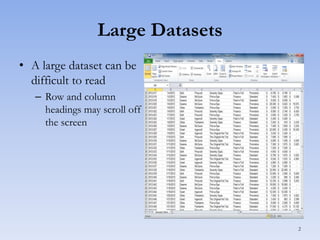
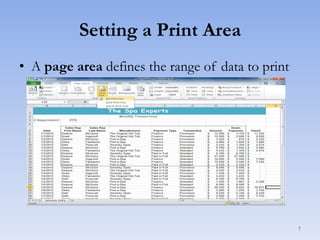
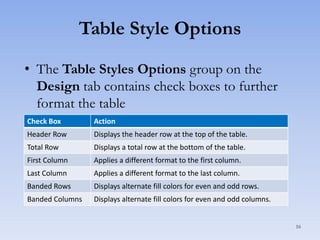
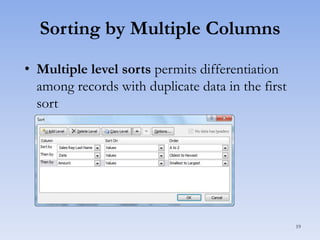
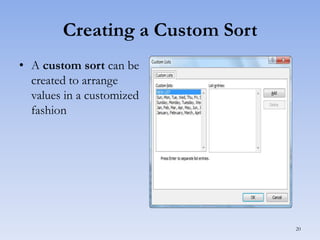
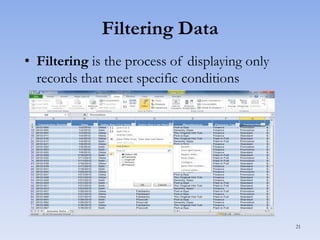
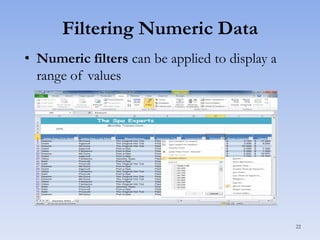
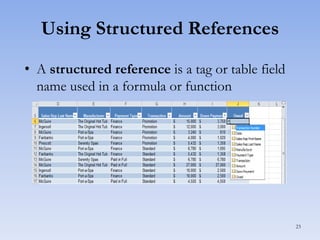
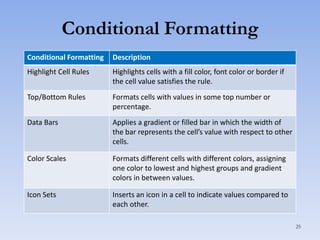
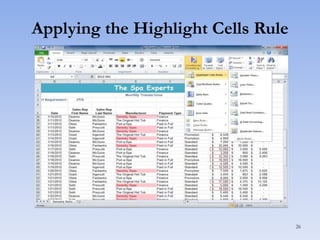
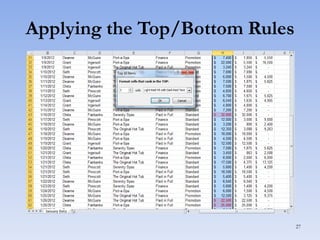
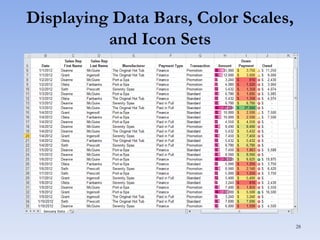
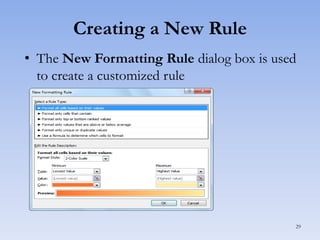
This document discusses features in Excel for working with large datasets and tables. It describes how to freeze rows and columns to keep headings visible while scrolling, print large datasets using page breaks and print areas, and create and format tables. Tables offer features like sorting, filtering, conditional formatting, and total rows. Sorting can be done on one or multiple columns. Filters display only records that meet conditions. Conditional formatting highlights or formats cells based on rules.