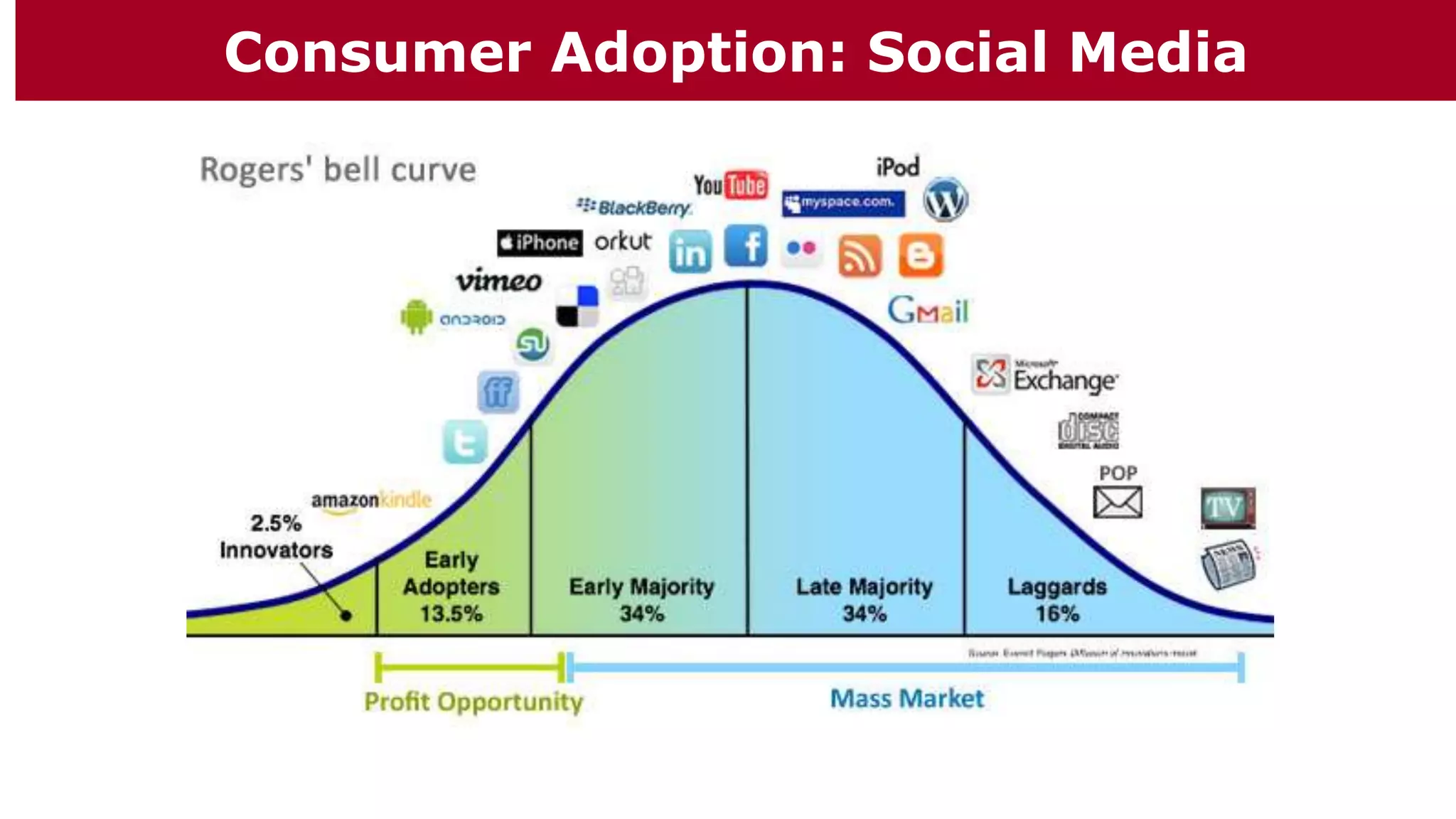
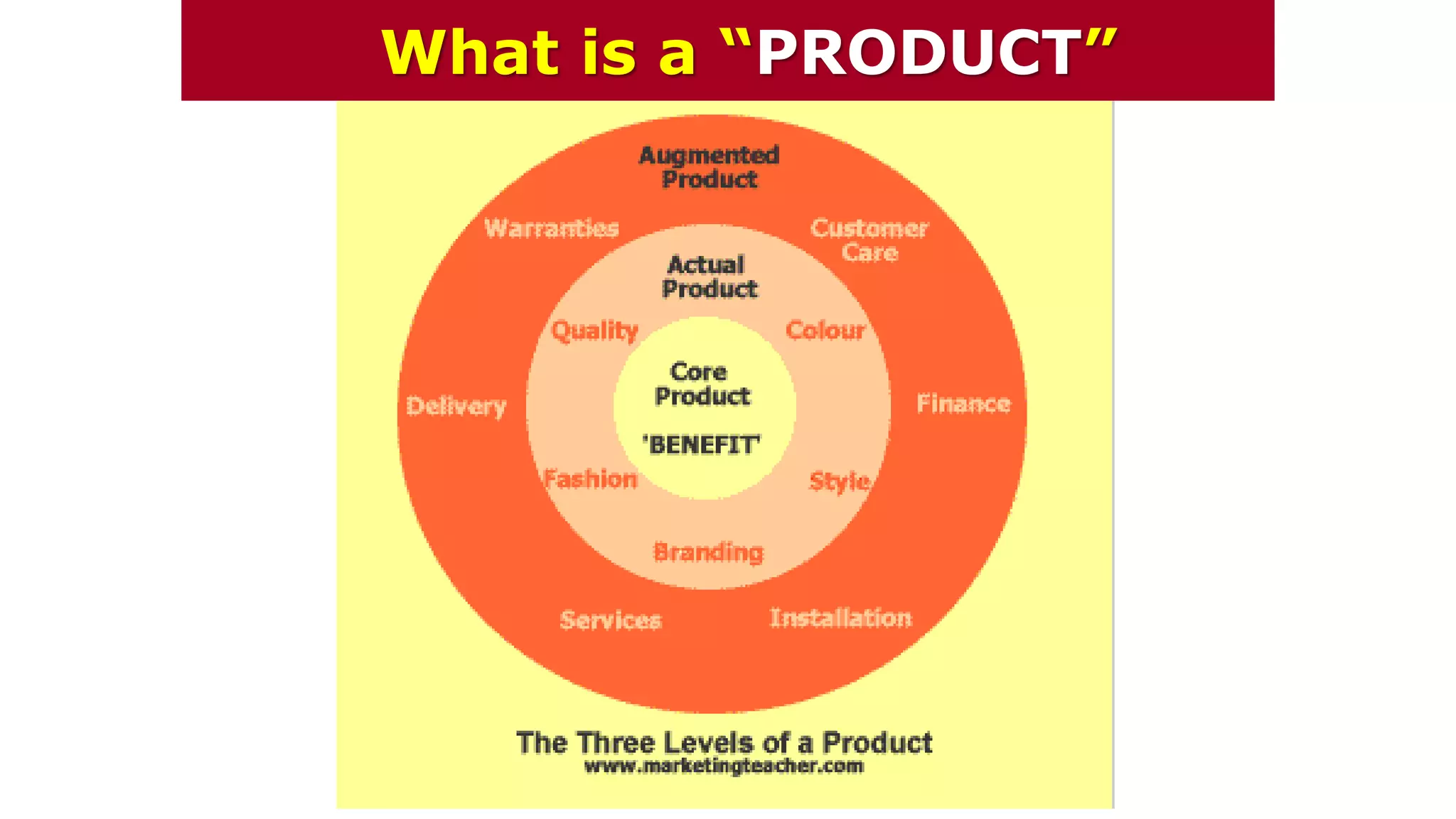
This document provides an overview of a marketing communications course taught by Professor Ethan Chazin. It includes an agenda for the first week which focuses on introductions and a review of the syllabus. Background information is provided on the professor and his areas of expertise. Various marketing topics that will be covered in the course are briefly outlined such as consumer behavior, social media adoption, strategic market management, and the objectives and role of marketing communications.