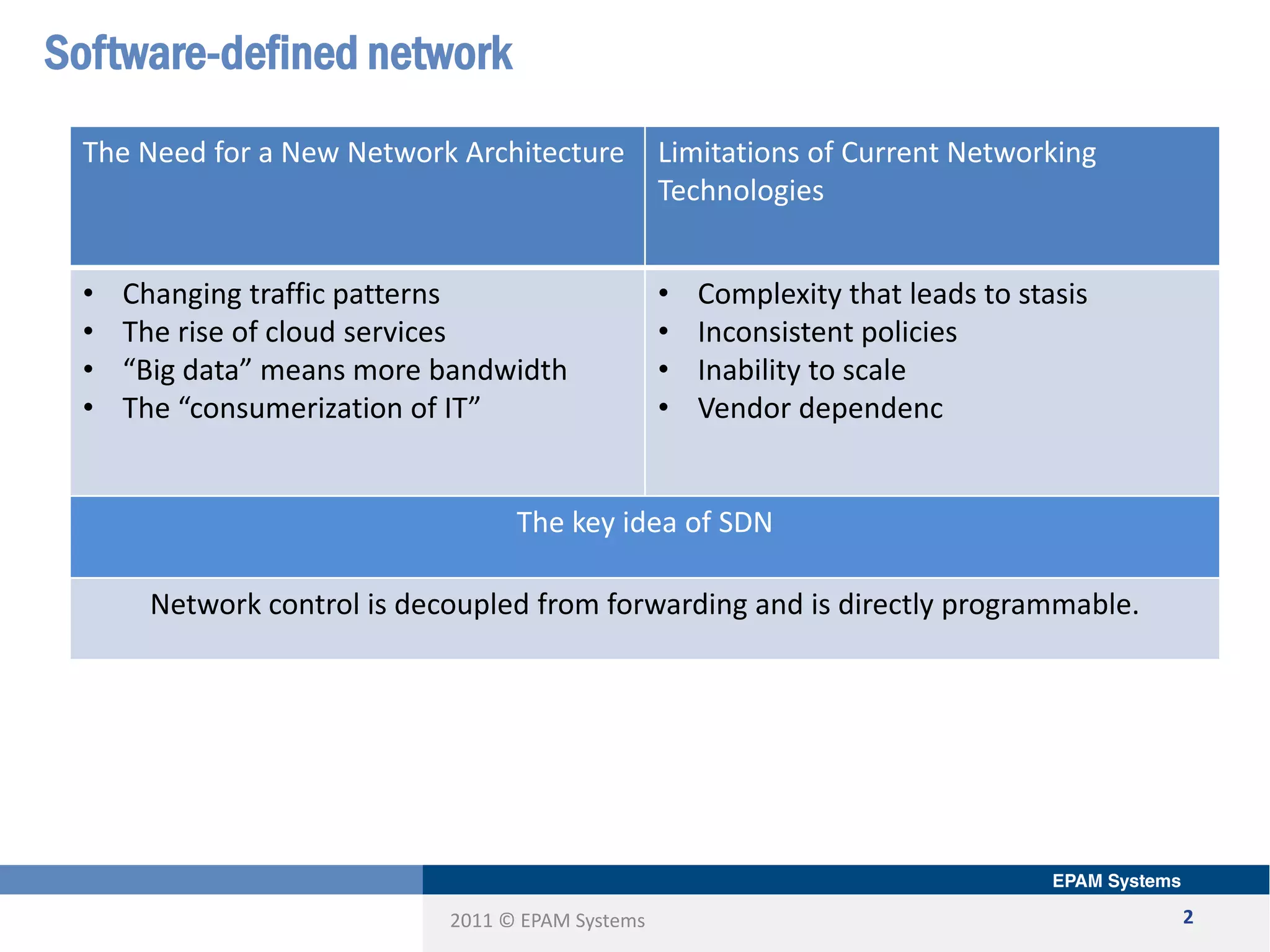
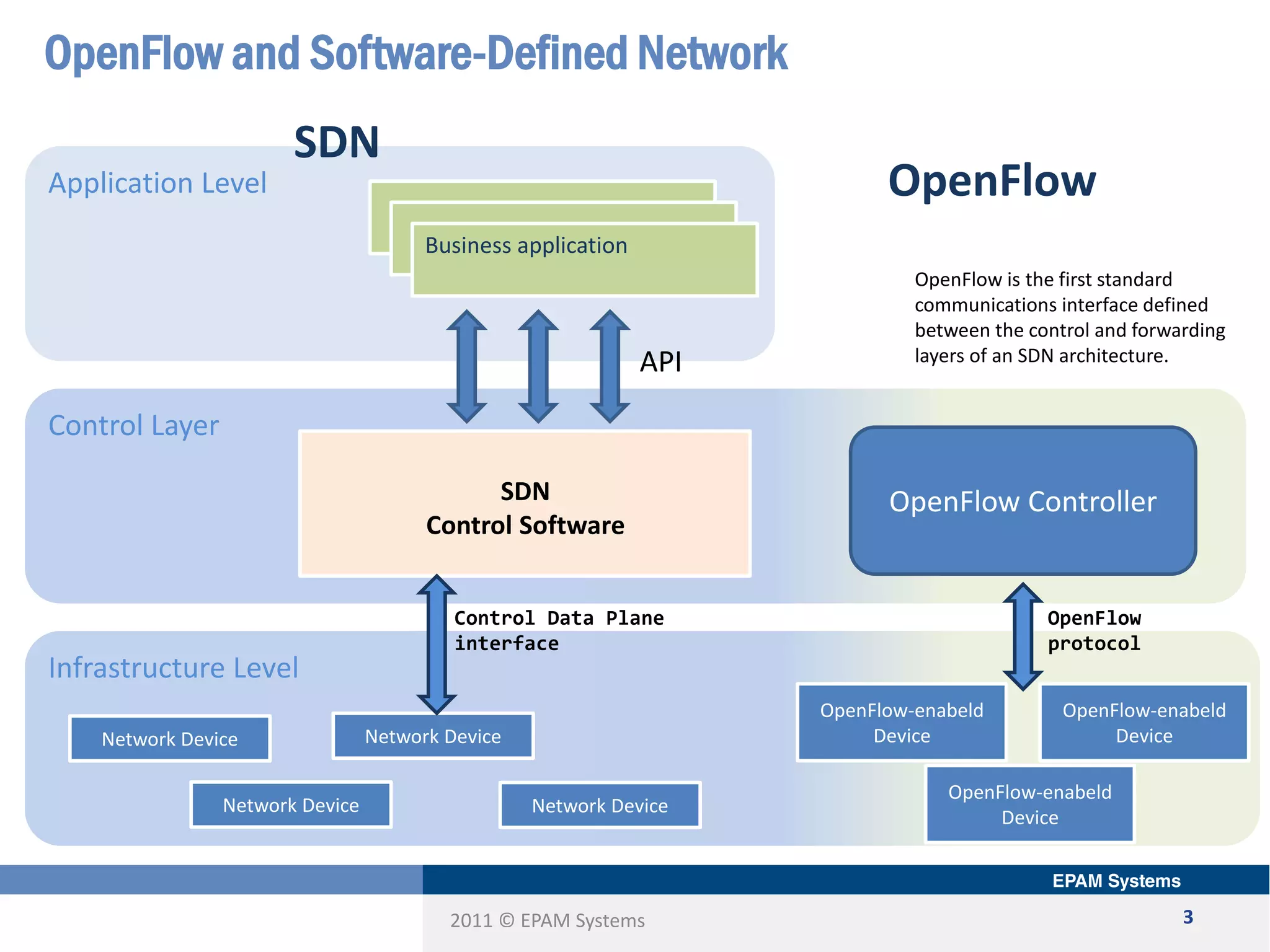
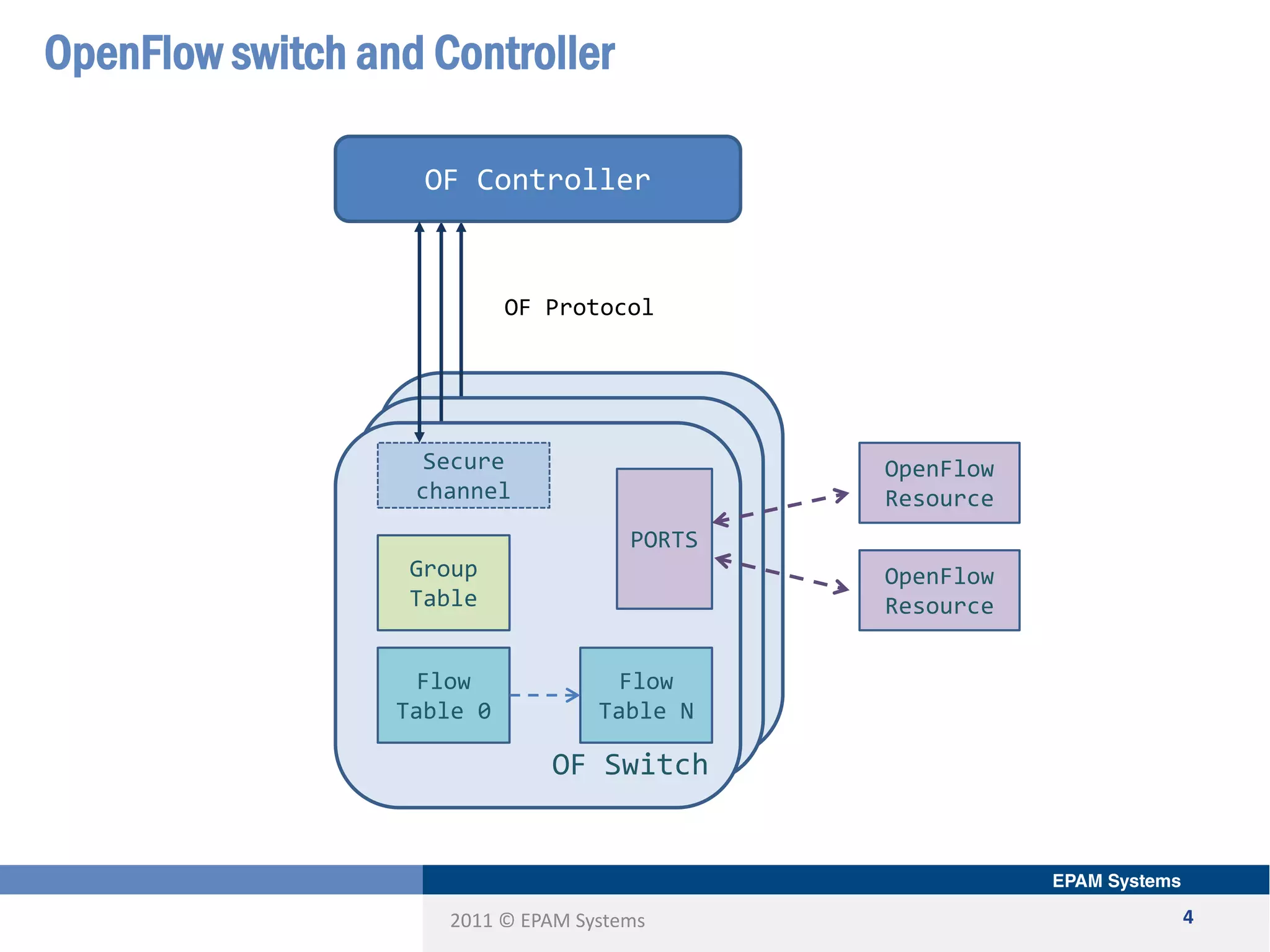
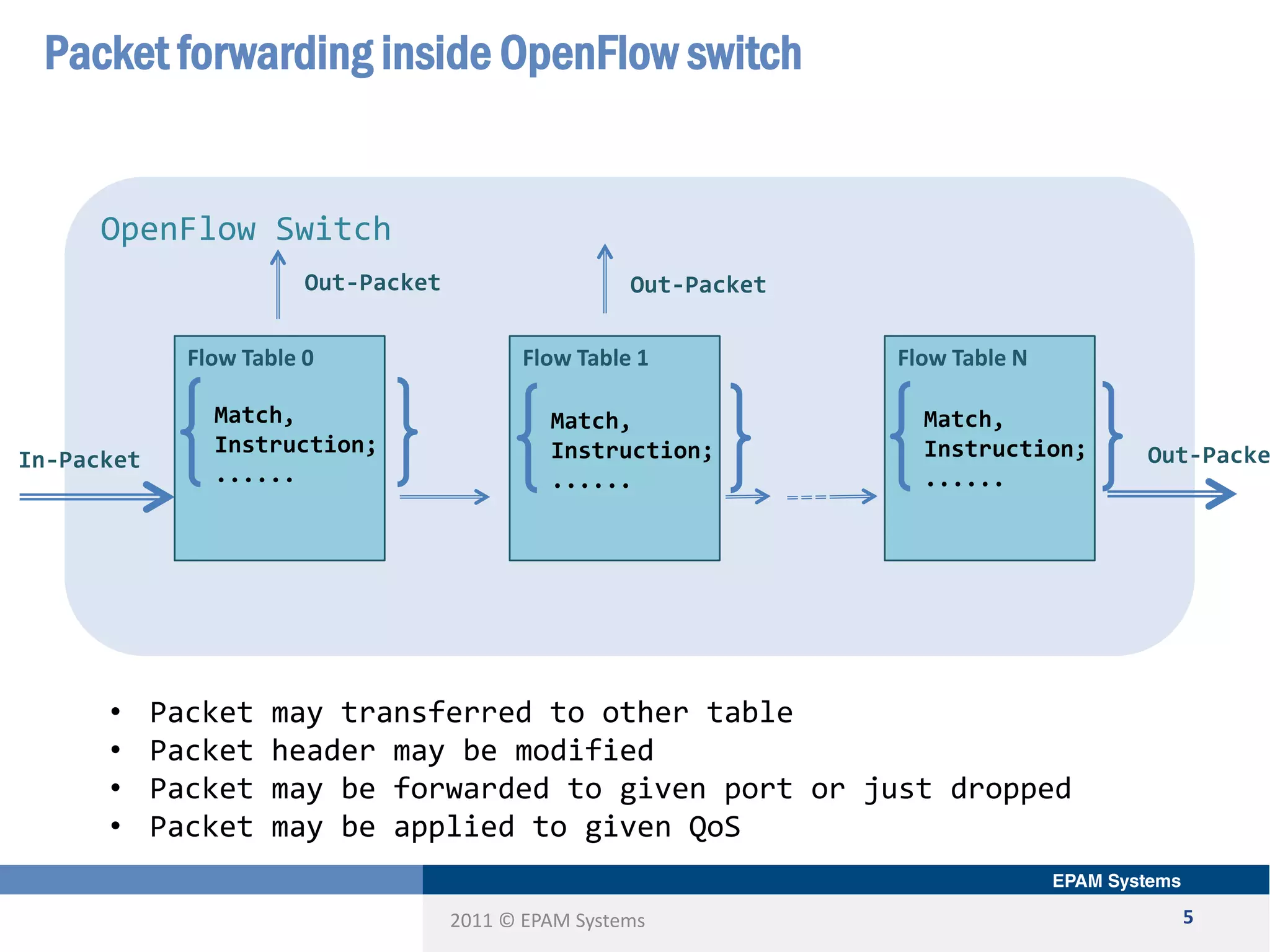
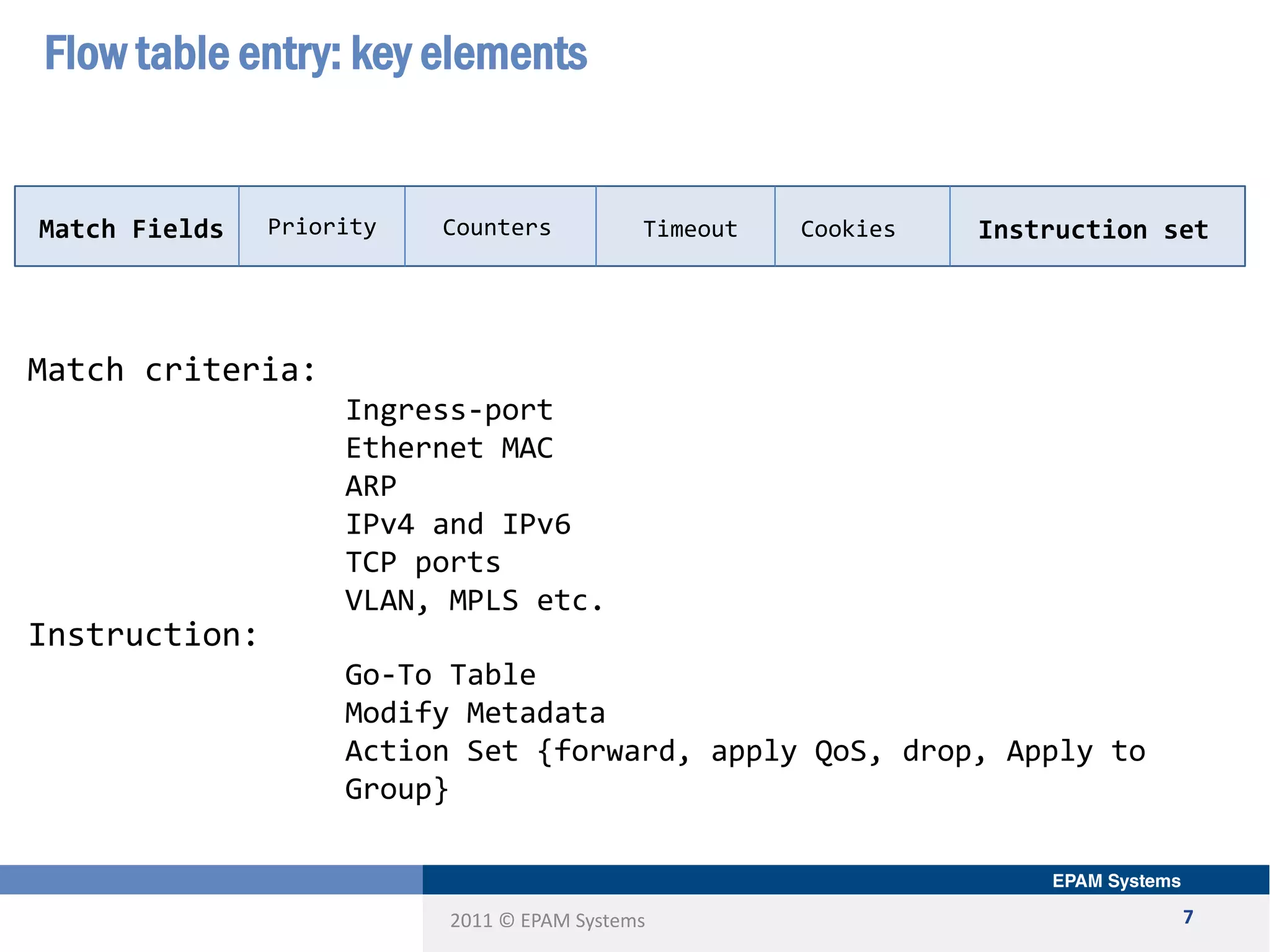
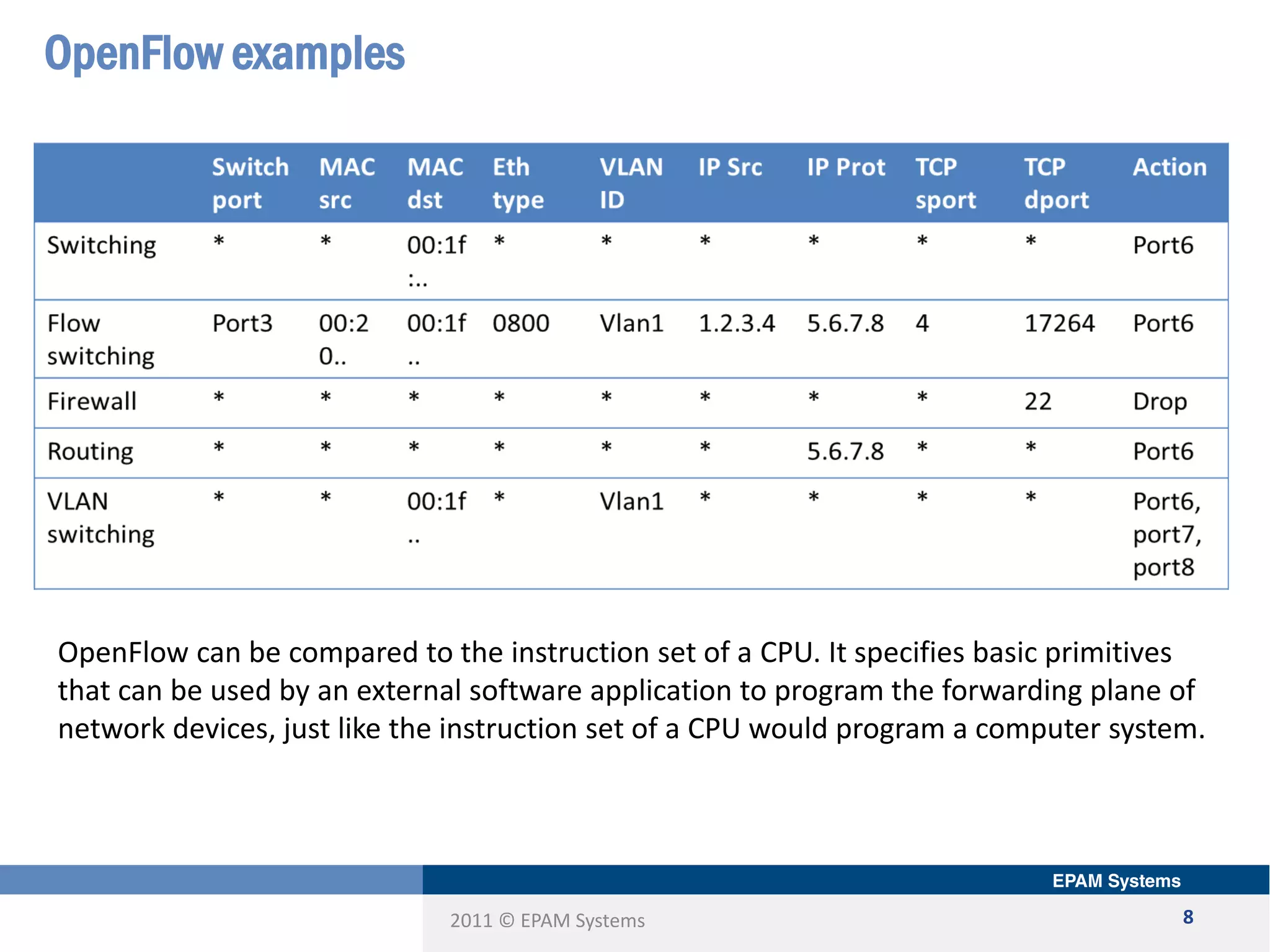
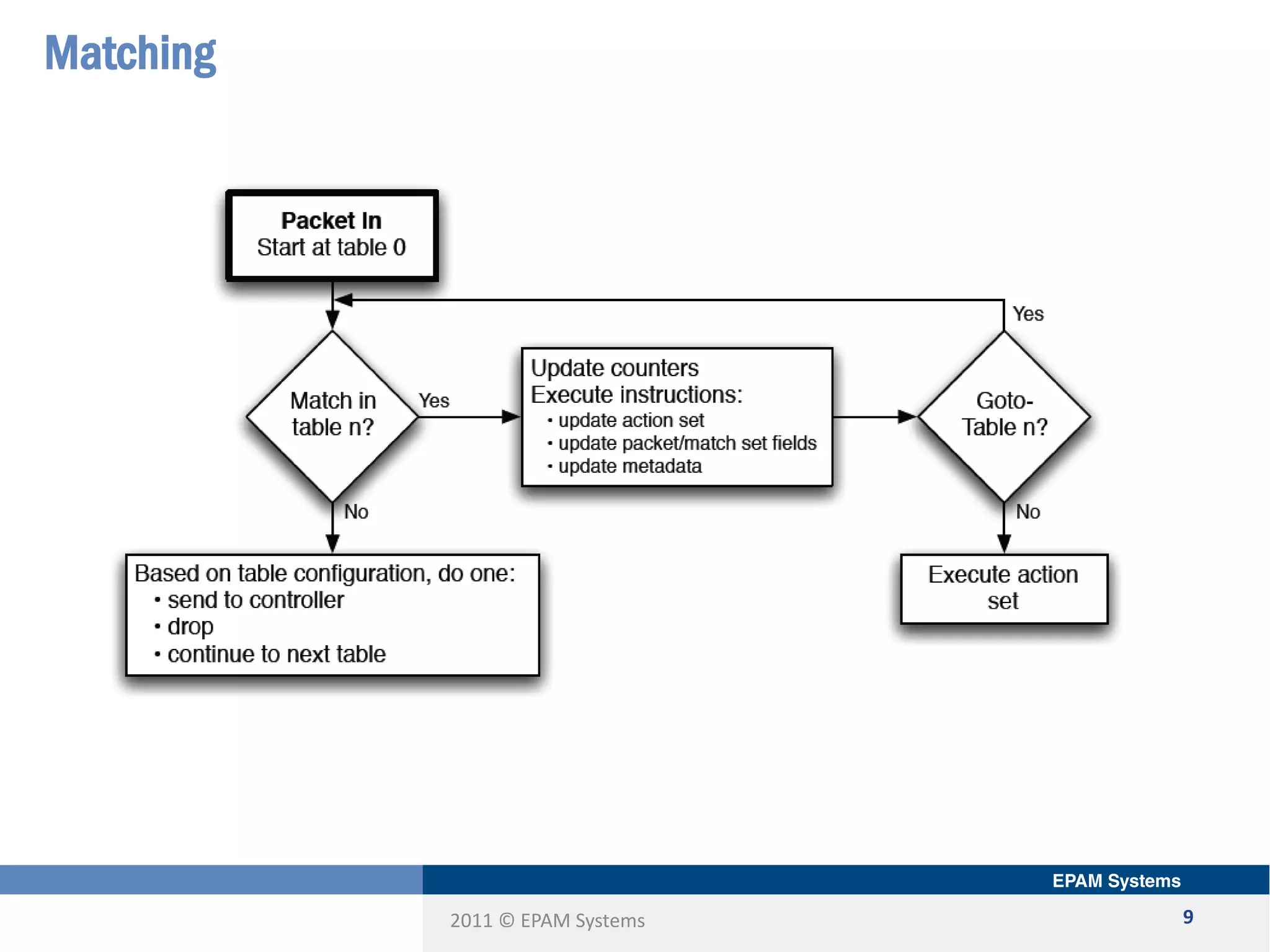
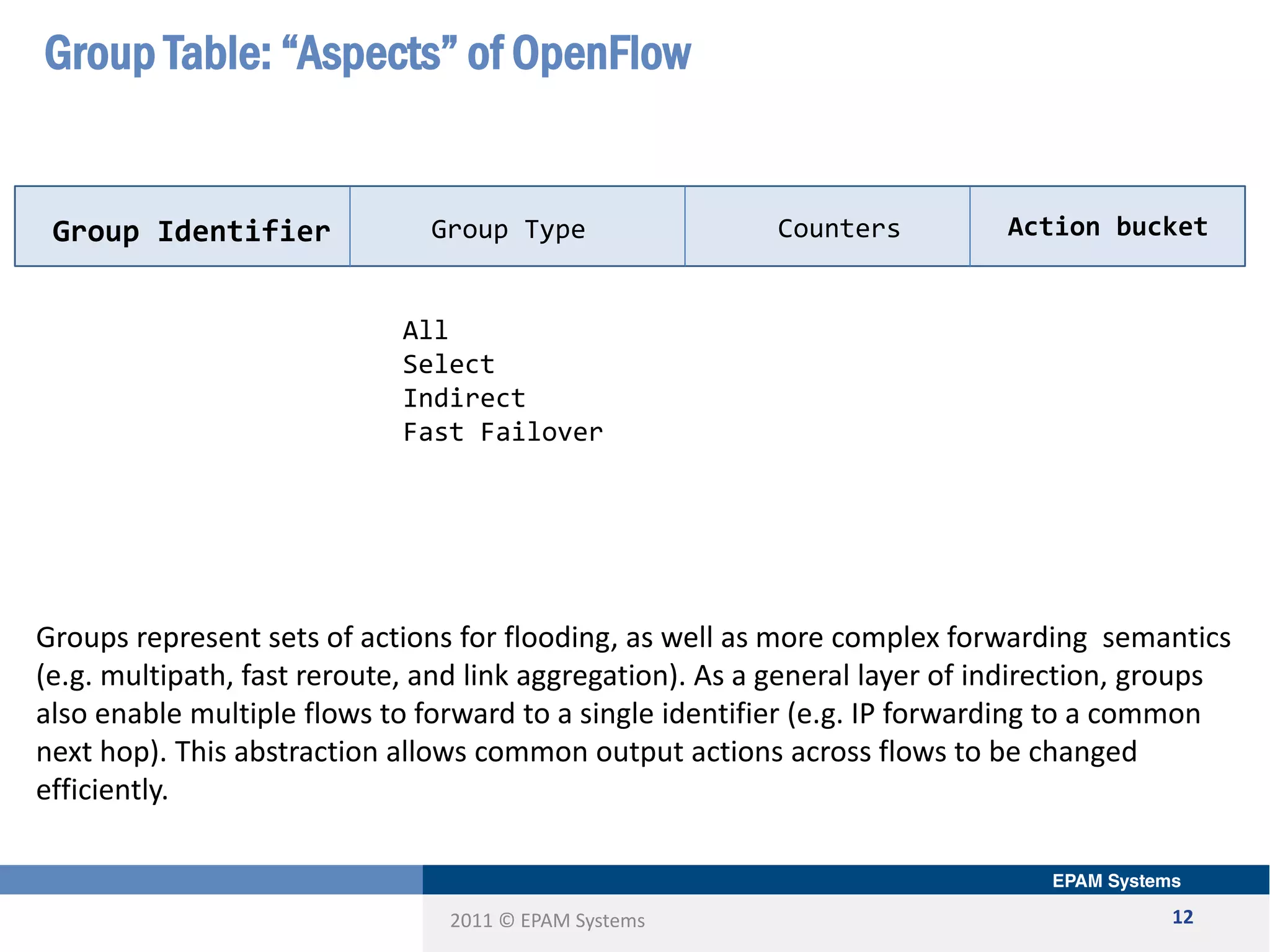
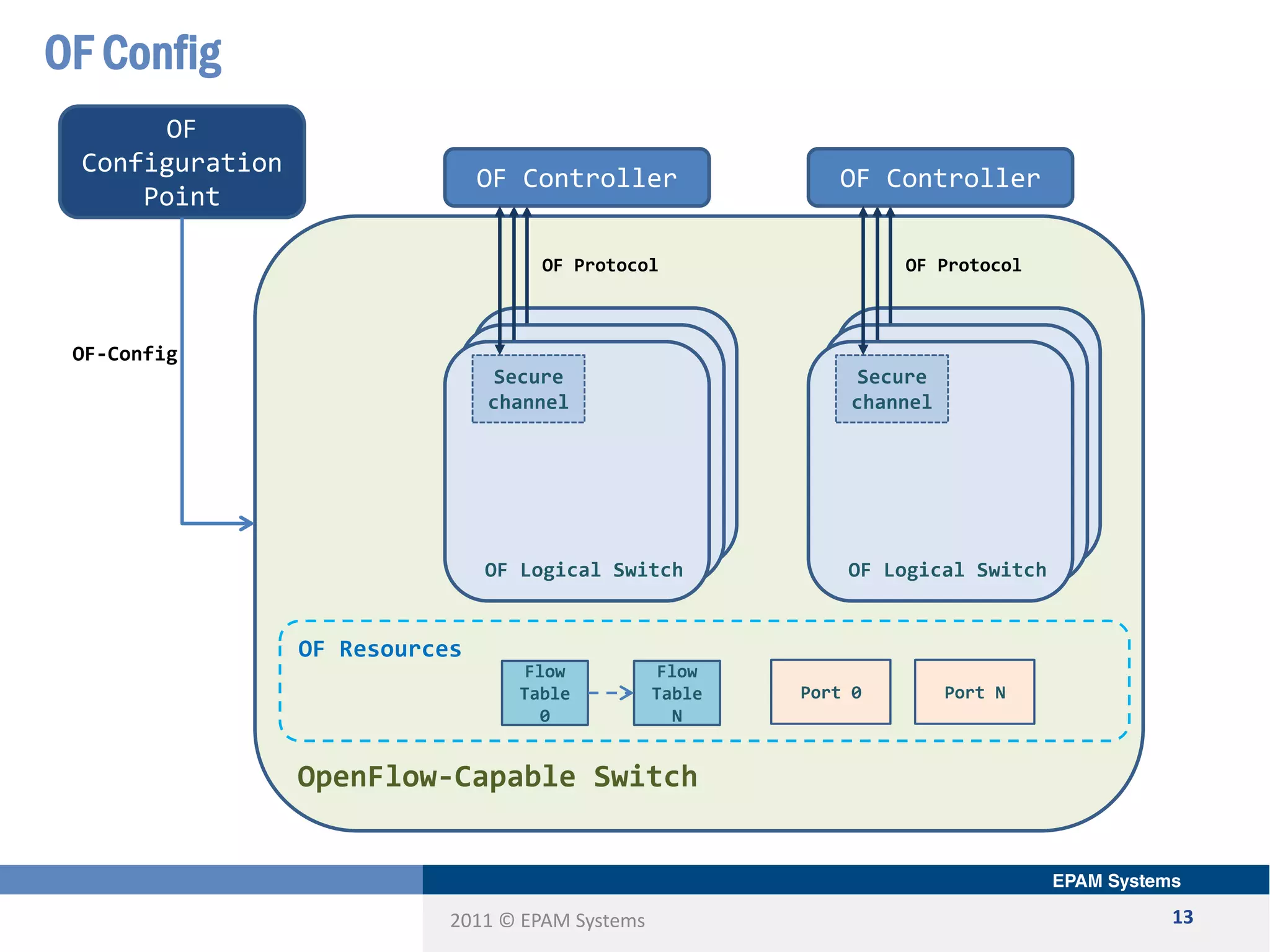
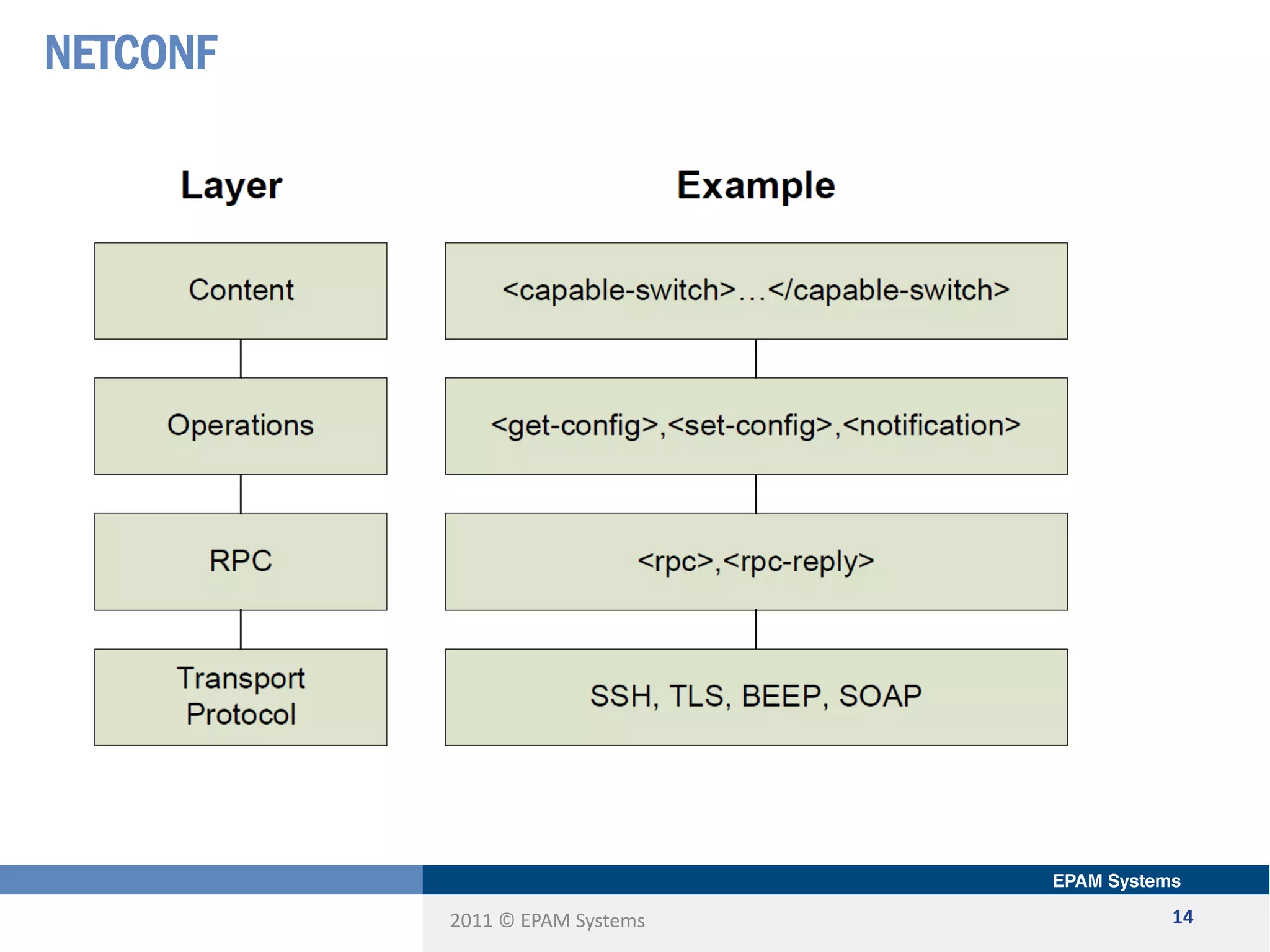
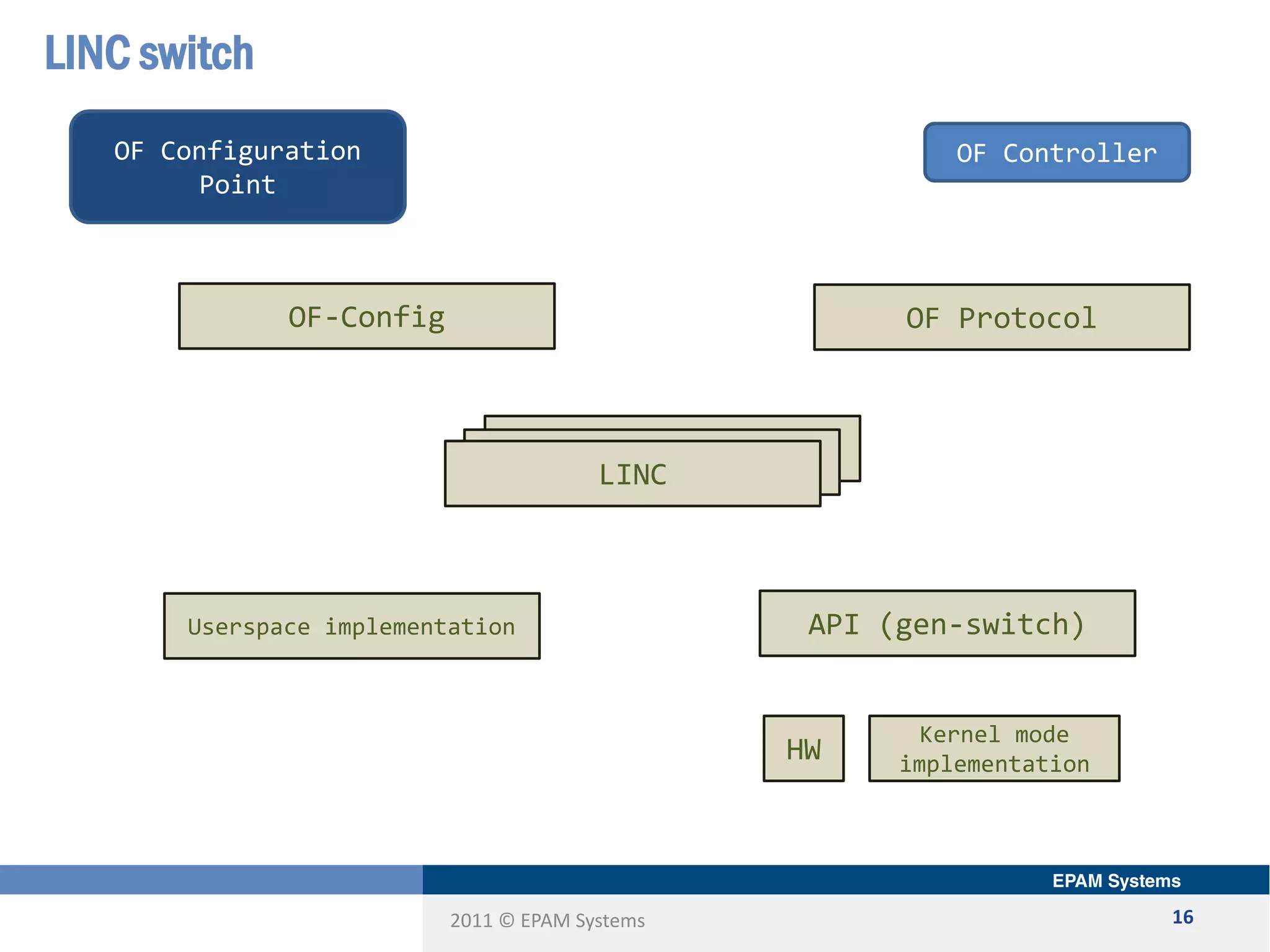
The document discusses the limitations of current networking technologies and introduces OpenFlow as a key standard for software-defined networks (SDN). It highlights the decoupling of network control from forwarding, the architecture of OpenFlow, and its role in enabling programmability across network devices. Additionally, it covers the key elements of OpenFlow, including its protocol, flow tables, and the interaction between switches and controllers.