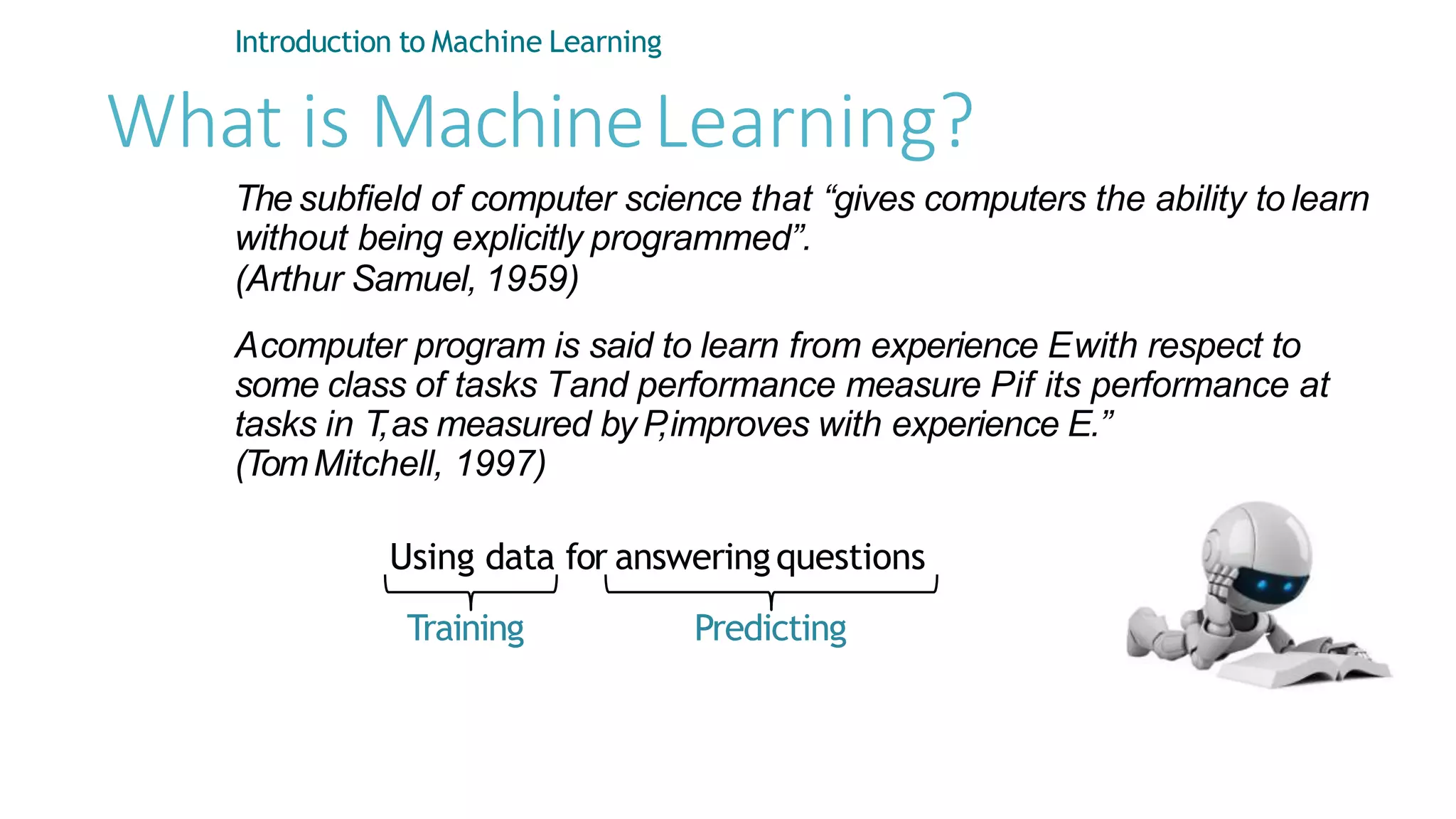
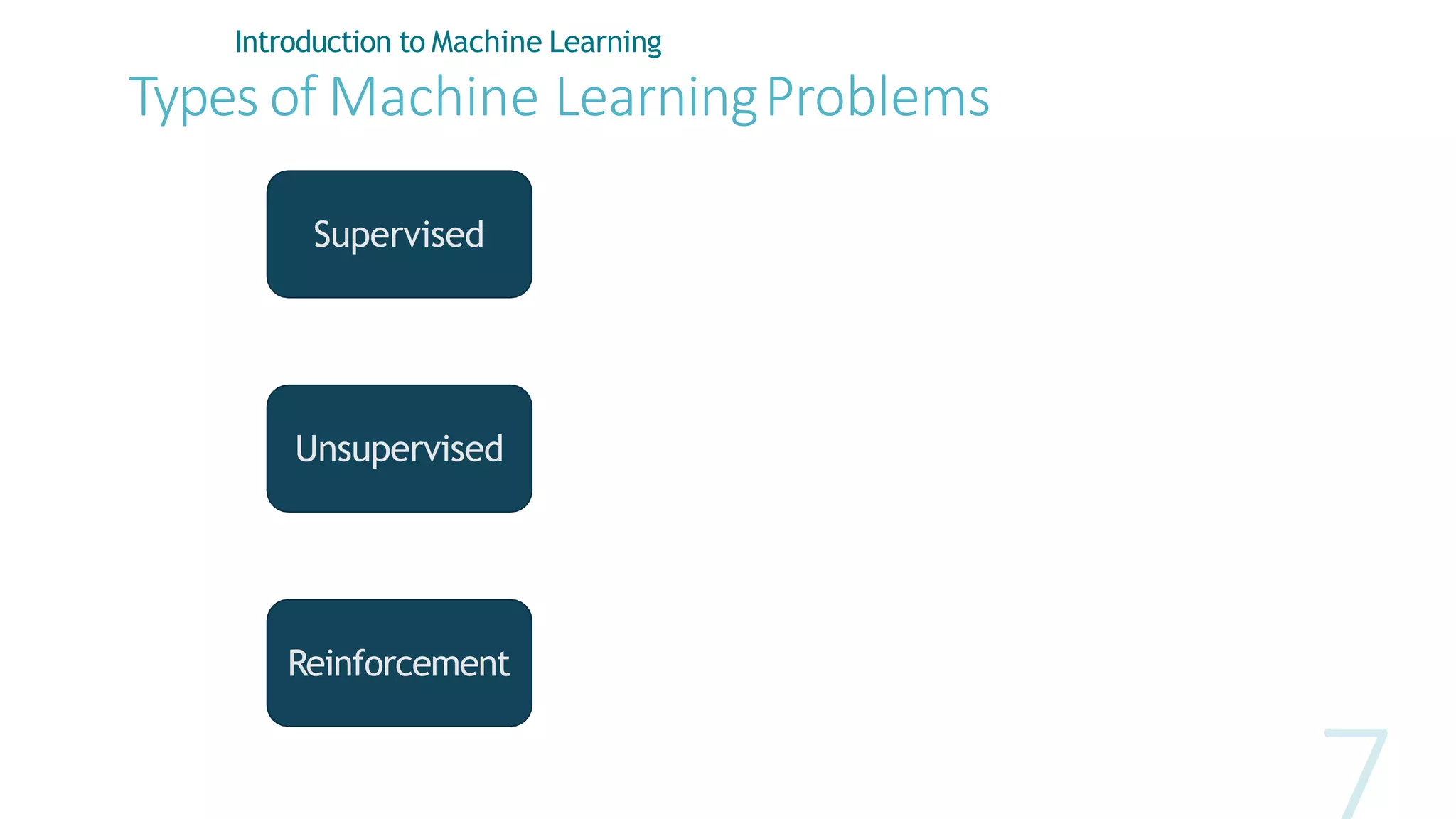
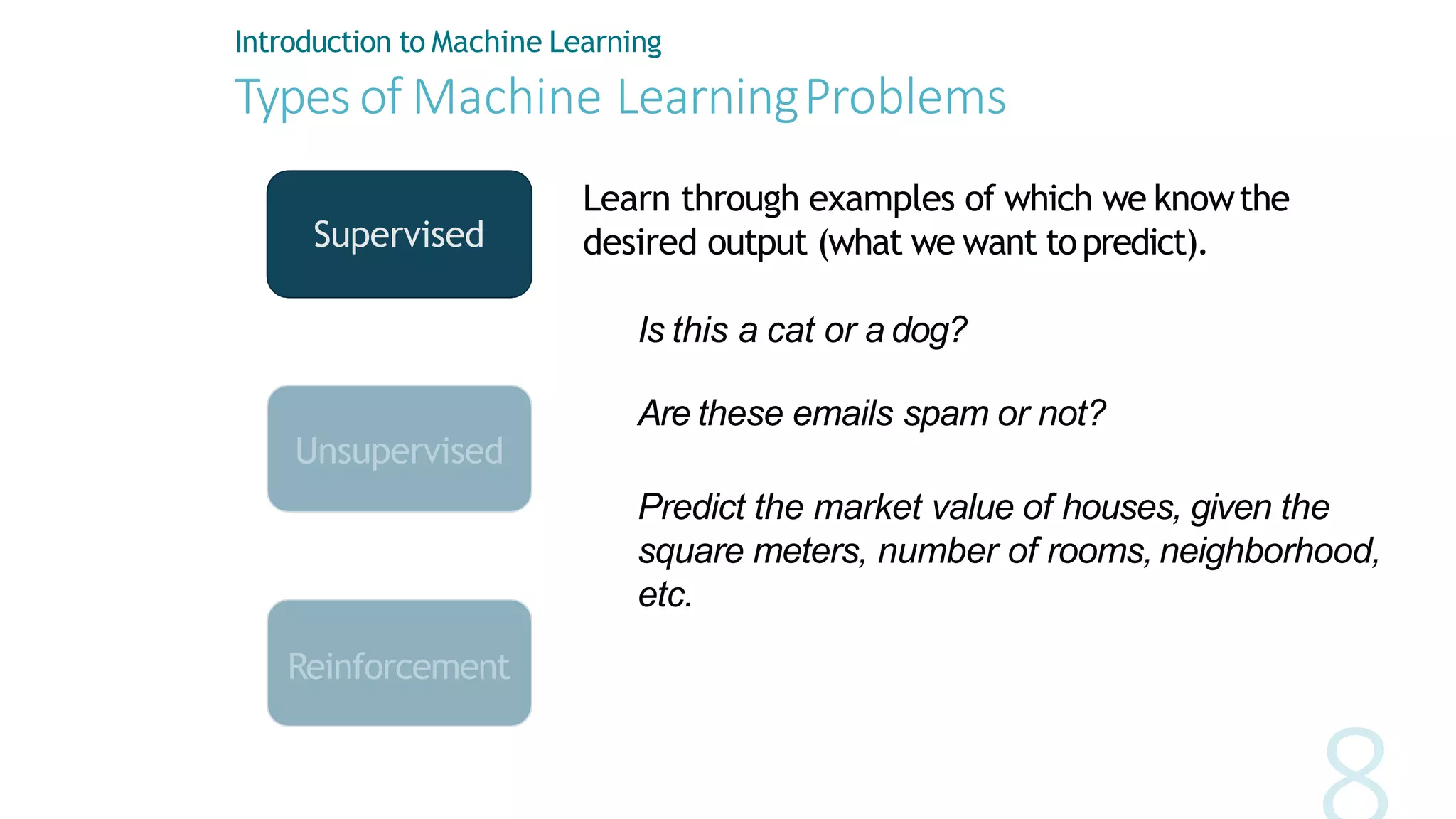
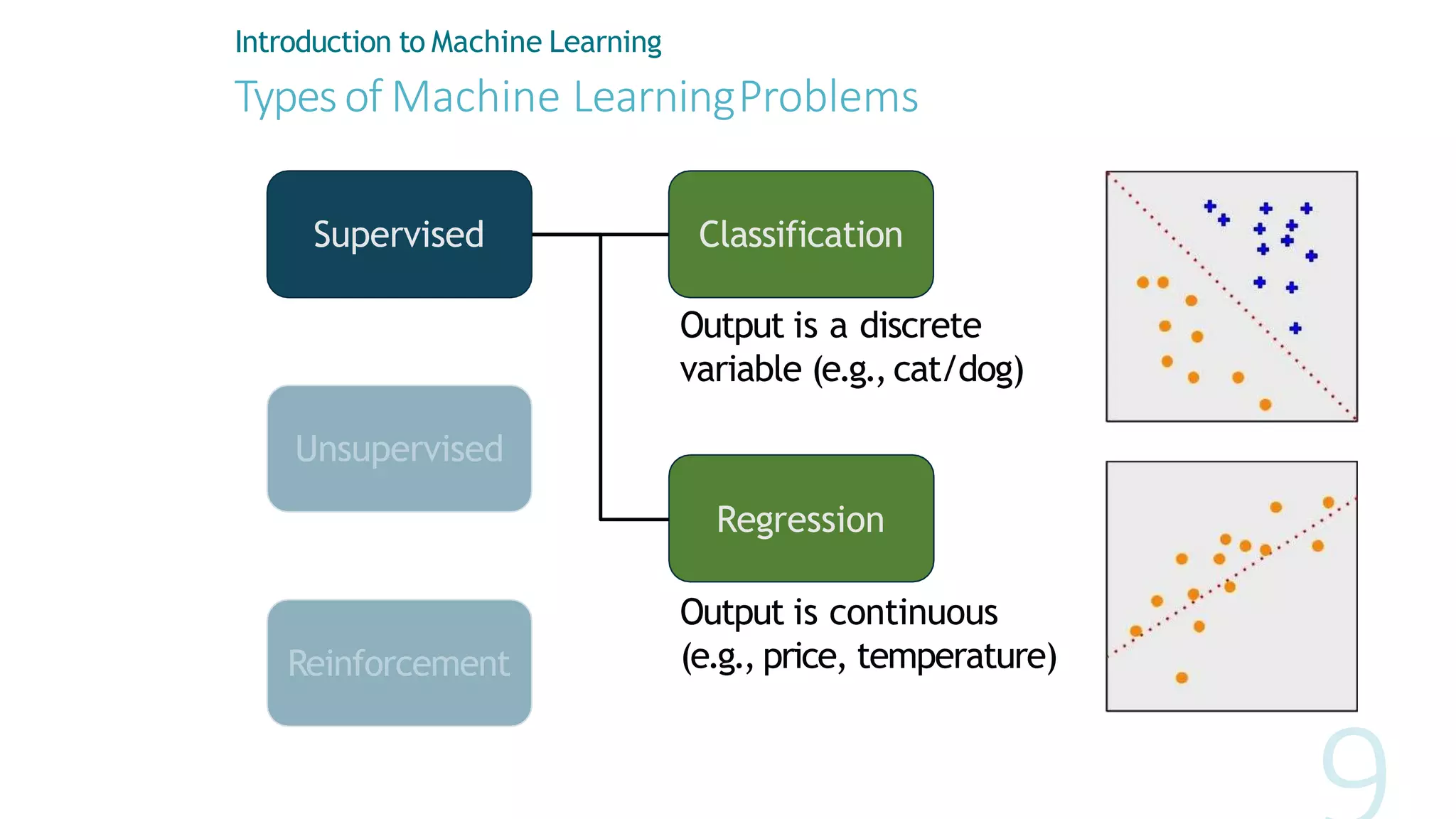
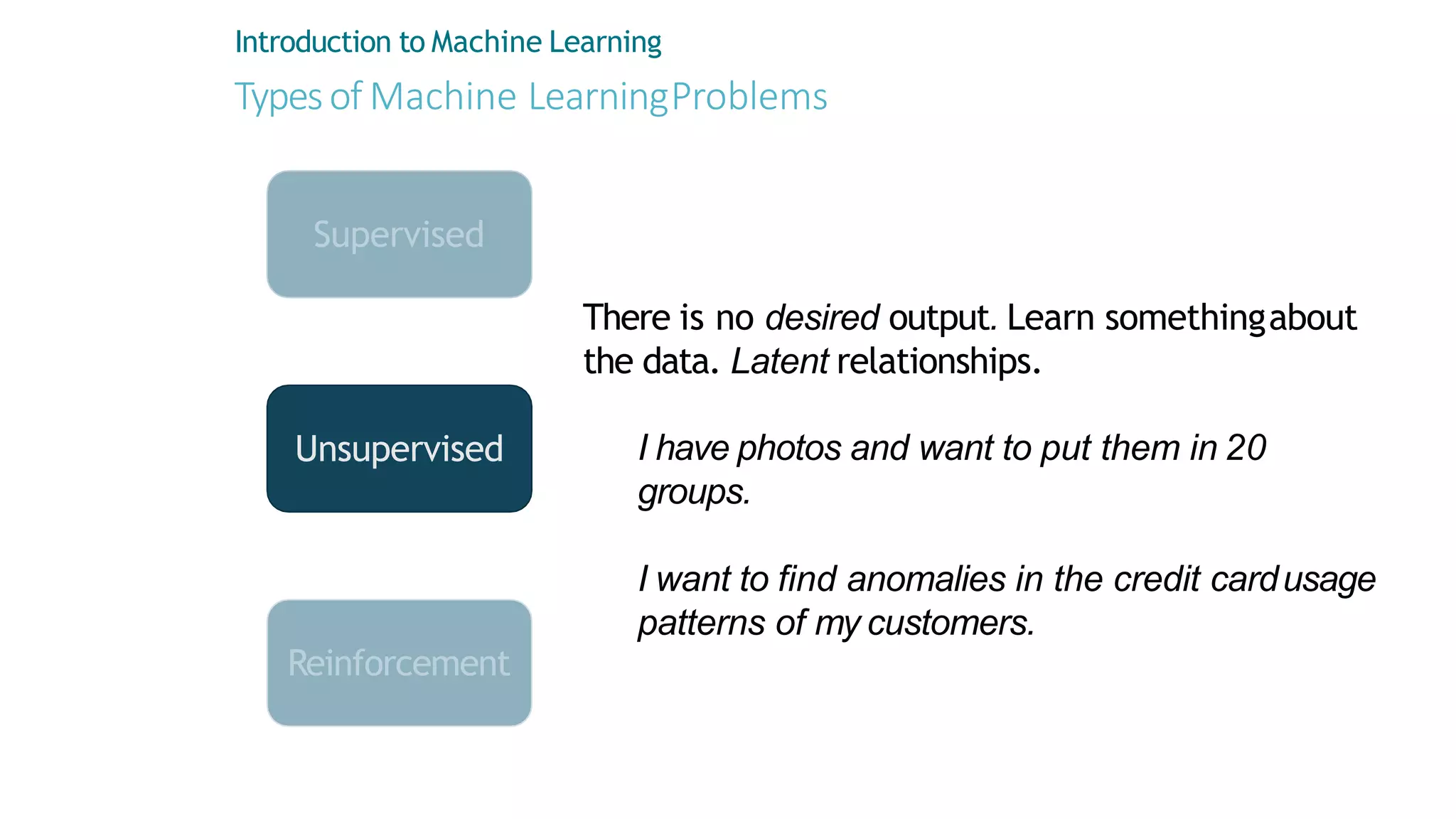
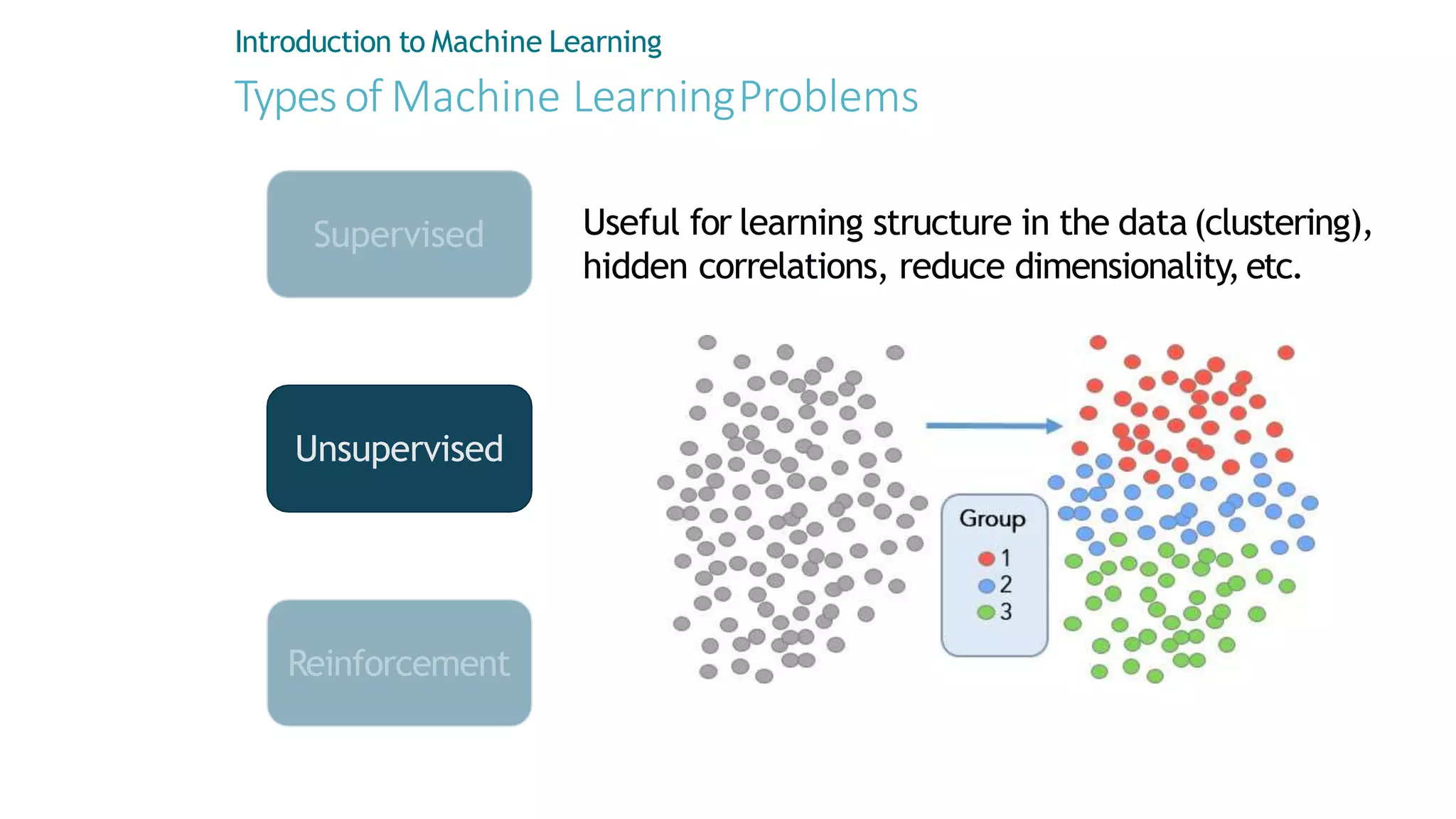
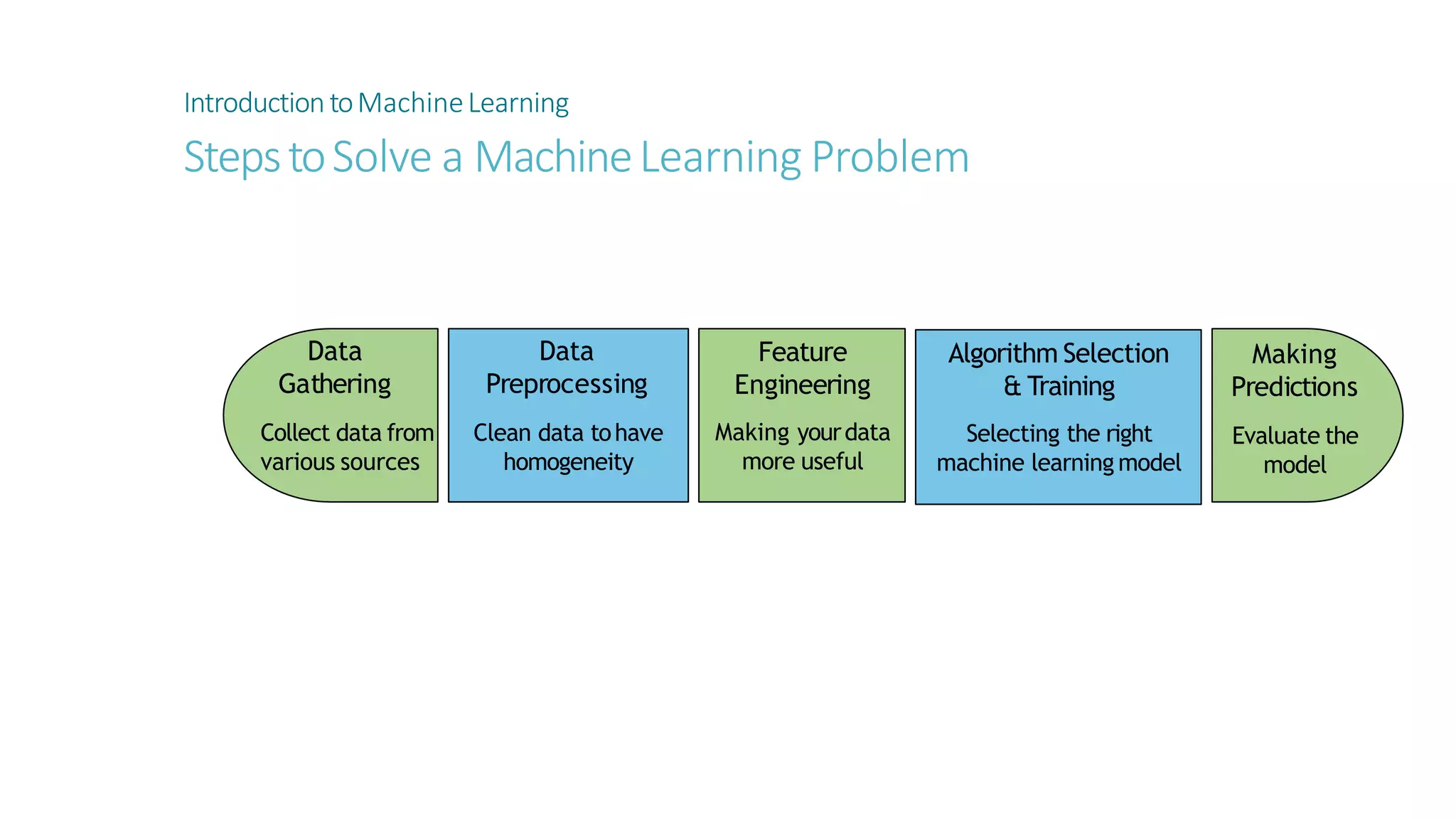
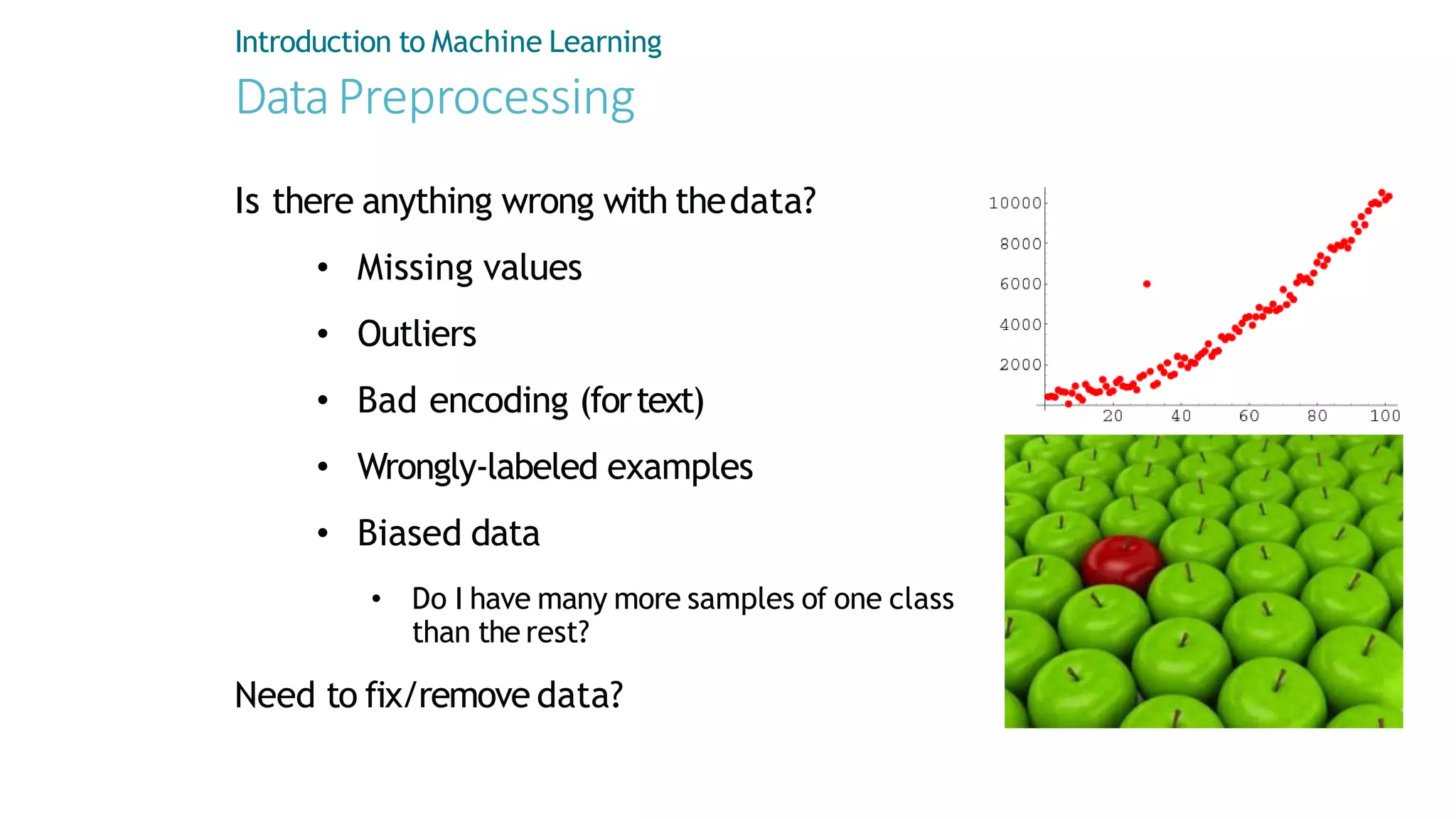
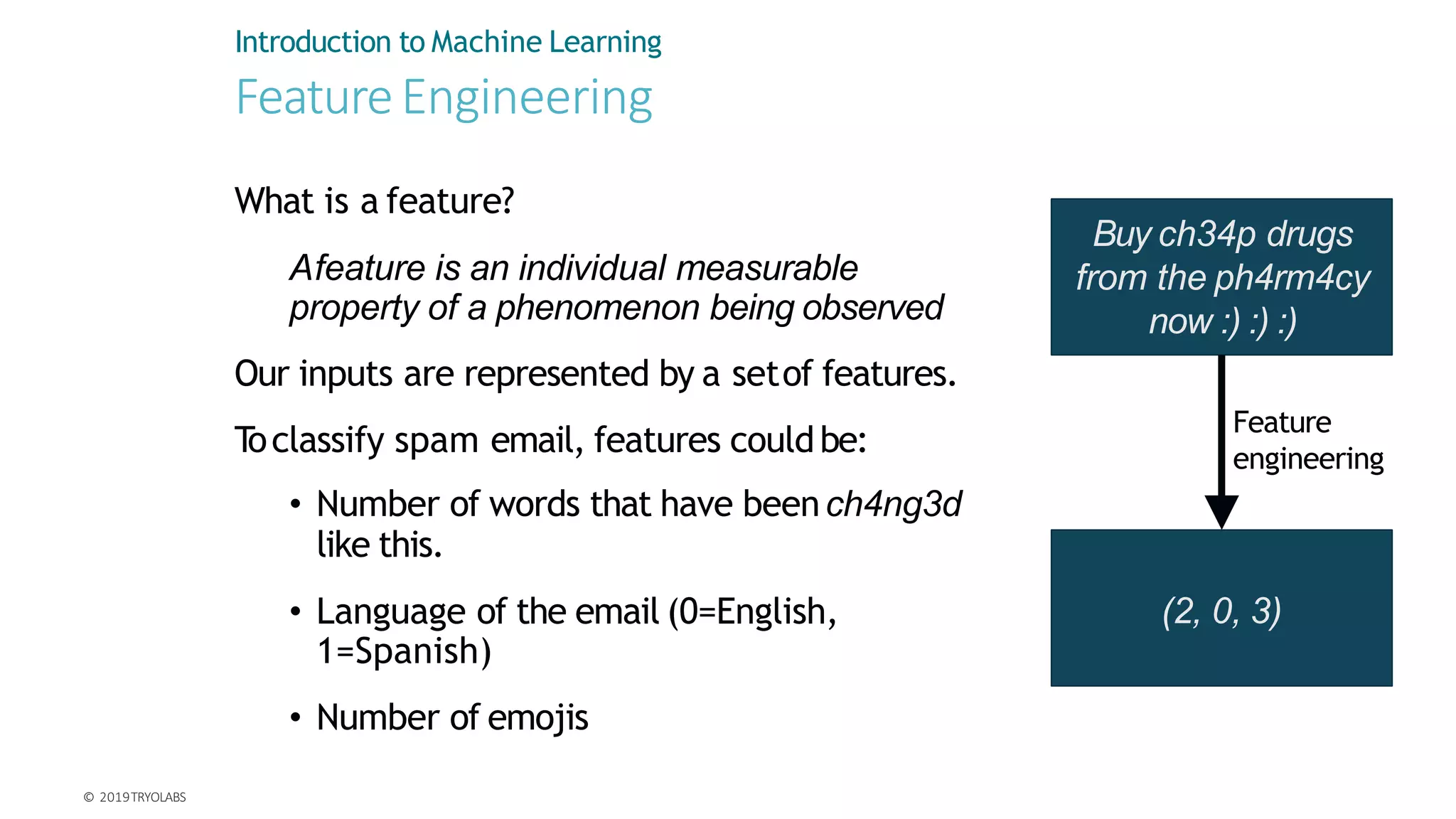
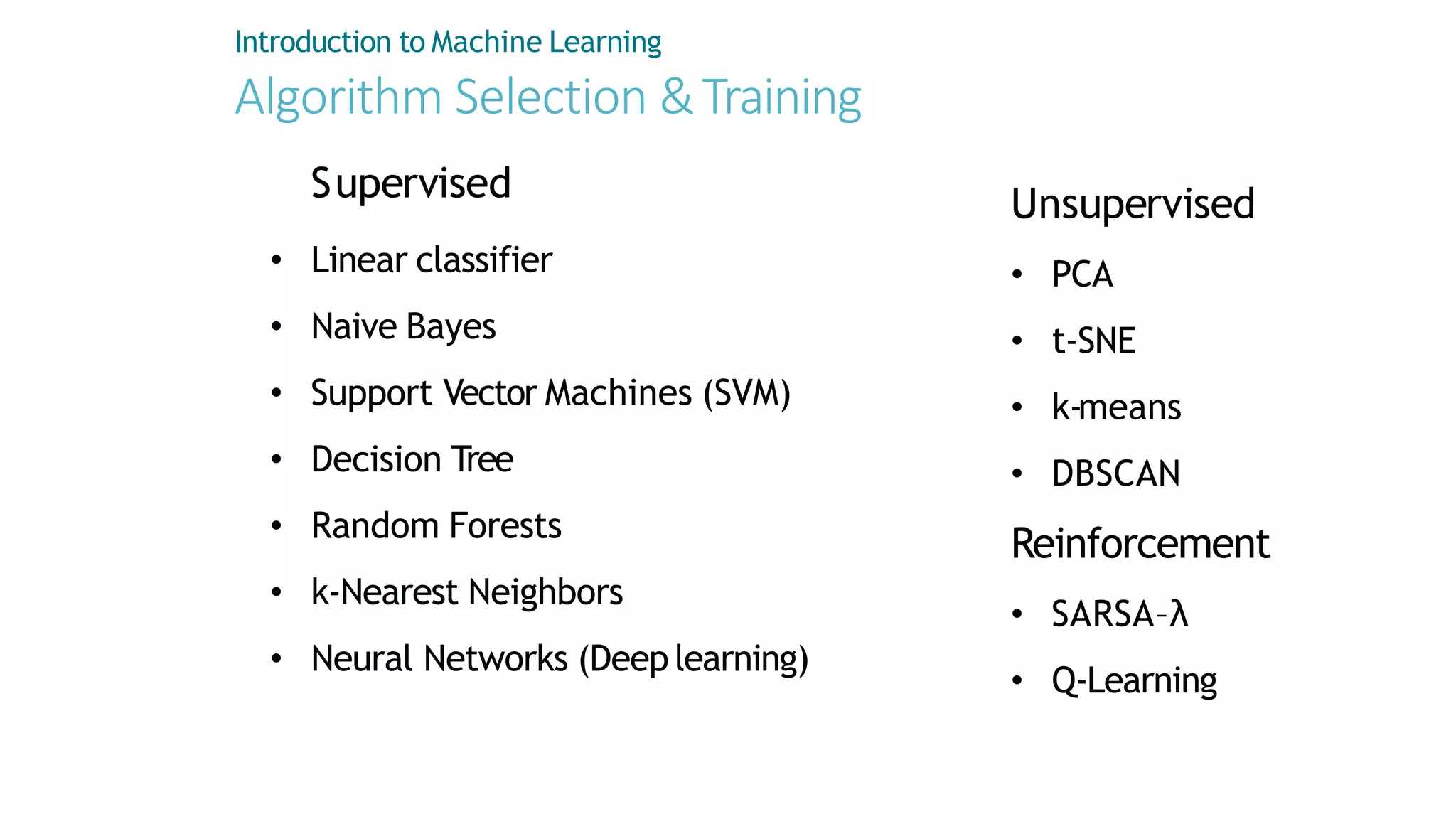
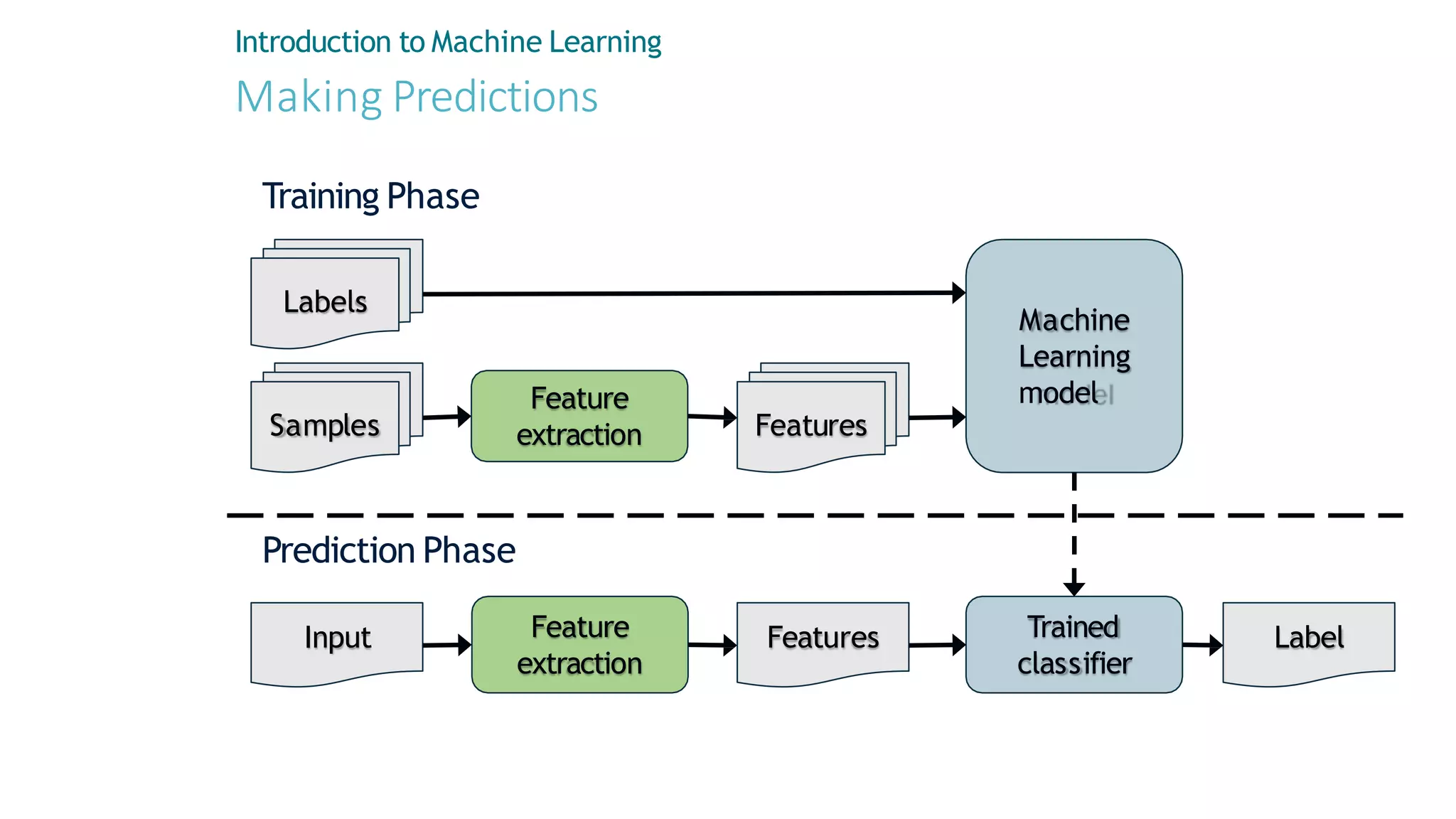
Machine learning involves using data to answer questions and make predictions. There are three main types of machine learning problems: supervised learning which involves predicting outputs given labeled examples; unsupervised learning which finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data; and reinforcement learning where an agent learns through trial-and-error interactions with an environment. To solve a machine learning problem typically involves five steps: gathering and preprocessing data, engineering features, selecting and training an algorithm, and using the trained model to make predictions.