Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times


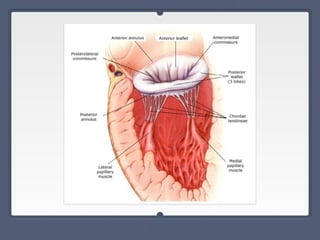
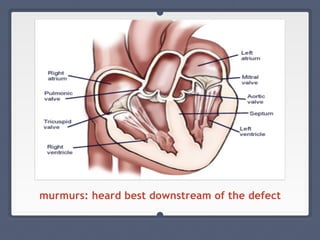
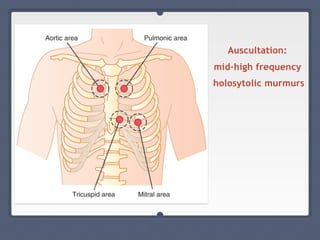
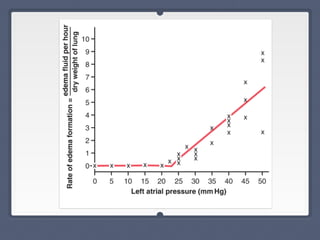
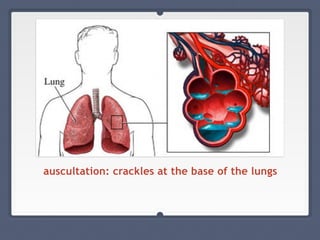

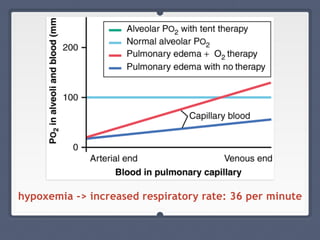
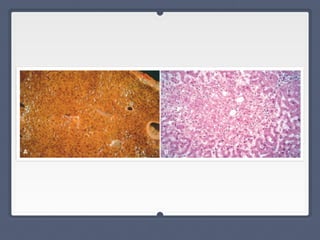
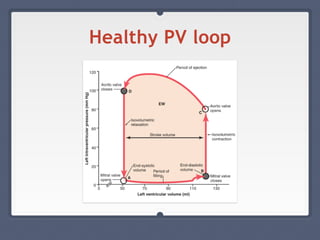
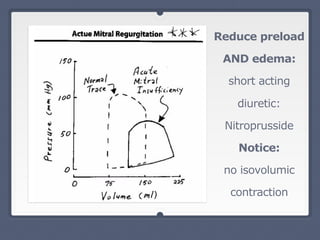
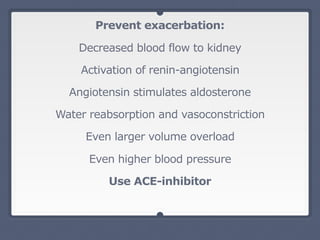
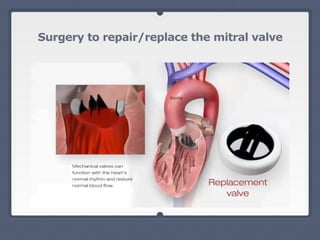


Mitral regurgitation is a heart valve condition where the mitral valve does not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward in the heart. It has various etiologies and risk factors. Diagnosis involves listening for murmurs downstream of the defect via auscultation. Treatment aims to reduce preload on the heart through diuretics and vasodilators like nitroprusside. Surgery to repair or replace the mitral valve may be needed.
















