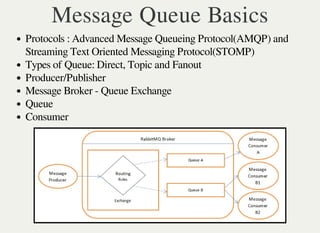
Message queues facilitate inter-process communication and asynchronous messaging, allowing producers to send messages via a message broker for consumption by consumers. Key benefits include decoupling, scalability, and reliability, with RabbitMQ as a prominent implementation supporting various protocols. Effective logging and monitoring are essential for managing message queues and ensuring system performance.