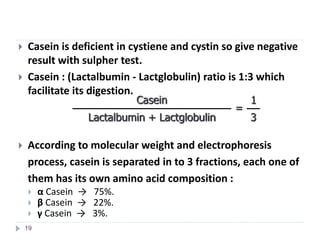
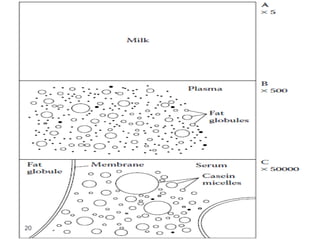
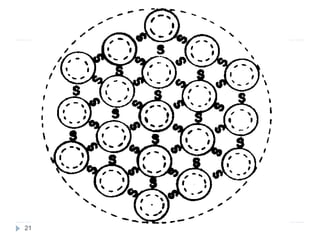
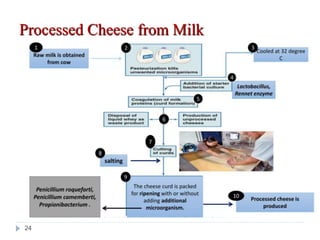
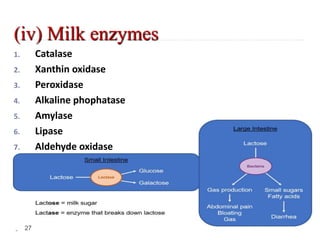
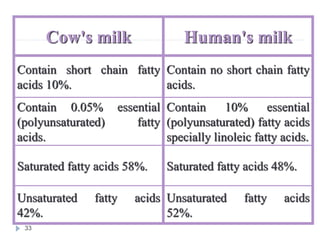
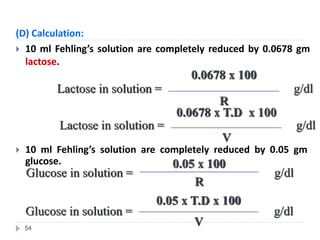
Milk is the secretion of mammary glands in humans and animals after childbirth. It provides complete nutrition for newborns as it contains carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, minerals, and vitamins. Milk's composition varies between species, with human milk containing less protein and minerals than cow's milk. Milk is made up of water, organic constituents like proteins (casein, lactalbumin, lactoglobulin), lipids, and carbohydrates (lactose), and inorganic constituents including minerals and vitamins. Its physical properties include white color, slightly acidic pH, specific gravity, taste, odor, and freezing/boiling points. Milk undergoes changes through processing like pasteurization, sterilization, and cheese/