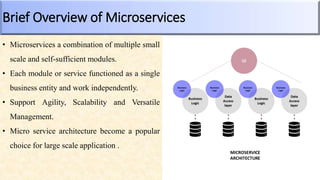
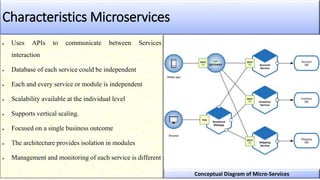
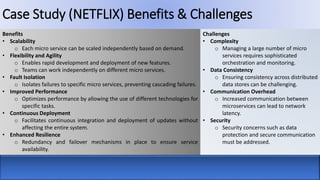
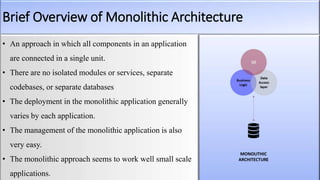
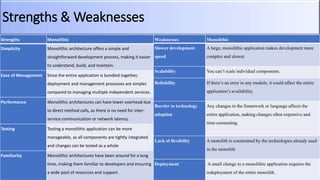
The document provides an overview of microservices architecture compared to monolithic architecture. It discusses the characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses of both microservices and monolithic architectures. It also includes a case study on how Netflix transitioned from a monolithic to a microservices architecture and the benefits and challenges they experienced. The document is a class project for an advanced software architecture course covering these topics.