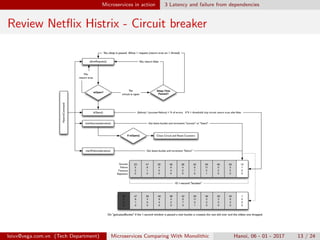
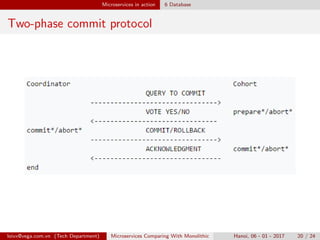
The document compares monolithic architecture to microservices architecture. Monolithic architecture involves a single code base and deployment, while microservices involve multiple independent components. Microservices provide benefits like scalability, availability and modifiability but introduce complexity around coordination, performance, and database management. The document discusses how tools like service discovery, circuit breakers, event sourcing and distributed transactions can help overcome disadvantages of the microservices approach. While microservices provide advantages, the document notes it is not a silver bullet and introduces new challenges compared to monolithic architecture.