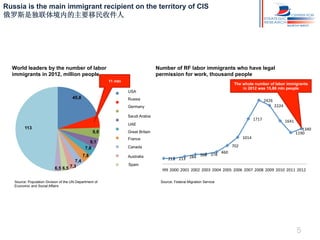
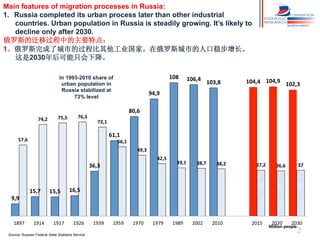
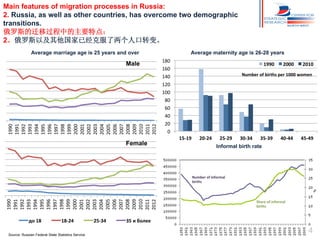
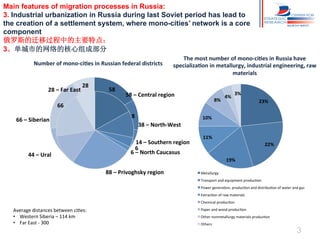
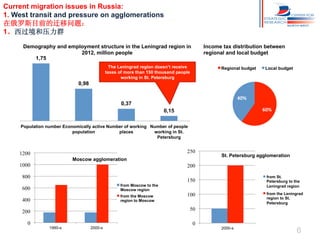
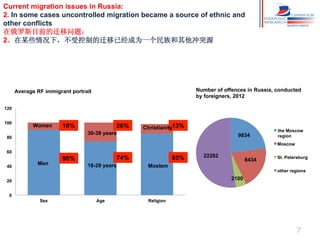
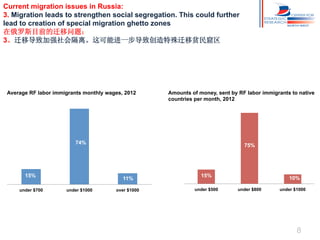
Russia has experienced significant migration trends in recent decades. It is now the main recipient of immigrants in the CIS region, with over 11 million legal labor immigrants in 2012. However, migration has also created challenges, including pressure on major cities, potential for ethnic and religious conflicts, and social segregation. To address issues like brain drain and economic competition, Russia needs new policies to adapt to changes in population structure and support development in mono-cities.