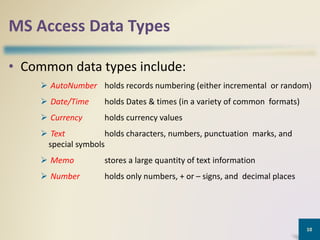
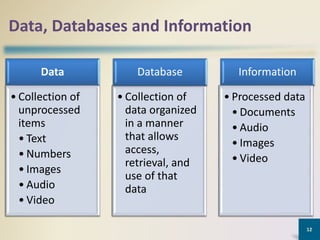
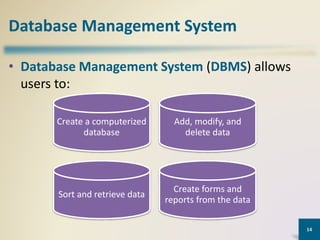
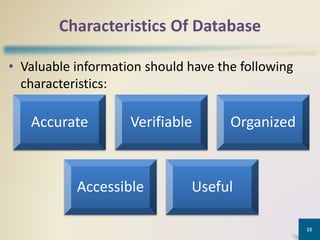
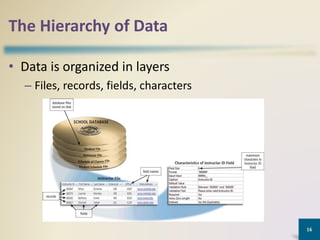
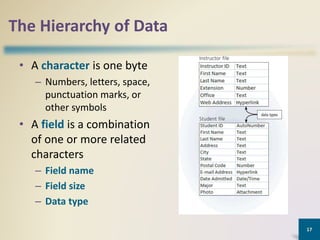
This document provides an overview of MS Access database objects and concepts. It discusses the key components of an MS Access database including tables, queries, forms and reports. It defines common data types like text, number, date and currency. It also explains what a database management system is, the characteristics of databases, and the hierarchy of data from characters to fields to records. Finally, it provides some keyboard shortcuts for navigating and editing in MS Access.