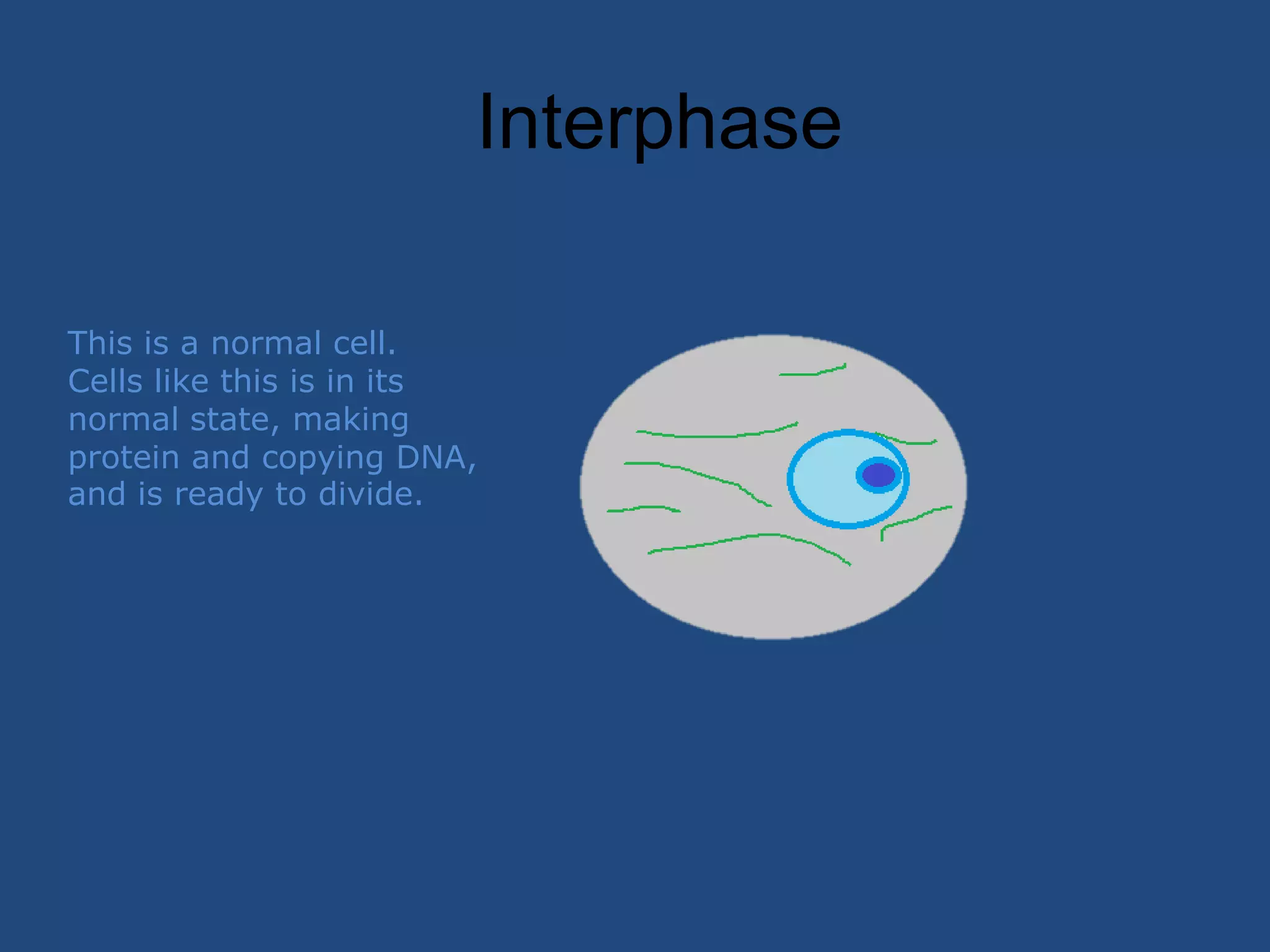
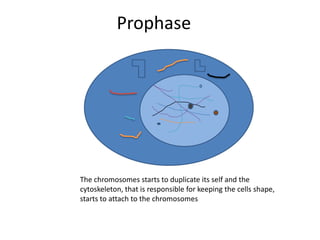
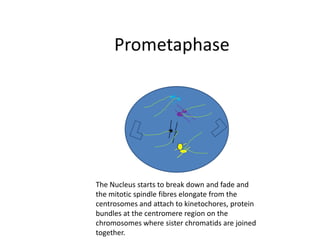
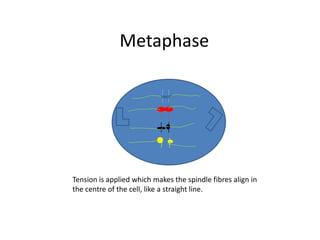
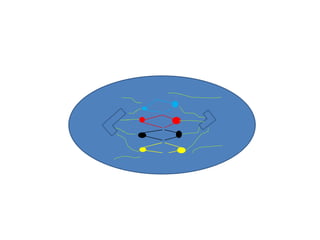
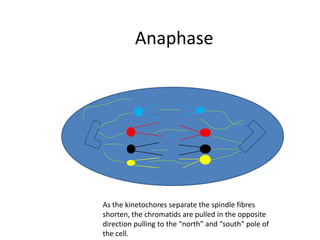
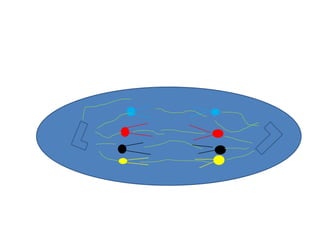
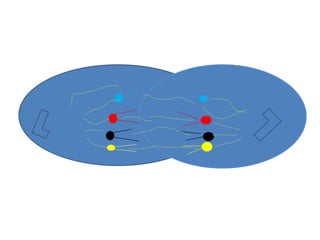
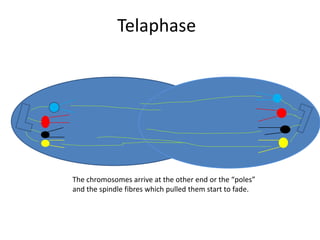
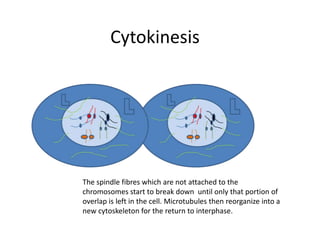
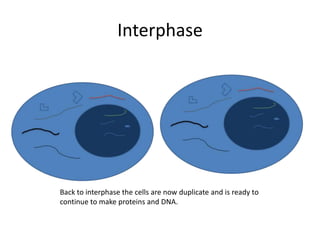
This document describes the stages of cell division: Interphase where the cell is ready to divide, Prophase where the chromosomes duplicate, Prometaphase where the nucleus breaks down and spindle fibers attach to chromosomes, Metaphase where chromosomes align in the center, Anaphase where chromatids separate and move to opposite poles, Telophase where chromosomes reach the poles, Cytokinesis where the cell divides into two daughter cells, and the cells return to Interphase ready to divide again.