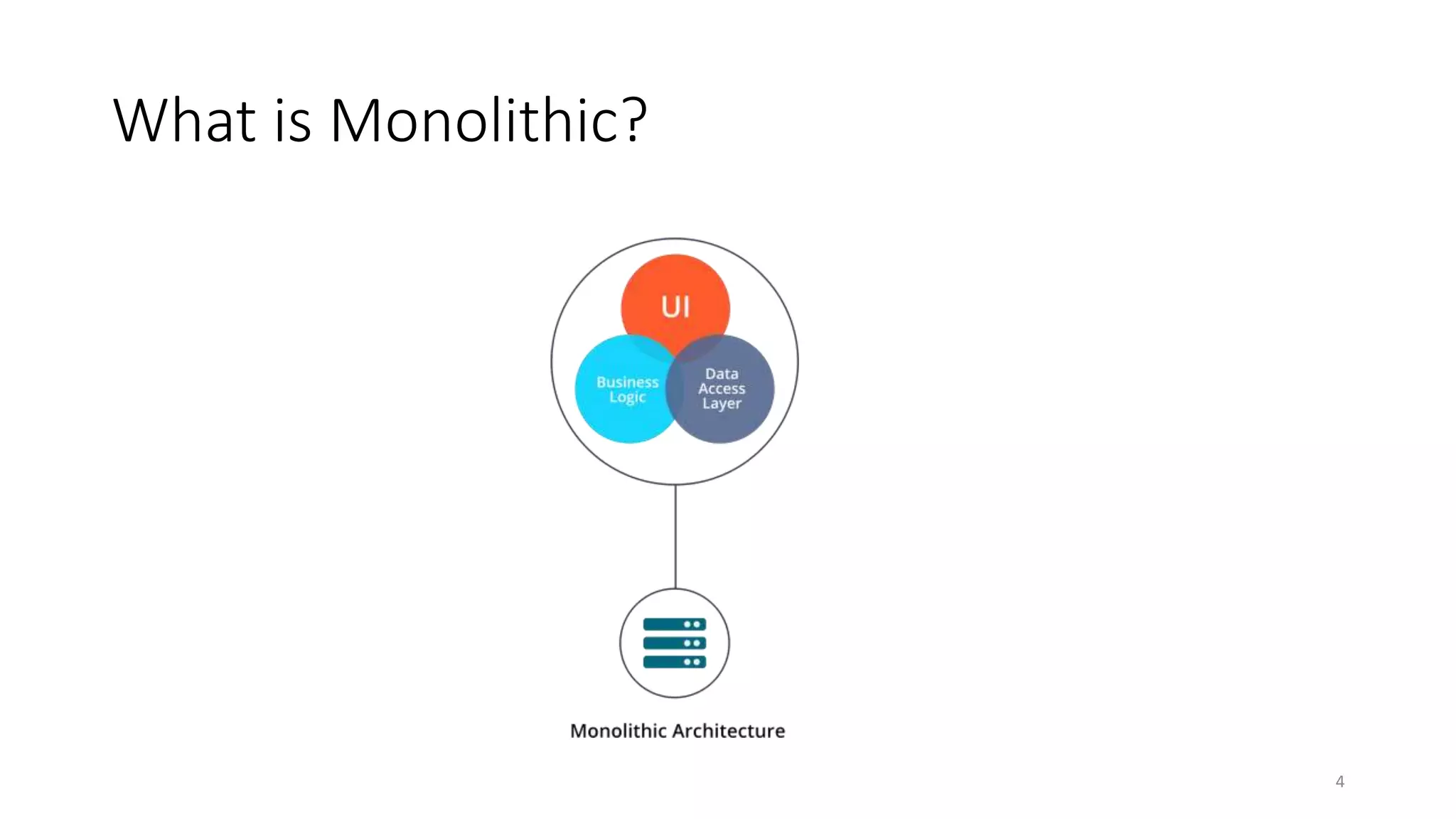
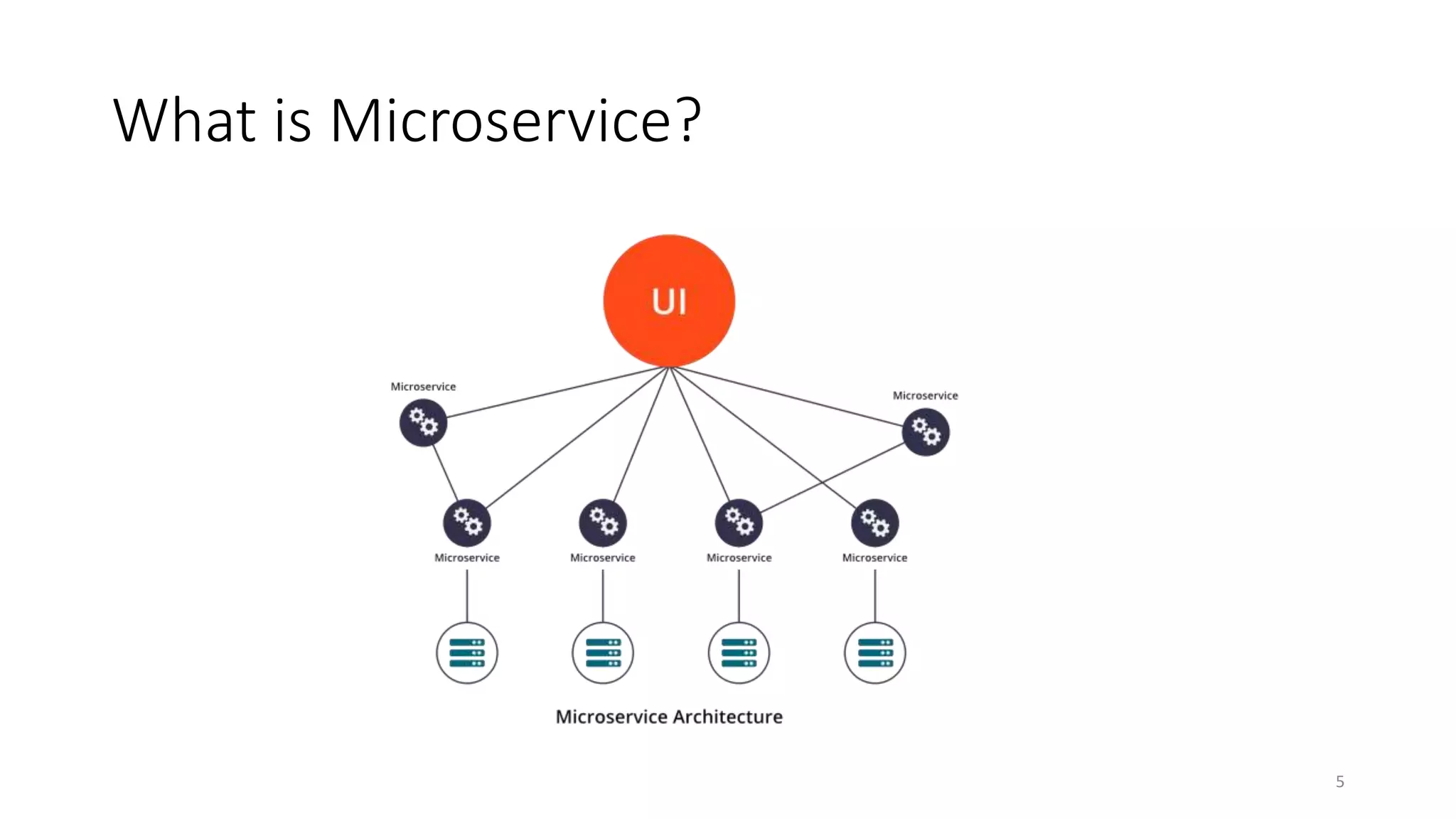
The document discusses microservice architecture, providing definitions and comparisons to monolithic and SOA architectures. It describes microservices as independently deployable services that work together to provide business capabilities. The benefits of microservices include evolutionary design, auto-scaling, and increased system resilience. Some challenges are also outlined, such as distributed logging and transaction spanning.