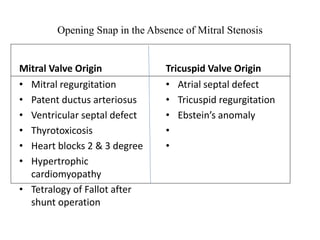
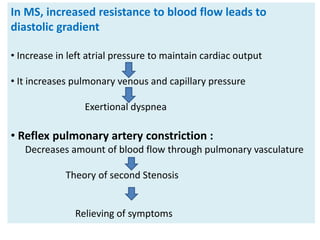
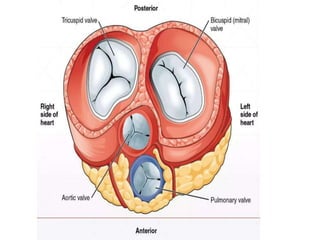
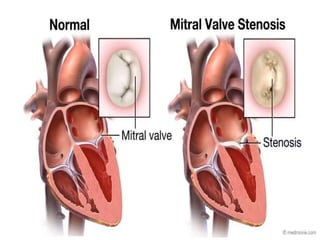
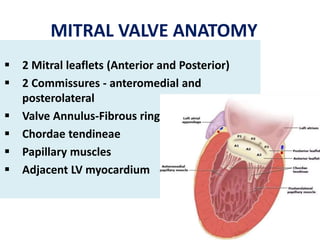
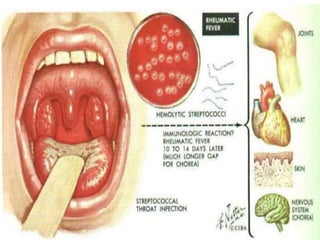
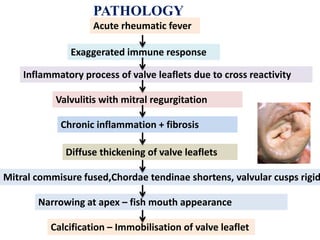
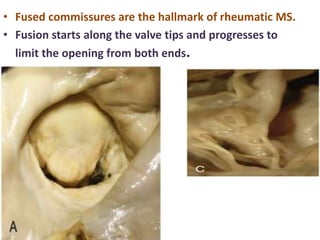
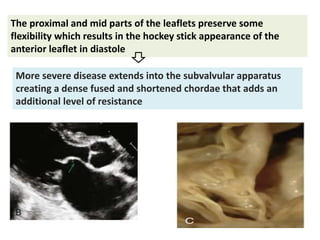
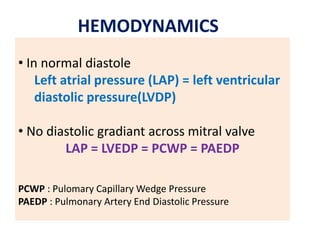
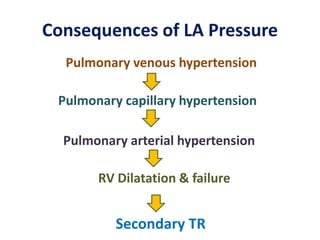
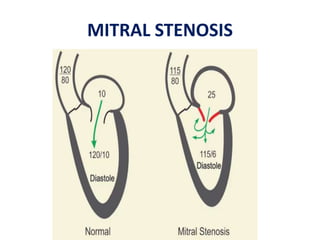
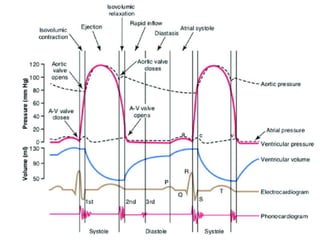
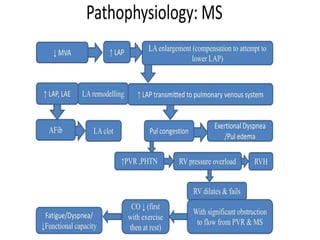
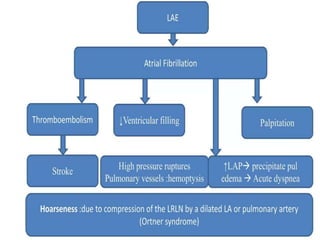
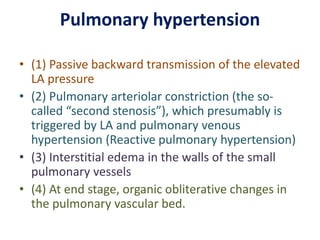
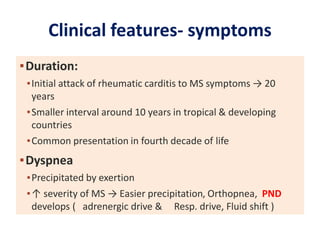
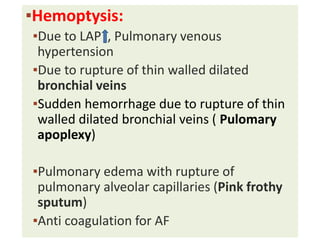
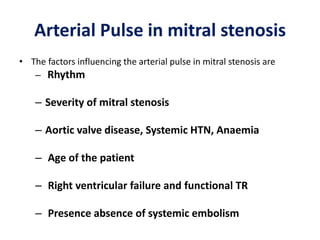
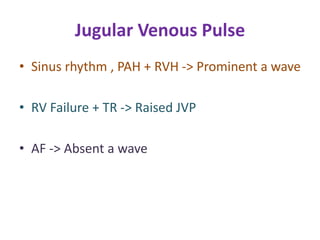
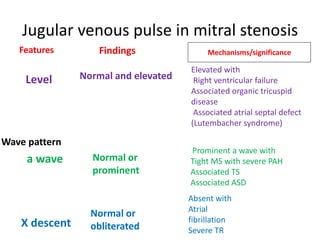
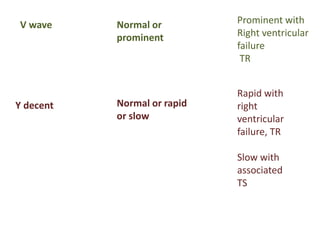
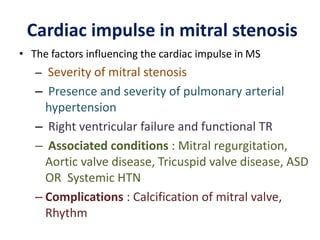
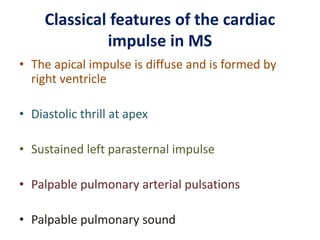
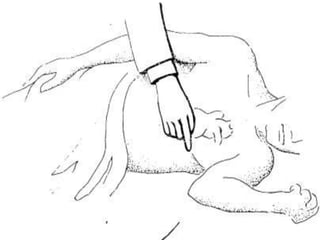
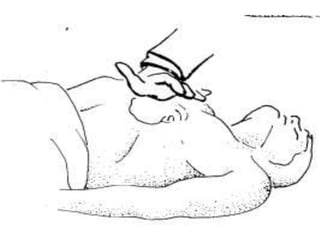
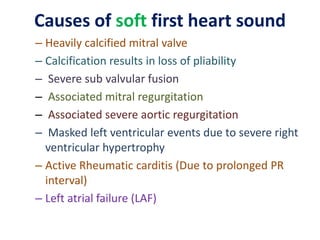
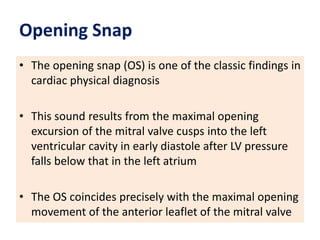
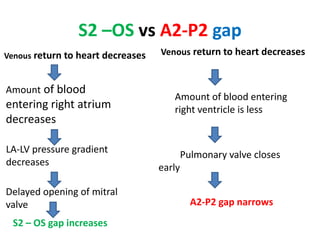
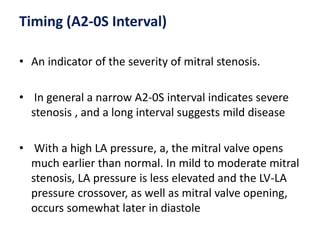
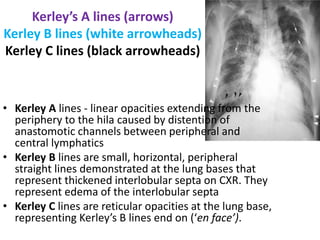
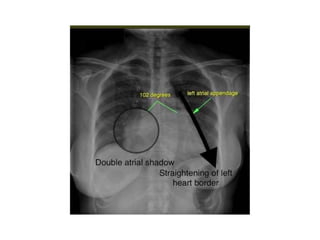
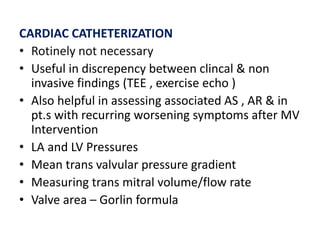
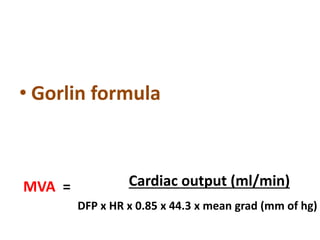
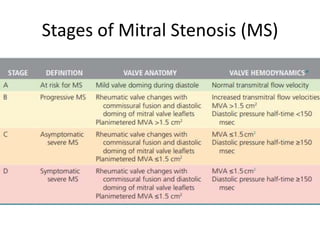
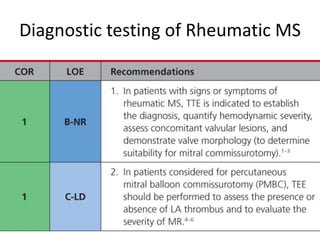
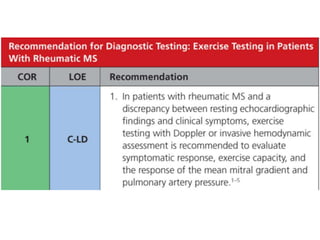
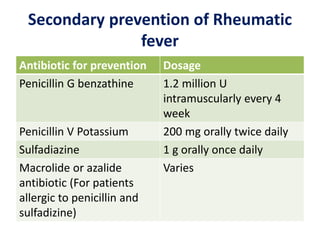
Mitral stenosis (MS) is characterized by narrowing of the mitral valve, impeding blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, often resulting from rheumatic fever or degenerative causes. Symptoms typically develop over decades and include dyspnea, cough, fatigue, and pulmonary complications. Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, echocardiography, and imaging, revealing characteristic auscultatory findings and changes in heart structure that reflect disease severity.










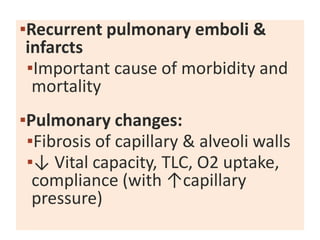

























![ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS :
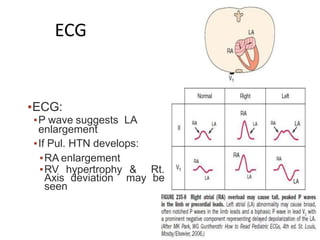
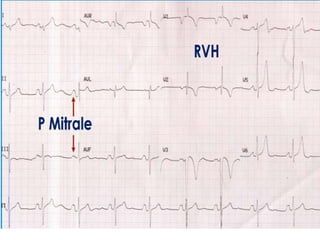
In severe MS & sinus rhythm – P waves usually
suggest LA enlargement (90%)
P-WAVE : Tall peaked in lead ll
upright in V1 [ when severe
pulmonary HTN or TS complicate MS & RA
enlargment
QRS – normal [ with severe pulmonary HTN -
right axis deviation , RV hypertrophy ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mitralstenosis-ugfinaldrjtr-240724003843-85c40d77/85/MITRAL-STENOSIS-UG-Final-by-Dr-JTR-pptx-75-320.jpg)



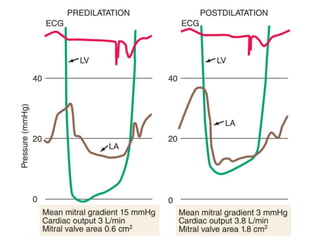
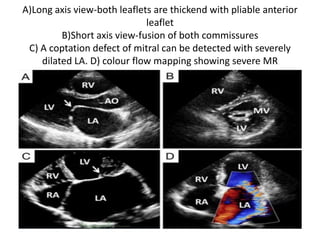
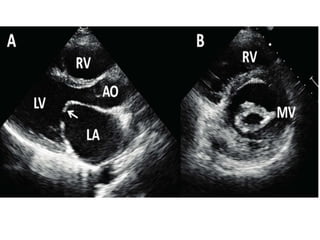
![ECHOCARDIGRAM :
Transthoracic echo with color flow
&spectral doppler imaging shows
• Measurements of mitral inflow velocity during
early[ E-waves ] & late [A-waves] in pts with
sinus rhythm – diastolic filling
• Estimates transvlavular peak , mean gradients,
& mitral area orifice
• Severity of any association of MR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mitralstenosis-ugfinaldrjtr-240724003843-85c40d77/85/MITRAL-STENOSIS-UG-Final-by-Dr-JTR-pptx-83-320.jpg)
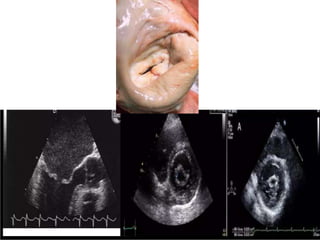
![• Extent of leaflet calcification & restriction
• Degree of distortion of subvalvular apparatus
• Anatomy for percutaneous mitral balloon
commissurotomy
also assessment of LV,RV function
chamber size
Estimation of PA systolic pressure based on
tricuspid regurgitation velocity
Pressure & severity of associated valvular
leions [AS/&AR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mitralstenosis-ugfinaldrjtr-240724003843-85c40d77/85/MITRAL-STENOSIS-UG-Final-by-Dr-JTR-pptx-84-320.jpg)



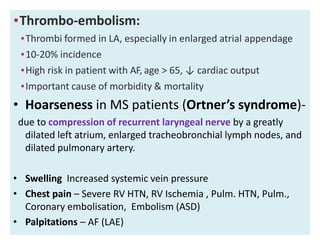
![Indications for Anti coagulation
• AF
• Any prior embolic event
• LA Thrombus
Warfarin [INR 2-3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mitralstenosis-ugfinaldrjtr-240724003843-85c40d77/85/MITRAL-STENOSIS-UG-Final-by-Dr-JTR-pptx-99-320.jpg)



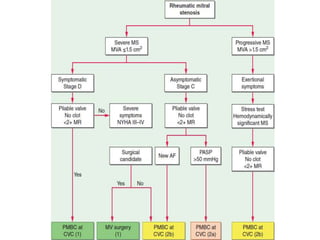
![:
INDICATIONS [AHA]
1. Symptomatic pt.s [NYHA II , lll , lV ] ; Severe
Rheumatic MS ; favorable MV morphology &
No clot in LA / Less than moderate MR
2. Favourable valve morphology wilkins < 8
3. Less than moderate MR < 2 +
4. TEE prior to BMV
5. Avoid BMV in commissural calcification
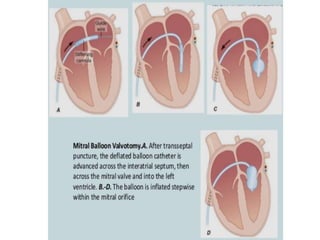
PERCUTANOUS MITRAL BALLON VALVOTOMY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mitralstenosis-ugfinaldrjtr-240724003843-85c40d77/85/MITRAL-STENOSIS-UG-Final-by-Dr-JTR-pptx-103-320.jpg)