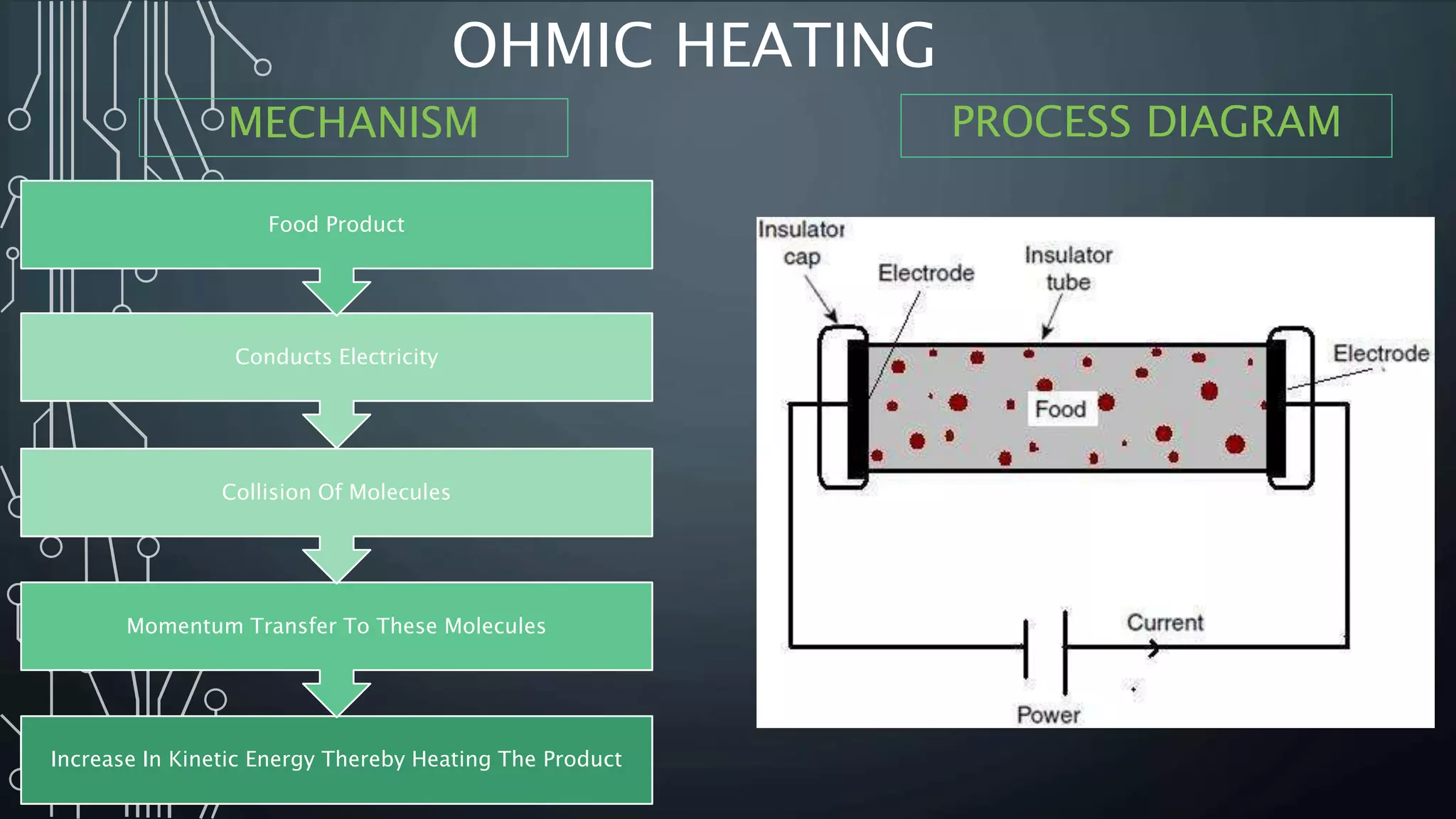
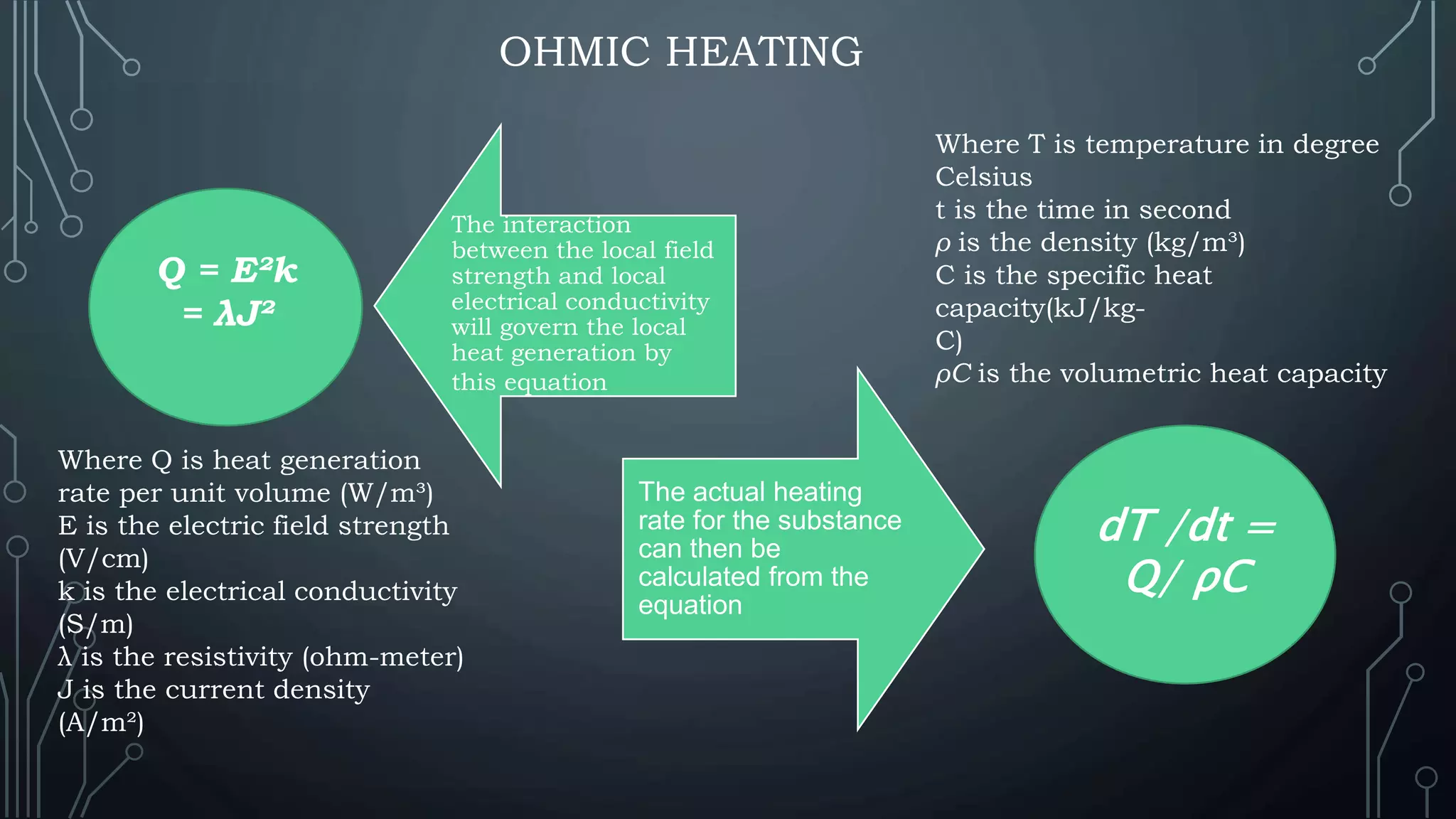
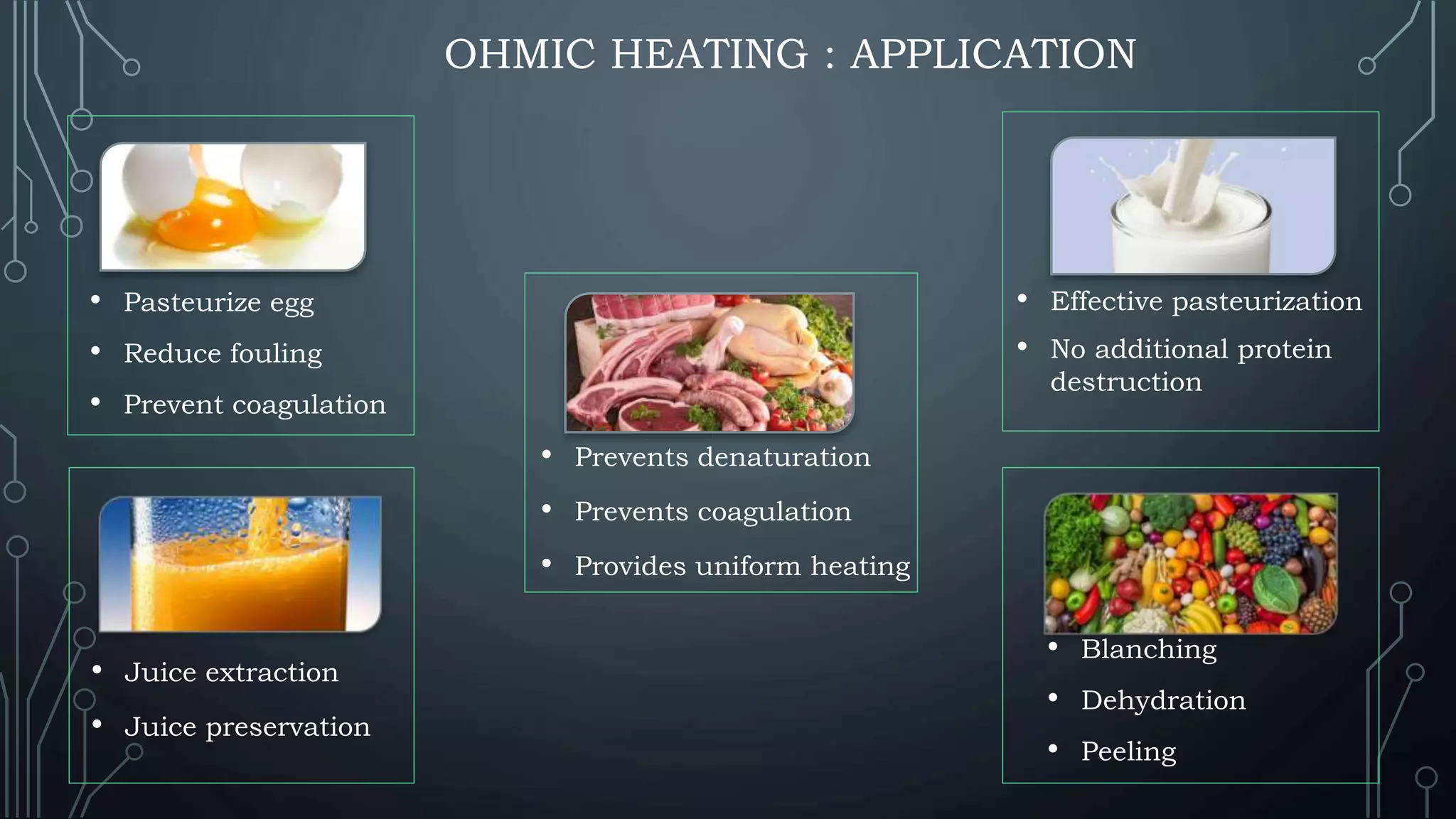
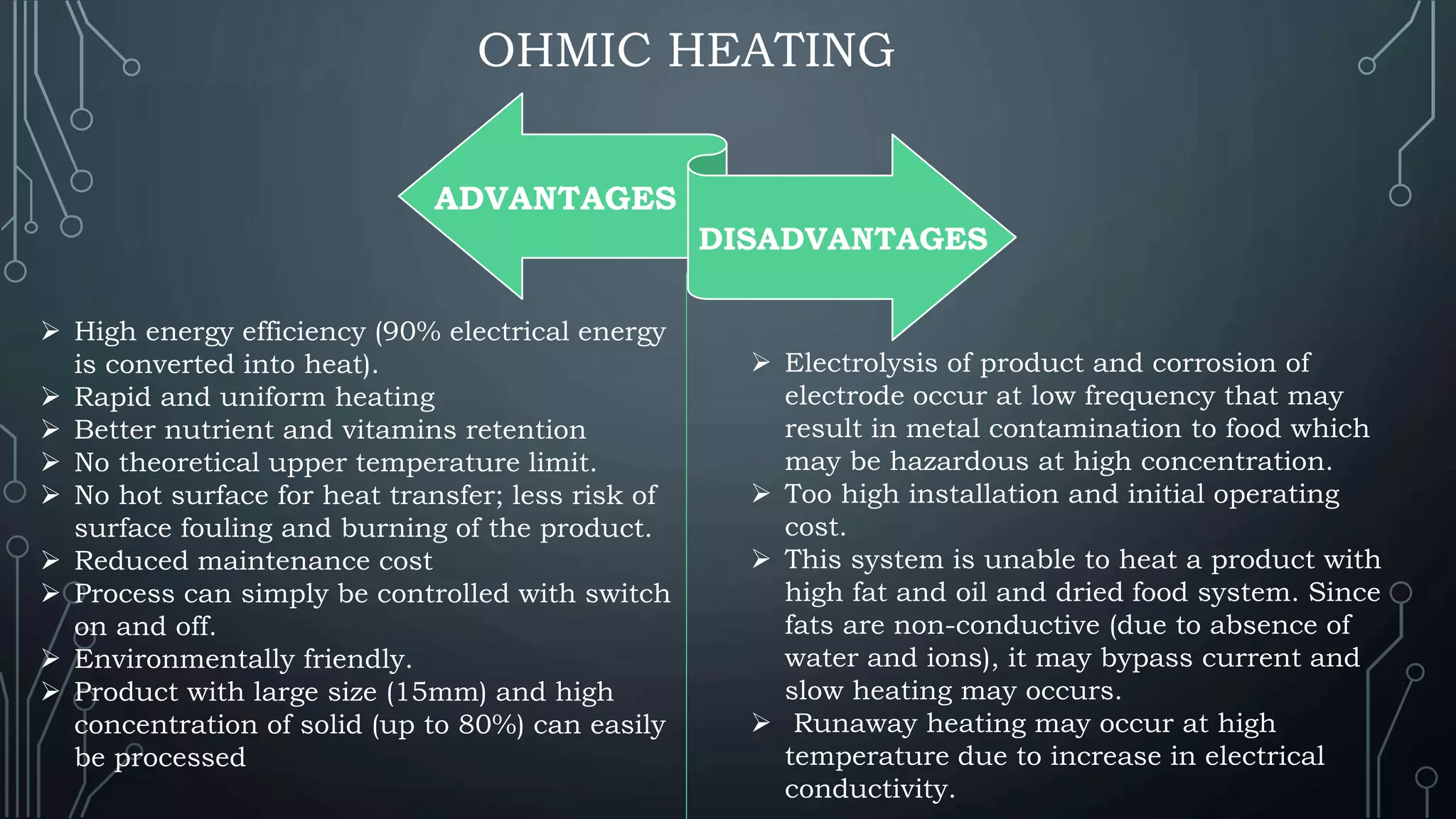
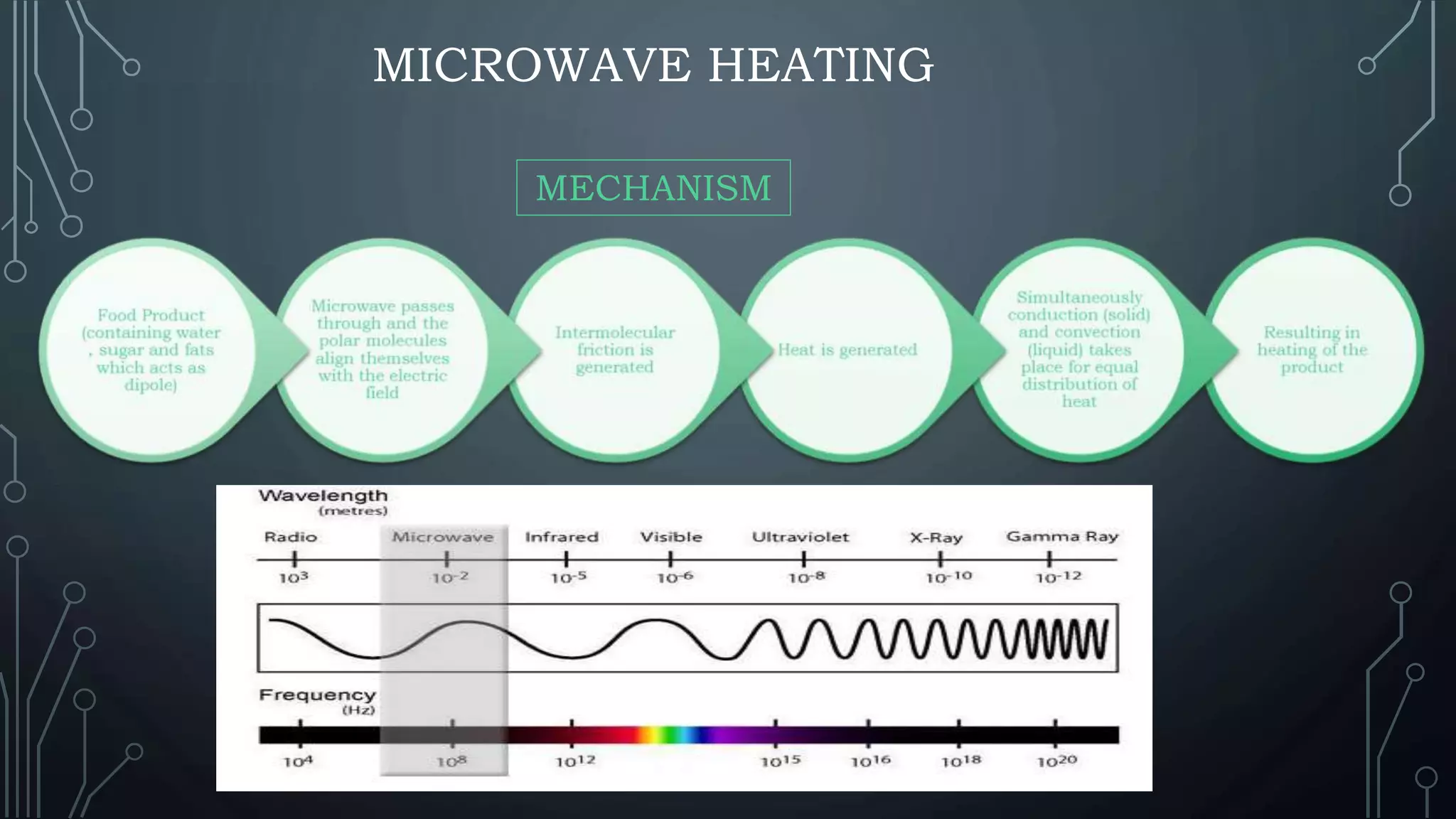
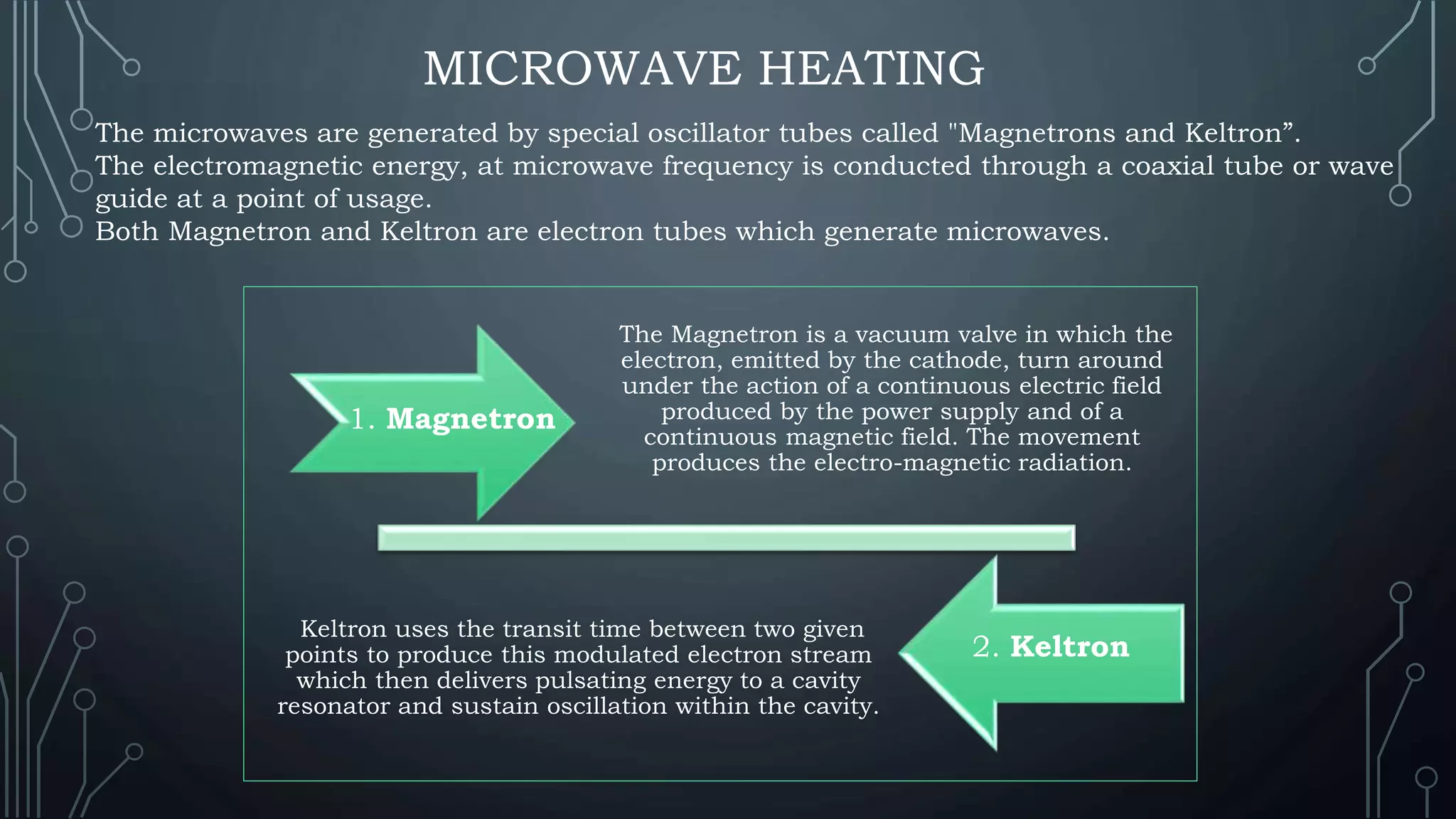
This document presents a comparative study of ohmic and microwave heating in food processing. Ohmic heating directly utilizes electrical resistance to generate heat in food, offering high energy efficiency and rapid, uniform heating, while microwave heating uses electromagnetic waves to heat food through molecular friction, though it has limitations such as non-uniform heating and low penetration depth. The conclusion emphasizes that both heating methods are beneficial for food preservation, enhancing shelf life, and inactivating microbes, while suggesting further research for optimization.