b. You may need to change the variables x and y to variables that are meaningful for the problem. 3. Substitute the slope for m and an ordered pair on the line for x and y. Solve the resulting equation for b. NOTE: If you can see the y-intercept from the table or graph, you can skip this step. 4. Write the slope-intercept form with the values of m and b included. For example, assume a line passes through (-2, 6) and (3, 11). Since the slope is not given, we need to find it. Since we do not have the y-intercept, we will pick a point on the line and substitute it into the equation to find b. (3, 11) is easier to work with than (-2, 6) since is has no negative numbers in it. Plug in m = 1 and the point (x, y) = (3, 11) into y = mx + b and solve for b: Writing the linear equation, we get: y = 1x + 8 or y = x +8.
- 5. 9. Find the linear equation for each situation. a. m = 4, line passes through (0, -8) b. Line passes through (2, 6) and (4, 10) c. Horizontal line passing through (-6, 7). d. Vertical line passing through (1, -2). Draw a graph with a vertical line passing through (1, -2). Complete this table with points from the line: x y Use inductive reasoning and the table to write an equation. Notice, horizontal lines have the form y = b where b is a number. Vertical lines have the form x = a where a is a number. Equations for vertical lines cannot be written in y = mx + b form.
- 6. Connect 10. Carbon chains also exist in a cyclic form with double bonds as shown in the table. Write the formulas indicating the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each structure. Then complete the last column in the table by writing an ordered pair to indicate the number of carbon atoms and the number of hydrogen atoms in each structure. Name Structural Formula Formula (C, H) cyclopropene C3H4 (3, 4) cyclobutene cyclopentene cyclohexene nth alkene CnH_______ (n, ) 11. Find a linear model that gives the number of hydrogen atoms for a given number of carbon atoms.
- 7. 12. Use the model for cyclic alkenes to answer the following questions. If a cyclic alkene has 12 carbon atoms, how many hydrogen atoms does it have? If a cyclic alkene has 12 hydrogen atoms, how many carbon atoms does it have? Is it possible to have a cyclic alkene with an odd number of hydrogen atoms? 13. How many carbons are necessary for this model to make sense? 14. On the following grid, create a graph that shows the ordered pairs and the linear model. Use your answer from #13 when creating the graph.
- 8. Reflect Lesson wrap-up: What’s the point? Sometimes a linear relationship is apparent from the description of the situation. When it is not, we can use the linear equation form y = mx + b and information about the situation to write the equation. What did you learn? How to write the equation of a line using a point and slope or two points How to model linear situations in context Cycle 4 Question: How big is big? At what point should you use y = mx + b to find a linear model? When does a problem become too big or messy for intuitive approaches? 4.8 Homework Skills Write the equation of a line using a point and slope or two points. Model linear situations in context. Skill Check 1. Write the equation of the line passing through (6, -3) and (-5, 2). 2. A student pays $1175 to take 4 credit hours at a local college. Another student pays $2175 to take 8 credit hours at the same college. Write a linear model for the cost of attending the college based on the number of credit hours a student takes.